- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
How to treat a cough in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy: what can pregnant women do from a cough in the third trimester
The content of the article:
-
What can pregnant women from coughing in the third trimester and what not
- Drinking regime
- Inhalation
- Folk remedies
- What is prohibited
- Causes and risk factors for developing cough during pregnancy
- The nature of the cough and the accompanying symptoms in various diseases
- How a cough during pregnancy can be dangerous for the mother and unborn child
- Prevention of cough during pregnancy
- Video
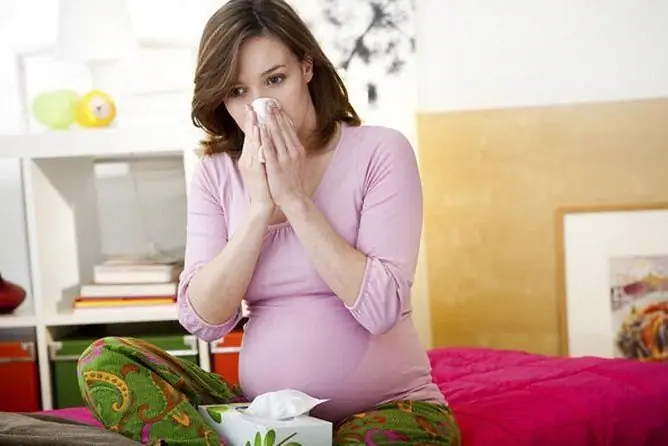
It is necessary to treat a cough in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy only under the supervision of a doctor. It is extremely dangerous to self-medicate, especially in the later stages.
A debilitating dry or lingering wet cough in pregnant women in the 3rd trimester can not only bother the woman herself, but also have a negative effect on the developing fetus.

In the event of a cough in a pregnant woman in the 3rd trimester, treatment should be prescribed by a doctor
Complicating cough treatment is that the list of approved medicines is limited. Before starting therapy, it is imperative to identify the cause of the cough and determine the diagnosis. Any medications and treatment methods should be used only after consulting your doctor.
What can pregnant women from coughing in the third trimester and what not
In most cases, cough treatment in a pregnant woman is carried out at home, and only in those situations that the doctor may consider as threatening the health of the mother or child, hospitalization and treatment in a hospital are required. Treatment tactics depend on the cause of the cough.
When coughing against the background of otorhinolaryngological diseases and viral infections, rinse the nose with saline solutions, rinse the throat with antiseptic solutions.
In case of an allergic cough, first of all, it is necessary to exclude contact with the substance, contact with which caused the development of allergies. You may also need to use antihistamines.
When coughing caused by acute respiratory infections, whenever possible, try to use soft medicines from herbal ingredients - preparations based on ivy, plantain, licorice root, marshmallow, thyme.

In the treatment of cough, preference is given to herbal preparations
In some cases, it becomes necessary to take antibiotics (for example, in severe forms of bronchitis), the doctor will select those that will not harm the health of the mother and baby.
Massage, physiotherapy exercises, breathing exercises can be prescribed as auxiliary methods.
Drinking regime
A plentiful drinking regime is recommended. The use of warm liquid promotes the dilution of bronchial secretions and their early elimination, moisturizing the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract.
Patients can use:
- tea with lemon;
- tea with the addition of honey;
- compotes, juices, fruit drinks from fruits and berries;
- mineral water;
- warm milk mixed with alkaline mineral water in a 1: 1 ratio.
If a pregnant woman has edema, fluid intake is usually limited; in this case, the drinking regimen is adjusted by the doctor, taking into account the available clinical signs.
Inhalation
Local agents are safer than systemic agents, therefore, for the treatment of cough in pregnant women, they are often prescribed by inhalation. This method is also good in that it allows you to deliver the medicine directly to the area of inflammation.
In addition to being more secure, they are also significantly more efficient. The advantages of inhalation with a nebulizer include the possibility of using drugs that lose their effectiveness when heated, as well as the absence of the risk of the patient getting burns to the skin and mucous membranes.
For inhalation, antimicrobial, expectorant, mucolytic, anti-inflammatory drugs, alkaline mineral water, saline can be used.
Inhalation requires compliance with a number of rules:
- Food should be taken no later than 1 hour before the procedure and no earlier than 1 hour after it.
- During the procedure, inhale through the mouth and exhale through the nose.
- During inhalation, do not talk or engage in any other activity.
- After inhalation, you must not go outside during the cool season for 1-2 hours.
- In the first hour after inhalation, one should not speak loudly or sing.
- You need to wash the nebulizer after each procedure (in accordance with the instructions for use)
- In case of deterioration of the patient's well-being during inhalation, it is necessary to stop the procedure early and consult a doctor.
Folk remedies
In the 3rd trimester of pregnancy, coughing at home with folk remedies should also be treated under medical supervision, since some natural ingredients can negatively affect the course of pregnancy.
To strengthen the protective forces of a woman during the period of bearing a child, it may be recommended to use decoctions and infusions, which include wild rose, sea buckthorn, cranberry, viburnum.
In the absence of allergy to bee products, natural remedies with honey can be used, since it has many beneficial properties, including:
- has anti-inflammatory effect;
- softens the mucous membranes of the throat;
- relieves attacks of dry cough;
- improves the discharge of phlegm with a wet cough.

Warm milk with honey is one of the safe and beneficial remedies for soothing coughs
The most popular recipes include:
- Honey with milk. A teaspoon of honey is dissolved in a cup of warm milk (not higher than 60 ° C). For a strong dry cough, a little butter can be added to milk with honey.
- Milk with figs. 1-2 pieces of figs are poured over 1.5 cups of milk and boiled for 20-30 minutes, then allowed to cool and brew for 1-2 hours. Warm milk is drunk several times a day, and figs extracted from it can be eaten.
- Lime tea. Several inflorescences of linden (about 5 g) brew 200 ml of boiling water, let it brew for 5-10 minutes, drink for coughing attacks.
- Radish juice with honey. Thoroughly wash the black radish with a brush, cut off the top, remove the middle, making a depression with a volume of 2-3 tablespoons. Put a tablespoon of honey in the depression, leave for 6-8 hours. Released rare juice, mixed with honey, take a dessert spoon 5 times a day. One radish can be used to prepare several doses of medicine.
What is prohibited
During pregnancy, it is forbidden to use warming compresses, mustard plasters, cans and hot foot baths.
Causes and risk factors for developing cough during pregnancy
The most common causes of cough development include inflammatory diseases of the upper and lower respiratory tract.
Also, a cough can occur when:
- otorhinolaryngological diseases;
- allergies;
- bronchial asthma;
- tuberculosis;
- whooping cough;
- tumors of the respiratory system;
- some diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- ingress of foreign substances or objects into the respiratory tract;
- inhalation of chemical vapors, dust;
- long-term smoking.
The nature of the cough and the accompanying symptoms in various diseases
The cough can be dry or moist, depending on whether the patient has sputum. The nature of sputum differs in various diseases.
| Pathology | The nature of the sputum |
| Acute bronchitis | Sputum mucous (transparent and colorless), is excreted in small quantities, then becomes mucopurulent and more abundant |
| Chronical bronchitis | Mucopurulent sputum is usually excreted in large quantities. During remission, scanty mucous sputum is separated |
| Pneumonia | Mucopurulent sputum, may have a rusty tint |
| Bronchial asthma | Viscous and transparent (glassy) sputum in small amounts |
| Bronchiectasis | Abundant (especially in the morning) mucopurulent sputum with an unpleasant odor |
| Lung abscess | When an abscess breaks out, abundant purulent sputum with an unpleasant odor is released |
| Lung cancer | Mucopurulent sputum, in which blood impurities can be found; the amount of sputum depends on the stage of the disease |
| Tuberculosis | Mucopurulent sputum, often with blood impurities |
The nature of the cough also differs depending on the origin.
A cold cough is accompanied by a runny nose, pain or discomfort in the throat, headache, fever, pain in the chest. A cough that develops at night can cause sleep disturbances, further impairing overall well-being.
A cough against a background of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastritis with high acidity, etc.) is accompanied by heartburn, sour belching, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, and bloating.
An allergic cough develops on contact with the causative allergen (immediate reaction) or some time after that (delayed reaction). This cough is often accompanied by nasal discharge, watery eyes, itching in the throat and / or nose, and skin rashes. At the same time, body temperature remains within normal limits.

Medicines for pregnant women should only be taken as directed by a doctor.
How a cough during pregnancy can be dangerous for the mother and unborn child
A persistent, debilitating cough while carrying a baby can cause high blood pressure.
A prolonged dry cough in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy can lead to the following complications:
- development of fetal hypoxia - a tearful cough can increase the tone of the uterus and cause a lack of oxygen;
- premature birth - a significant increase in uterine tone can provoke contractions;
- bleeding - the risk of developing significantly increases in the last trimester of pregnancy.
Diseases of an infectious etiology, against which a cough develops, pose a danger to the developing fetus, as they can provoke intrauterine infection. The most dangerous respiratory illness for an unborn child is flu.
Prevention of cough during pregnancy
To prevent the development of cough in women during pregnancy, it is recommended to take a number of measures designed to strengthen the immune system and minimize contact with the infection:
- Avoid visiting crowded places, especially during seasonal epidemics.
- Use a gauze bandage when visiting medical facilities.
- Coming home from the street, wash your hands thoroughly.
- If possible, limit contact with sick people.
- Spend more time outdoors, away from industrial plants and highways.
- Eat properly.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Ventilate living quarters regularly, often wet clean.
- Avoid sudden changes in climatic zones, long trips.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.