- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Treatment of cough in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy
The content of the article:
- How to treat a cough in a pregnant woman in the 2nd trimester
- Physiotherapy treatments for cough in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy
- Treatment with folk remedies
- Prevention of cough during pregnancy
- Cough reasons
- Why is a cough during pregnancy dangerous?
- Video
Cough in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy in women occurs quite often. His appearance always causes fear in the expectant mother. In this article, we will talk about the causes of cough, as well as how to treat it.
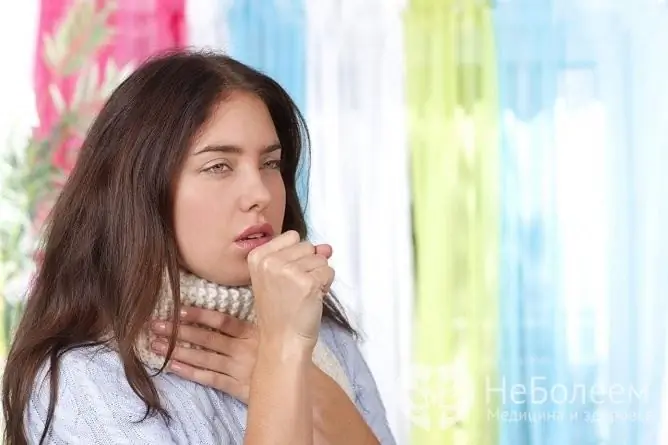

Treatment of cough in pregnant women requires a special approach, since a number of procedures and drugs are prohibited
How to treat a cough in a pregnant woman in the 2nd trimester
During pregnancy, only drugs can be used to treat cough, the effectiveness and safety of which for the formation of the fetus is proven. Therefore, cough therapy, regardless of the cause that caused it, should be prescribed only by a doctor.
To treat dry cough in the second trimester of pregnancy, your doctor may prescribe the following drugs:
| Herbal medicines | Synthetic drugs | |
| Clinically proven to be safe for fetal development | Marshmallow root syrup, Mukaltin | Coldrex Knight (the composition includes paracetamol, therefore the use of this drug is justified only when the body temperature rises to 38 ° C and above) |
| The use is permitted only if the expected effect of treatment significantly outweighs the potential risk to the fetus | Gedelix, Bronchicum | Bromhexin, Falimint, Stopussin, Libeksin |
The following drugs are used to treat wet coughs:
| Herbal medicines | Synthetic drugs | |
| Clinically proven to be safe for fetal development | Stoptussin-phyto syrup, Doctor Theis, Prospan | Tussin |
| The use is permitted only if the expected effect of treatment significantly outweighs the potential risk to the fetus | Herbion, Bronchicum, Linkas | Fluifort, Ambrobene |
There is a number of medications that are strictly contraindicated to take during pregnancy:
- Codelac;
- Codterpin,
- Travesil;
- Bronchodilator;
- Thermopsis;
- ACC.
Physiotherapy treatments for cough in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy
Some physiotherapy techniques are effective in treating cough in pregnant women, such as gargling (if the cough is associated with sore throat) and inhalation. Are categorically contraindicated for pregnant women:
- mustard plasters;
- banks;
- hot baths, including foot baths;
- electrotherapy;
- any kind of radiation (UHF, magnetotherapy).
Steam inhalation is carried out using one of the following solutions:
- infusion of sage herb (a tablespoon of the herb is brewed with a glass of boiling water and infused for 15-20 minutes);
- baking soda solution (dissolve 50 g of baking soda in one liter of boiled water);
- infusion of eucalyptus with garlic (chopped garlic clove, 10 g of eucalyptus leaves, pour a liter of boiling water and cool to 55-60 ° C).
When carrying out inhalation, the following rules should be observed:
- the procedure can be carried out only at a body temperature not higher than 37.5 ° C;
- the duration of inhalation should not exceed 10 minutes;
- inhalations should be repeated 3-4 times a day;
- after the procedure, you should not eat, drink any liquid or talk for half an hour.
Herbs are not used in a nebulizer; as a solution for inhalation, the doctor can prescribe a drug, alkaline mineral water, saline.
To rinse the throat, it is necessary to prepare a medicinal solution immediately before the procedure and cool it to the required temperature. Most often used:
- infusion of chamomile flowers;
- infusion of linden blossom;
- infusion of plantain leaves.
To prepare any of the listed solutions, you should take 10 g of medicinal raw materials and pour a glass of boiling water. Insist for 20-30 minutes. Strain and cool to a comfortable temperature.
Gargling well removes the feeling of a sore throat and thus reduces coughing. This method is especially effective for dry, unproductive cough and can be used as a means of quickly helping the patient.
Treatment with folk remedies
Despite the fact that there are effective medicines in the arsenal of doctors, many pregnant women prefer to be treated with folk remedies, believing that due to their naturalness they are safer. But in fact, medicinal herbs cannot be considered completely harmless, since many of them are capable of provoking an allergic reaction. In addition, there are a number of herbs that are contraindicated for use in pregnant women. These include:
- St. John's wort - reduces the effectiveness of antibacterial drugs and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- comfrey medicinal, mother and stepmother - contain pyrrolizidine, which has a carcinogenic and mutagenic effect;
- echinacea, eleutherococcus, ginseng - often provoke allergic reactions, increase blood pressure;
- gingko biloba - reduces blood clotting, which increases the risk of uterine bleeding.
Therefore, the use of alternative methods of treating cough during pregnancy is permissible only in consultation with the attending physician. The most commonly used tools are:
- Honey with milk. Dissolve 1-2 teaspoons of honey in a glass of warm (not hot!) Milk. Drink 2 times a day half an hour before meals.
- Black radish juice with honey. Wash one large radish well under running water and scald with boiling water. Cut off the upper part and carefully cut out the cavity with a sharp knife, fill it with honey and close the "lid" cut off earlier. Place in a deep cup. The juice will be ready in 10-12 hours. It should be taken 3-4 times a day in a tablespoon. The course of treatment is 3-5 days.
- Black radish juice. Wash the radish well under running water, peel and grate on a fine grater. Sprinkle the resulting mass with granulated sugar and mix. Leave for a few hours. Squeeze the juice through a cheesecloth folded in several layers. Take a tablespoon 3 times a day half an hour before meals.
- Onion broth. Peel and chop a large onion in a blender. Pour over a glass of milk, bring to a boil and simmer for 10 minutes. Cool, strain and add a tablespoon of honey. Take 1 tablespoon before meals 2-3 times a day.
- Infusion of calamus roots. Pour two tablespoons of chopped calamus roots with a glass of boiling water. Insist 12 hours. Strain. Take 3 times a day, half a glass on an empty stomach.
- Honey infusion of currant berries. Wash 100 g of black currant under running water and grind them with a blender. Mix the resulting puree with 3 tablespoons of honey, leave for 12 hours. Take 3 times a day for a tablespoon.
- Thyme and linden tea. Take 2 tablespoons of thyme herb and 3 tablespoons of linden flowers. Place the plant materials in a porcelain teapot and pour boiling water over it. Drink herbal tea hot several times a day. You can sweeten it with a teaspoon of sugar or honey if desired.
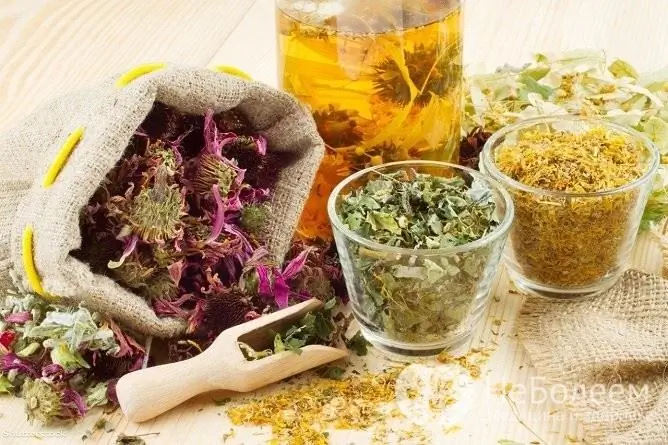

Some herbs used in the treatment of coughs are prohibited during pregnancy.
Prevention of cough during pregnancy
Vaccine prophylaxis plays a major role in preventing influenza infection. The results of clinical studies have proven the complete safety of modern influenza vaccines, since they are devoid of embryonic toxic and teratogenic effects.
To prevent diseases that most often cause coughing, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- avoid contact with patients with any infectious diseases;
- during a period of high incidence of influenza and ARVI, try not to visit places with a large crowd of people (cinemas, theaters, shopping and entertainment complexes);
- to prevent infection with viral infections, before leaving the house, lubricate the nasal cavity with oxolinic ointment or wear a medical mask;
- after returning home, wash your hands thoroughly under running water and soap and rinse the nasal cavity and throat with warm saline solution;
- carry out wet cleaning daily and ventilate living rooms several times a day;
- refuse to travel long distances.
Cough reasons
Cough is a protective reaction of the body aimed at cleansing the respiratory tract from the accumulated mucus, microbes, and dust particles. This is not an independent disease, but just a symptom characteristic of a number of pathologies of the respiratory system, cardiovascular system and even the gastrointestinal tract.
The most common cause of coughing is:
- Acute respiratory infections. During pregnancy, a woman's immune system weakens. This is necessary so that an immune conflict does not develop and fetal rejection does not occur, that is, spontaneous abortion. But due to a decrease in the immune response, the body of the expectant mother is poorly protected against various viruses and pathogenic microbes. Therefore, during pregnancy, colds, SARS, influenza, bronchitis are often observed.
- Increased intra-abdominal pressure. In the second trimester of pregnancy, the uterus leaves the pelvic cavity into the abdominal cavity and begins to grow rapidly. This leads to increased pressure in the abdominal cavity and, as a result, to a weakening of the lower esophageal sphincter. As a result, acidic stomach contents are periodically thrown into the esophagus and through it enters the pharynx. In this case, irritation of the nerve receptors of the mucous membrane of the throat occurs and an attack of dry cough occurs.
- Allergy. Upon contact with substances to which a woman has increased individual sensitivity (sensitization), an attack of dry cough may occur, sometimes with the separation of a small amount of transparent mucous sputum.
Another reason for coughing during pregnancy is passive and sometimes active smoking. Tobacco smoke irritates the bronchial mucosa, which can lead to coughing. Smoking during pregnancy can cause great harm to the unborn baby. It contributes to the development of placental insufficiency, which in turn causes fetal hypoxia, impaired motor activity.
Why is a cough during pregnancy dangerous?
Any disease during pregnancy causes a well-founded concern in a woman, since it can have an adverse effect on the formation of the fetus and cause a number of complications.
Depending on the gestational age, pregnancy is divided into three periods:
- first trimester - from the moment of conception to 12 weeks;
- second trimester - from 13 to 24 weeks;
- third trimester - from 25 to 40 weeks.
The most dangerous in terms of risks is the first trimester. During it, almost any disease can lead to spontaneous miscarriage, undeveloped (frozen) pregnancy, or gross malformations of the fetus.
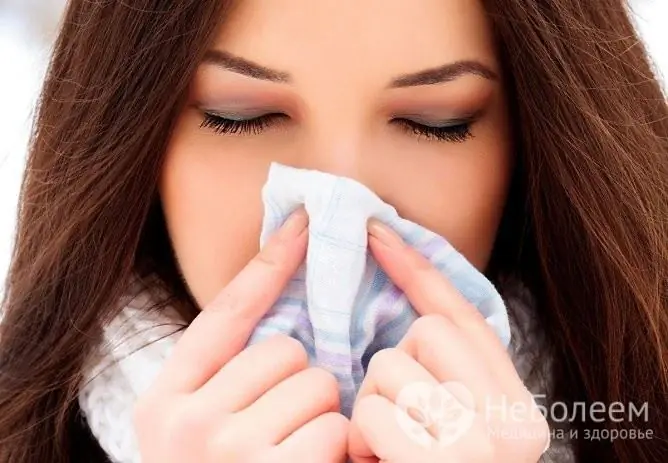

Seasonal viral infections are the most common cause of cough in pregnant women
In the second and third trimesters, thanks to the formed placenta, viral infections can no longer cause the child the same serious consequences as at the very beginning of pregnancy. But this does not mean that a cough in the 2nd trimester is not fraught with threats. If its cause is not established and appropriate treatment is carried out, then a banal cough can lead to the following consequences:
- Fetal hypotrophy and hypoxia. Any viral infection can impair uteroplacental blood flow. In turn, this leads to insufficient supply of oxygen and nutrients to the fetus. In addition, during a cough, gas exchange in the lungs of a woman worsens. It also becomes the cause of oxygen starvation of the baby, disruption of the correct development of his nervous system.
- Bone formation disorders. During cough tremors, there is a significant increase in pressure in the abdominal cavity and compression of the uterus. The fetal bone tissue is very soft, and such compression provokes abnormal development of bones and joints.
Starting from the second trimester, lung excursion worsens. Therefore, any respiratory infection increases the risk of complications such as bronchitis and pneumonia.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Elena Minkina Doctor anesthesiologist-resuscitator About the author
Education: graduated from the Tashkent State Medical Institute, specializing in general medicine in 1991. Repeatedly passed refresher courses.
Work experience: anesthesiologist-resuscitator of the city maternity complex, resuscitator of the hemodialysis department.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.