- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Osterapar
Osterepar: instructions for use and reviews
- 1. Release form and composition
- 2. Pharmacological properties
- 3. Indications for use
- 4. Contraindications
- 5. Method of application and dosage
- 6. Side effects
- 7. Overdose
- 8. Special instructions
- 9. Application during pregnancy and lactation
- 10. Use in childhood
- 11. In case of impaired renal function
- 12. Drug interactions
- 13. Analogs
- 14. Terms and conditions of storage
- 15. Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
- 16. Reviews
- 17. Price in pharmacies
Latin name: Osterepar
ATX code: M05BA04
Active ingredient: alendronic acid (alendronic acid)
Producer: POLPHARMA SA (Poland)
Description and photo updated: 20.11.2018
Prices in pharmacies: from 200 rubles.
Buy
Osterapar is a bone resorption inhibitor.
Release form and composition
Dosage form Osterepara - tablets: oblong, biconvex, white (4 pcs. In blisters, 1 blister in a cardboard box).
Composition of 1 tablet:
- active ingredient: sodium alendronate trihydrate - 91.36 mg (which corresponds to the content of alendronic acid - 70 mg);
- additional components: magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, lactose monohydrate, anhydrous colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
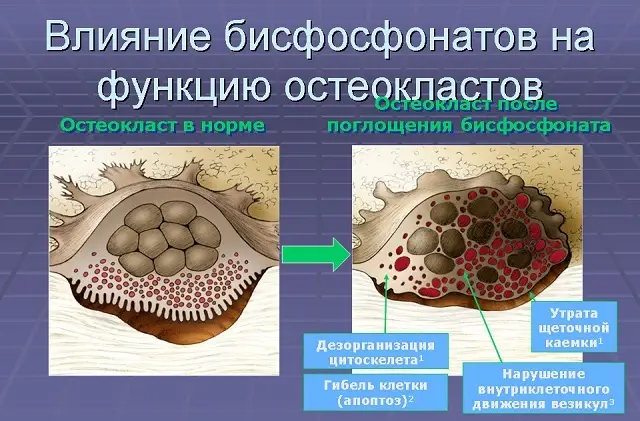
Alendronate is a member of the bisphosphonate group. Localized in areas of active bone resorption (under osteoclasts), it inhibits the process of bone resorption caused by osteoclasts.
Osterapar has no direct effect on the formation of new bone tissue. Although bone resorption and the appearance of new bone tissue are interrelated, the degree of reduction in bone formation is less than that of resorption, as a result of which the bone mass increases.
Alendronate promotes the formation of normal bone tissue by incorporating into the matrix, but remaining pharmacologically inactive.
When used in therapeutic doses, Osterapar does not cause osteomalacia.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration of alendronate in doses of 5-70 mg on an empty stomach no later than 2 hours before the morning meal, its bioavailability is: in women - 0.64%, in men - 0.6%. When the drug is taken 1-1.5 hours before breakfast, bioavailability decreases by about 40%.
In the case of osteoporosis, Osteopar has been shown to be effective when taken on an empty stomach no later than 30 minutes before the first intake of any food or liquid.
If the drug is taken with food or within 2 hours after a meal, the bioavailability of alendronate is negligible. Coffee and orange juice reduce its bioavailability by about 60%.
A significant change in the bioavailability of alendronate is not observed with the simultaneous use of prednisolone (20 mg three times a day for 5 days).
The average volume of distribution of the active substance of Osterepara in an equilibrium state (excluding bone tissue) is at least 28 liters. When taken in therapeutic doses, the plasma concentration of the drug is insignificant (less than 5 ng / ml). Alendronate is characterized by a high binding to plasma proteins - about 78%.
There is no evidence that alendronate is metabolized when it enters the human or animal body.
In clinical studies, during which alendronate labeled with carbon atoms (14 C) was administered once intravenously, it was found that approximately 50% of the dose is excreted in the urine within 72 hours. Fecal excretion was not detected or was insignificant. After a single injection of the drug at a dose of 10 mg, the renal clearance of alendronate was 71 ml / minute. After 6 hours, the plasma concentration decreased by more than 95%. The final elimination half-life exceeds 10 years, which indicates a gradual release of the drug from the bone tissue.
Alendronate does not interfere with the excretion of other drugs through the acidic and major transport systems of the kidneys.
The parameters of bioavailability and elimination of alendronic acid in elderly and young patients are similar.
The pharmacokinetic differences of the drug by race have not been studied.
In case of impaired renal function, there is no need to adjust the dose of Osterepara, since alendronic acid is not metabolized and is not excreted in the bile.
Indications for use
- osteoporosis in postmenopausal women: prevention of fractures, including compression fractures of the spine and hip fractures;
- osteoporosis in men: preventing fractures.
Contraindications
Absolute:
- hypocalcemia;
- anomalies of the esophagus and other factors that impede the patency of the esophagus (for example, achalasia or stricture, etc.);
- severe disorders of mineral metabolism;
- vitamin D deficiency;
- chronic renal failure (creatinine clearance <35 ml / min);
- the patient's inability to remain upright (even sitting) for 30 minutes;
- lactase deficiency, galactose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption;
- childhood;
- the period of pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- hypersensitivity to drug components.
According to the instructions, Osterepar should be used with caution due to the risk of complications in the following cases:
- diseases of the digestive tract in the acute phase, such as duodenitis, gastritis, diseases of the esophagus, ulcers, dysphagia;
- serious diseases of the gastric tract in the previous 12 months, such as gastrointestinal bleeding, peptic ulcer, etc.;
- surgical intervention (the exception is surgery on the spastic pylorus of the stomach).
Instructions for use of Osterepara: method and dosage
Osterapar is intended for oral administration. The tablets should be taken in the morning on an empty stomach, at least 30 minutes before meals, liquids (including mineral water) or other medicines, since they can reduce the absorption of the drug.
To reduce the risk of esophageal irritation, the following guidelines are recommended:
- take pills immediately after getting out of bed;
- do not chew or dissolve tablets (ulcers in the mouth and pharynx may form);
- drink the drug with plenty of water (1 glass);
- do not go to bed after taking pills;
- take food no earlier than 30 minutes after taking the pills;
- do not take the drug in the morning while lying in bed and before going to bed.
For osteoporosis, men and women are prescribed 1 Osterepar tablet once a week.
The optimal duration of therapy has not been established. The need to continue taking Osterepara should be regularly assessed, especially after 5 years of use.
In addition, the intake of calcium and vitamin D preparations is shown if these substances are not supplied in sufficient quantities with food.
If you miss taking Osterapar, you need to take a pill in the morning of the next day. In the future, you need to return to the reception on the day of the week from which the treatment began. It is forbidden to take two doses in one day.
Side effects
According to a one-year clinical study, the safety profiles of alendronate at a dose of 70 mg per week and at a dose of 10 mg per day in postmenopausal women are similar.
According to data from three-year clinical studies, when using alendronic acid at a dose of 10 mg per day in postmenopausal women, its overall safety profiles are similar to placebo.
In wide clinical practice (including in clinical trials and post-marketing experience of use), the following side effects of Osterepara have been established:
- from the digestive system: often (from ≥ 1/100 to <1/10) - sour belching, diarrhea or constipation, abdominal pain, dyspeptic disorders, bloating, dysphagia, esophageal ulcer; infrequently (from ≥ 1/1000 to <1/100) - melena, nausea, vomiting, esophagitis, gastritis, esophageal erosion; rarely (from ≥ 1/10 000 to <1/1000) - ulceration of the oropharynx, esophageal stricture, ulcers, perforation, bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract;
- from the musculoskeletal system: very often (≥ 1/10) - joint pain (sometimes severe), bone pain, myalgia; often - joint swelling; rarely - atypical fractures of the femoral body, osteonecrosis of the lower jaw;
- from the skin and skin appendages: often - alopecia, itching; infrequently - erythema, skin rash; rarely - a rash with photosensitivity, severe skin reactions, including toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome;
- from the central nervous system: often - dizziness, headache; infrequently - a violation of taste;
- on the part of the organs of balance and vision: often - imbalance; infrequently - scleritis, uveitis, episcleritis;
- allergic reactions: rarely - hypersensitivity reactions, including urticaria, angioedema;
- on the part of the body as a whole: often - peripheral edema, asthenia; infrequently - transient symptoms of the acute phase reaction (malaise, myalgia, less often - fever), usually at the initial stage of therapy;
- on the part of laboratory parameters: rarely - symptomatic hypocalcemia (especially in patients with risk factors).
Overdose
In case of an overdose of Osterepara, dyspeptic disorders, abdominal pain, heartburn, gastritis, esophagitis, dysphagia, hypophosphatemia, hypocalcemia are possible.
Treatment is aimed at eliminating the violations that have arisen. To bind alendronate, it is recommended to take antacids and milk. In case of overdose, do not induce vomiting, as there is a risk of damage to the esophagus. The patient should be in an upright position (do not lie down).
special instructions
When prescribing Osterepara, it is necessary to take into account other causes of osteoporosis, in addition to age, estrogen deficiency and the use of glucocorticoids.
Like other bisphosphonates, Osterepar can cause gastrointestinal side effects, sometimes leading to esophageal perforation and strictures. In some cases, these complications may require hospitalization. There are isolated cases of gastric and duodenal ulcers, including severe and complicated ones (however, the causal relationship of its appearance with alendronate intake has not been proven). Therefore, patients should be warned about the need for immediate medical attention if they notice pain when swallowing or behind the breastbone, the appearance or aggravation of heartburn, dysphagia. The risk of adverse events from the digestive system increases if the recommendations for taking pills are violated or if the drug is continued after the onset of symptoms of irritation of the esophagus. That is why it is so important to adhere to the rules for taking Osterepara.
With extreme caution, the drug should be prescribed to patients with exacerbations of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in the upper sections. The doctor makes the decision on the appointment of Osterepara in each case individually after assessing the degree of risk and expected benefit, especially for patients with Barrett's esophagus.
There have been isolated reports of the development of local osteonecrosis of the jaw, associated mainly with a prior local infection (including osteomyelitis) and / or tooth extraction, often with slow recovery. Most often, osteonecrosis of the jaw occurs in cancer patients who are injected with bisphosphonates intravenously. Also, risk factors for this complication include smoking, poor oral hygiene and comorbidities (for example, infection, periodontal disease and / or other dental diseases, coagulopathy, anemia), as well as concomitant therapy (for example, radiation, chemotherapy or corticosteroid therapy). In the case of the development of osteonecrosis of the jaw, the patient requires medical assistance from a maxillofacial surgeon, while the issue of canceling bisphosphonates is considered on an individual basis.
If it is necessary to carry out an invasive dental intervention, the patient should definitely warn the doctor about taking Osterepara. The dentist chooses the tactics of treatment, assessing the benefits and risks.
Some patients experience joint, bone and / or muscle pain during treatment. Often these symptoms are severe, up to and including disability. The time before the onset of such pain varies from one day to several months from the start of Osterepara. In most cases, discontinuation of the drug is sufficient for the symptoms to subside, but in some patients, after the resumption of therapy with the same drug or another bisphosphonate, pain recur.
There are rare reports of the occurrence of pathological (i.e., occurring spontaneously or under the influence of slight force) subtrochanteric fractures and fractures of the proximal femoral diaphysis in patients receiving bisphosphonates. Some fractures are classified as stress fractures that occur without injury. Some patients experienced prodromal pain in this area for several weeks or months before a complete fracture. These cases are few, and stress fractures with similar clinical features have also been reported in patients who did not take bisphosphonates. In the event of a stress fracture, it is necessary to provide orthopedic care to the patient, examine him, as well as assess the causes and risk factors, such as increased or excessive stress, fracture of the lower limb, arthritis,a history of stress fracture, vitamin D deficiency, diabetes mellitus, malabsorption, chronic alcoholism, corticosteroid use. In about a third of cases, the stress fracture was bilateral, therefore, in the case of a femoral body fracture, an examination of the contralateral femur is also required. It may be necessary to stop taking the drug until results are obtained, depending on the balance of benefit and risk.
In patients with hypocalcemia, it is necessary to normalize the level of calcium in the blood before taking Osterepara. Other disorders of mineral metabolism, including vitamin D deficiency, should also be eliminated. During therapy, these patients should be monitored for calcium levels in the blood and monitored for symptoms of hypocalcemia.
Osterapar increases the content of minerals in the bones, and therefore an asymptomatic decrease in the concentration of phosphates and calcium in the blood serum is possible, especially in patients with an initially increased rate of bone metabolism, with Paget's disease, as well as in patients receiving glucocorticosteroids at the same time. It is especially important for this category of patients to ensure adequate intake of vitamin D and calcium.
Influence on the ability to drive vehicles and complex mechanisms
There is no information on the effect of Osterapar on attention and reaction rate. However, you should take into account the likelihood of some side effects that can negatively affect the ability to drive vehicles and perform potentially hazardous work.
Application during pregnancy and lactation
There are no data on the safety of using alendronic acid in pregnant women. In studies conducted on animals, it was found that the drug, when used in high doses, disrupts the formation of fetal bone tissue. Also revealed dysfunction of labor, caused by hypokalemia. In this regard, Osterepar is contraindicated in pregnant women.
There is no information on the penetration of alendronate into breast milk, therefore Osterapar is also contraindicated during lactation.
Pediatric use
Osterapar is not prescribed in childhood due to the lack of clinical data on the safety and effectiveness of its use.
With impaired renal function
Osterapar is contraindicated in chronic renal failure if creatinine clearance is less than 35 ml / min.
When creatinine clearance is more than 35 ml / min, dose adjustment is not required.
Drug interactions
The absorption of alendronate is reduced by antacids, some oral forms of other drugs, calcium, food and drinks (including mineral water). Food should be taken no earlier than 30 minutes after Osterepara, medications - at least 1 hour.
Ranitidine increases the bioavailability of alendronate.
In the case of concomitant administration of hormone replacement therapy (estrogen and / or progestin), drug interactions were not observed. Also, there were no clinically significant reactions with the simultaneous use of glucocorticosteroids.
When Osterepara is combined in a daily dose of more than 10 mg with acetylsalicylic acid, the incidence of undesirable effects from the upper gastrointestinal tract increases. However, this effect was absent when Osterepara was taken at a dose of 70 mg once a week.
Alendronate should be used with caution in patients receiving non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs due to the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Analogs
Osterepara analogues are: Alendronat, Alendrokern, Binosto, Alendronat Pliva, Ostalon, Strongos, Tevanat, Forosa, Fosamax.
Terms and conditions of storage
Store for no more than 2 years out of the reach of children at temperatures up to 25 ° C.
Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
Dispensed by prescription.
Reviews about Osterapar
There are few reviews about Osterapar, which is due to the prophylactic specificity of its use - to prevent the occurrence of fractures. Specialists speak positively about bisphosphonates in the treatment of osteoporosis, because, according to research, they slow bone resorption, increase bone strength and maintain bone mass at the existing level (sometimes even increase it to 10%), thereby "controlling" the disease, preventing fractures.
Occurring negative reviews about Osterapar concern the development of side effects from the gastrointestinal tract during therapy. According to patients, even when taking pills during the period of stable remission of the digestive system disease, after 3-4 months, if not earlier, complaints of heartburn, belching, pain in the stomach, intestines and along the esophagus appear. Because of these symptoms, treatment with Osterepar had to be stopped.
The price of Osterapar in pharmacies
The price of Osterepar is 310-365 rubles per pack of 4 tablets.
Osterepar: prices in online pharmacies
|
Drug name Price Pharmacy |
|
Osterapar 70 mg tablets 4 pcs. RUB 200 Buy |

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Information about the drug is generalized, provided for informational purposes only and does not replace the official instructions. Self-medication is hazardous to health!