- Author Rachel Wainwright [email protected].
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Cyst of the choroid plexus of the brain in the fetus
The content of the article:
- Specifications
- Origin
- The reasons
- Effects
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Video
Fetal choroid plexus cysts are detected in less than 1% of cases. The possibility of their detection usually occurs in the interval between the 16th and 20th weeks of intrauterine development. As a rule, most of such neoplasms independently regress in the third trimester of pregnancy (closer to 28 weeks).

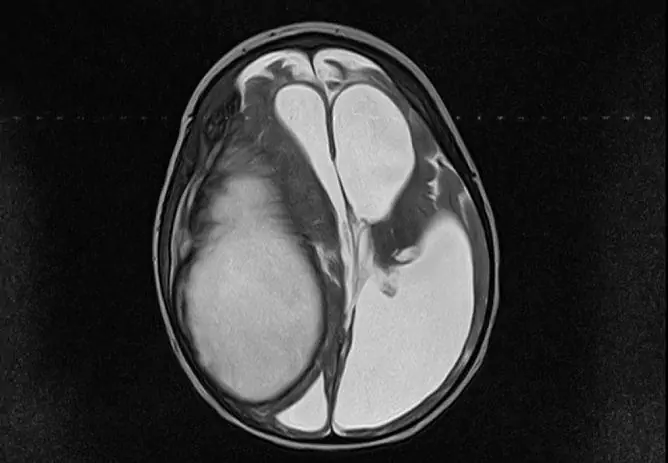
The cyst of the choroid plexus can be detected at the stage of intrauterine development, by the time of delivery it usually disappears
Specifications
The formation is an isolated cavity filled with a transparent liquid.
Features of the structure:
- They are small and tend to dissolve on their own.
- More often localized closer to the caudal part of the choroid glomus.
- Has clear, even contours.
- Does not show an upward trend.
- Signs of malignancy are not typical. Due to the peculiarities of the location, it should be differentiated with choroid carcinoma and choroid papilloma.
- There are no clinically significant symptoms. The exception is the development of occlusive hydrocephalus (violation of the normal outflow of cerebrospinal fluid and its accumulation in the head). Extremely rare.
- It is regarded as a stigma of dysembryogenesis (malformation). These newborns have a high risk of having chromosomal abnormalities (trisomy 18 chromosome - Edwards syndrome).
- The main diagnostic method is ultrasound. Discovered as a random find during screening.
- Pathology does not have serious consequences and does not affect the life and health of the child, therefore it does not require treatment.
- The forecast is favorable.
Origin
Choroid plexuses are derivatives of the pia mater that are localized in the ventricles of the brain. During embryogenesis at 4 weeks, 3 cerebral vesicles are formed from the neural tube:
- front;
- middle;
- diamond-shaped with internal cavities.
The walls of their cavities are lined with a layer of ependymal cells, and the bubbles themselves are filled with cerebrospinal fluid (the contents of a future cyst). Through the cells of the ependyma (the future pia mater), blood vessels grow and ensure its protrusion into the cavity of the cerebral vesicles, where folds of cells are formed. The choroid plexuses are formed in the following order:
- 4-5 weeks - a network in the fourth ventricle;
- 6-7 weeks - a network in the third ventricle;
- 7-9 weeks - lateral ventricles.
Thus, based on the peculiarities of the formation of vascular plexus cysts, we can conclude that they do not belong to typical cystic formations (regarded as a congenital malformation).
The reasons
The exact cause of the development of a cyst in the intrauterine state has not been established, but this is not required, given its harmlessness and ability to disappear after a short period of time.
Conditional factors include:
- Genetic mutations (trisomy 18 chromosome, trisomy 21 chromosome). In this case, the cyst is only one of the symptoms of the underlying disease. It is important to understand that it is not the cyst that causes the mutation, but the mutation that causes the formation of pathologies (for example, due to the divergence or underdevelopment of the bones of the skull). These pathologies are detected using karyotyping.
- Intrauterine infections. Herpes virus and cytomegalovirus are of particular importance. In this case, there is a risk that ultrasound examination reveals a cystic formation formed directly in the brain tissues (a vascular plexus cyst is formed only at the stage of formation of cerebral blisters long before the appearance of clearly differentiated organ tissue, but it is not possible to distinguish between these two types in utero). In this case, cysts will often be multiple, and will be located in the frontal and temporal lobes. The pathogenesis is based on necrosis of the nervous tissue. To clarify the nature of the neoplasms, PCR of the baby's blood after birth (DNA / RNA virus) is required.
- Traumatic injuries. They can occur either during fetal development or during childbirth. It must be understood that with screening ultrasound it is not always possible to view all tissues and structures of the fetus (due to the small diameter, the cyst of the choroid plexus is not always visible). If a cystic cavity is found in a child during the neonatal period (usually they do not persist until this time, but there are exceptions), it is necessary to carry out differential diagnostics with hematomas and other formations.
- As a consequence of ischemic stroke. It occurs extremely rarely and usually against a background of pronounced oxygen starvation (partial placental abruption, concomitant diseases of the mother).
- As a consequence of hemorrhagic stroke (ruptured aneurysm). Extremely rare.
Only general factors are given that can presumably cause cystic neoplasms.
Effects
Choroid plexus cysts have no health consequences. The following are the alleged complications of any cystic formation (suppuration, rupture):
- prolonged hypertonicity in newborns;
- focal symptoms with compression of brain structures (impaired vision, hearing, sensory or movement disorders);
- partial epileptic seizures.
One of the most formidable, but extremely rare complications is hydrocephalus. It occurs due to blockage of the cystic formation of the aqueduct of the brain. In this case, bypass surgery and a course of drugs to normalize brain function in the postoperative period are indicated. Signs of pathology:
- divergence of the bones of the skull due to increased intracranial pressure;
- bulging and pulsing fontanelles;
- lag in mental and physical development due to prolonged ischemia of the cerebral cortex.
Diagnostics
The following methods are used for diagnosis:
- Scheduled ultrasound in the second trimester. It should be noted right away that when a cyst is detected, the ultrasound doctor may not tell the expectant mother anything. The diagnosis is considered valid only if a cyst is present after 30 weeks. In this case, the diagnosis is placed on the card and after birth, the child is shown neurosonography (repeated at 3 months, 6 months and a year). In the case of an increase in the cyst, a change in its shape, more complex diagnostic measures are required (differential diagnosis with similar diseases and, if necessary, correction of the diagnosis).
- MRI / CT. They are used in case of a doubtful diagnosis (signs appear that are atypical for simple cysts of the vascular plexus).
- Laboratory studies are not carried out (with the exception of PCR), since they are not informative.
Diagnosis of pregnant women is based on critical or sensitive periods of fetal development (the greatest sensitivity to external influences and the greatest risk of developing pathologies, including cystic formations):
| Embryogenesis period | Time | Features: |
| Preimplantation or tubal period | First week of pregnancy | Development of ectopic pregnancy, violation of division processes and the occurrence of mutations (abnormal mitotic processes) |
| Second period | 3 to 8 weeks |
The initial period of organogenesis, when tissues are laid (the formation of the placenta takes 3 months, but begins in this period). It was during this period that the rudiments of the cerebral cortex (bone marrow hematopoiesis) are formed. The beginning of the formation of the cystic cavity |
| Stage three | From 20-24 weeks | This period is associated with the formation of all systems and structures of the body from tissue rudiments (cell differentiation). Estimated time of detection of a cystic cavity by ultrasound |
The periods are allocated conditionally, since it is problematic to identify the exact time of formation.

Screening ultrasound in the second trimester of pregnancy reveals a vascular plexus cyst in the fetus
Treatment
Not required in 95-98% of cases. Only observation of the child's condition is shown.
In the event of clinical manifestations, it is possible to prescribe medications:
- Antiviral agents - for laboratory-confirmed herpes virus (Acyclovir).
- Drugs that reduce intracranial pressure (diuretics) - when signs of hydrocephalus occur (Spironolactone).
- Anticonvulsants - they are prescribed not only with a formed epileptic focus in the brain, but also with a pronounced activity of the neural network (pre-epileptic state).
- Weak sedatives - with increased excitability (Glycine).
- Antioxidant complexes and nootropics - to restore metabolic processes in the brain and normalize blood circulation.
All these groups of drugs are used only to eliminate symptoms.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.