- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
How to reduce intracranial pressure at home
The content of the article:
- How to relieve intracranial pressure with medication
- How to reduce intracranial pressure at home
- What helps prevent increased intracranial pressure
- Signs of increased intracranial pressure
- Causes of intracranial hypertension
- Video
How to reduce intracranial pressure is an important question of interest to patients suffering from both prolonged and short-term increases in this indicator. Short-term deviations from the norm are found in healthy people, and long-term ones are usually caused by some kind of disease, most often - brain diseases. Long-term intracranial hypertension, even if it is mild, can worsen quality of life.
It should be noted that normalizing intracranial pressure is not the same as curing a disease. This is only a temporary relief of the condition. In order to achieve a lasting effect, etiotropic treatment is necessary, that is, the elimination of the cause that caused the hypertension. Since, as a rule, we are talking about quite serious diseases, a doctor should treat intracranial hypertension.

Headache is the main symptom of intracranial hypertension
With a slight increased intracranial pressure, you can provide first aid to a person at home using previously prescribed pills or folk remedies. These methods will not help if the hypertension is significant. When a person complains of an intense headache that grows rapidly and is accompanied by nausea, and then vomiting, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance, and not self-medicate.
How to relieve intracranial pressure with medication
Intracranial pressure lowering agents are, first of all, diuretics. Their use leads to the elimination of fluid from the body, thereby reducing the amount of cerebrospinal fluid, due to which the pressure inside the skull decreases.
In addition, drugs can be used that dilate blood vessels and promote blood outflow during venous stasis, glucocorticosteroids (for cerebral edema), plasma substitutes (to improve blood circulation), antispasmodics.
All these funds must be used strictly according to the doctor's prescription, since they have serious side effects.
How to reduce intracranial pressure at home
What if you don't want to take medications, what remedies can replace them? You can relieve pain syndrome with increased intracranial pressure without medication using massage. The massage is carried out with light pressing movements on the scalp, circular stroking movements in the neck, collarbone, nape, ears.
Of the methods of traditional medicine, the most popular are decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs, which have an antispasmodic, vasodilating and mild analgesic effect.
- Infusion of mulberry branches. 1 tablespoon of young branches is poured into 1 liter of boiling water and left to simmer for 3 hours. The infusion is taken 1-2 times a day for 1 glass, and before that it is diluted with water 1: 1. The recommended course is 1 month.
- Poplar buds decoction. 5 tablespoons of dry buds are poured into 1 liter of water and boiled for 10 minutes. The broth is filtered and taken twice a day (morning and evening) for 1 glass.
- Laurel inhalations. Prepare a strong decoction of bay leaves, cool it a little, pour into a cup and breathe in the steam.
- Infusion of bearberry, parsley and oregano. Mix the raw materials in equal proportions, pour boiling water over and leave overnight. The resulting infusion is drunk on an empty stomach once a day.
- A decoction of valerian herb (horsetail, peppermint, sage). 1 tablespoon of dry grass is poured with water, boiled for several minutes, then insisted for at least half an hour. Drink 50 ml of broth 3 times a day for 1 month, after which you should take a break.
- Tincture of meadow clover. Dry clover flowers are poured into a small jar up to half and filled with alcohol or vodka to the top. The tincture is left for 2 weeks in a cool dark place, and then filtered. Take the product ½ teaspoon 2 times a day, after diluting with a tablespoon of water.
Also, to reduce intracranial pressure at home, you can take infusions of lavender, rosehip, hawthorn, which have a diuretic effect.
All traditional medicines must also be approved by the attending physician.
What helps prevent increased intracranial pressure
In order to prevent the development of intracranial hypertension, moderate physical activity is indicated (physiotherapy exercises, walking at a brisk pace, swimming, yoga, etc.).
It is recommended to limit the amount of fluid you drink to 1.5 liters per day. Diet is also important. Canned food, pickles, pickles, smoked meats, tonic drinks should be excluded from the diet; limit table salt. The basis of the diet should be low-fat meat and fish, berries and fruits, dried bread, cereals, dairy and sour milk products. Since intracranial hypertension often develops in obese people, it is necessary to normalize weight by giving up high-calorie foods and reducing the total calorie content of the diet.
With a tendency to intracranial hypertension, proper rest is very important, especially a night's sleep - at least 8 hours of continuous night sleep. Without its normalization, the rest of the treatment may be ineffective or have only a short-term effect.
Signs of increased intracranial pressure
In adult patients, increased intracranial pressure is manifested by frequent headaches that do not have a specific localization, aggravated by coughing, sneezing, bending forward, turning the head. As a rule, the most pronounced pain sensations are noted at night (more often in the morning).
There are disturbances on the part of the visual analyzer (temporary loss of vision, decreased reaction to light, blurred vision, light flashes), nausea and vomiting not associated with food intake, increased sweating, shortness of breath, increased sensitivity of the skin, sudden mood swings, irritability, lethargy, fast fatiguability. Sometimes back pain and movement disorders appear.

Laurel inhalations can reduce mild intracranial hypertension
In children of preschool and school age, intracranial hypertension is manifested by drowsiness, apathy, or, on the contrary, irritability, anxiety, headache, aggravated in the lying position, refusal to eat, nausea and vomiting.
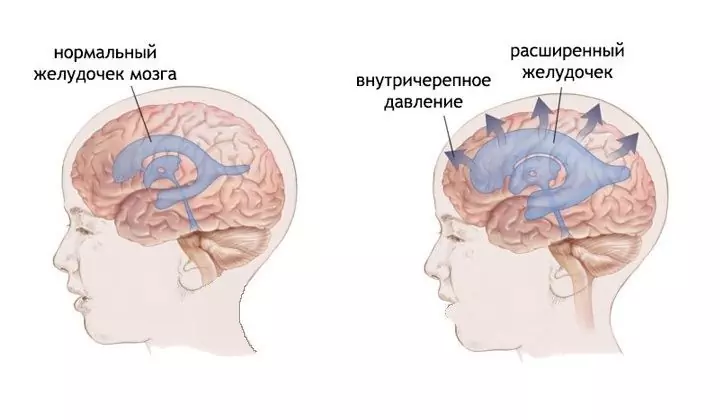
In newborns and infants, cranial hypertension can present with an enlarged head, squint, restless behavior, loud screaming for no apparent reason, frequent regurgitation or vomiting (regardless of feeding).
Causes of intracranial hypertension
Increased (as well as low) pressure inside the skull is a pathology that can lead to hydrocephalus, meningitis, encephalitis, otitis media, bronchitis, malaria, traumatic brain injury, intoxication, obesity. In addition, this condition occurs in women during pregnancy - in this case, examination and strict control is necessary, as this may be a sign of gestosis.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.