- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Intracranial hypertension in children and adults: causes, symptoms, treatment
The content of the article:
- Intracranial hypertension - what is it?
- Intracranial hypertension symptoms
- Why is cranial hypertension dangerous?
- Diagnostics
- Approach to the management of intracranial hypertension
- Lifestyle correction
- Forecast
- Video
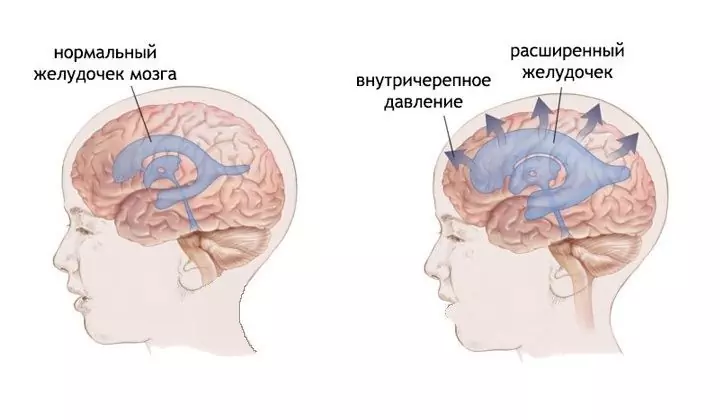
Intracranial hypertension (increased intracranial pressure, CSF-hypertensive syndrome, CSF hypertension syndrome) is a pathological condition caused by an increase in the pressure of cerebrospinal fluid in the cranium, which is usually a manifestation of a disease or a sign of brain damage. ICD-10 code - G93.2. It can develop in both adults and children.

Cranial hypertension is caused by impaired cerebral CSF flow
It is impossible to measure intracranial pressure at home in the same way as blood pressure is measured, which means that if suspicious signs appear, you must consult a doctor and undergo an examination.
Intracranial hypertension - what is it?
An increase in pressure inside the skull occurs due to a violation of the production and / or outflow of cerebrospinal fluid - cerebrospinal fluid, which is contained in the ventricles of the brain and between its membranes (arachnoid and soft). The reasons for this condition are most often neoplasms that prevent the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, for example, benign and malignant neoplasms, effusion of tissue fluid with cerebral edema, venous discirculation of the brain, hemorrhage in stroke or traumatic brain injury.
Other causes of increased intracranial pressure can be intoxication, internal hydrocephalus, encephalitis, meningitis, hyperthermia, hypercapnia, metabolic disorders, cardiovascular pathology, obesity, endocrine diseases, taking certain medications (antibacterial drugs, steroid hormones, oral contraceptives), Iron-deficiency anemia.
In children, an increase in cranial pressure can be caused by abnormalities in the development of cerebral vessels, birth trauma, fetal hypoxia, newborn asphyxia, intrauterine infection, prematurity.
In adolescents, an increase in intracranial pressure can occur due to changes in the hormonal background, with emotional overload.

An increase in cranial pressure often occurs in adolescents due to hormonal changes in the body
In some cases, it is not possible to establish the cause of the increase in intracranial pressure; this form of hypertension is called idiopathic. As a rule, it has a benign course and responds well to treatment.
Intracranial hypertension symptoms
The clinical picture depends on the primary disease, the rate of increase in intracranial pressure, and its degree.
There are three main symptoms of increased intracranial pressure in adults:
- moderate to intense headache;
- nausea and vomiting, not associated with food intake;
- visual impairment.
In addition, high intracranial pressure may be accompanied by arterial hypertension, decreased or increased heart rate, rapid fatigue, decreased performance, irritability, whistling sound in the ears, impaired memory and attention, increased sweating. Patients with increased intracranial pressure do not tolerate changes in atmospheric pressure, suffer from meteorological dependence.
Headache with increased intracranial pressure has features: a pressing, bursting character, aggravated at night closer to the morning (from 4 to 6 in the morning, increased production of cerebrospinal fluid occurs), aggravated by coughing, sneezing, bending forward, poorly relieved or not relieved by analgesics.
Mild cranial hypertension usually presents with only a mild headache. In severe hypertension, excruciating headaches are accompanied by nausea, up to vomiting. After vomiting, the intensity of the pain syndrome decreases.
In newborns and infants, an increase in intracranial pressure is manifested by anxiety, a loud cry for no apparent reason, frequent regurgitation, vomiting, sometimes muscle hypertonicity and convulsions. In children under the age of one year, divergence of the seams of the bones of the skull, bulging fontanelle, an increase in the volume of the head are possible. The vascular network becomes clearly visible on the scalp.
Why is cranial hypertension dangerous?
A sharp and rapid increase in pressure inside the cranium can cause the development of severe neurological pathology, up to disability and even death.
Prolonged compression of the brain causes its hypoxia, i.e., oxygen starvation, and, accordingly, deterioration of functions. Later, organic disorders join functional disorders, brain damage becomes irreversible, manifestations will depend on the location of the damage.
The consequence of prolonged intracranial hypertension in children is a delay in mental and physical development, which, under certain conditions, can become irreversible.
Diagnostics
The main method for diagnosing cranial hypertension in infants with open fontanelles is neurosonography, in older children and adults - ophthalmoscopy. Ophthalmoscopy allows you to detect signs of stagnation of blood in the fundus - swelling of the optic nerve, an increase in the vasculature and its overflow. This symptom, combined with clinical manifestations, allows a diagnosis to be made.
As part of the clarifying diagnosis, as well as to identify the root cause of the pathology, they resort to magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, spinal puncture, echoencephalography, and radiography.

Neurosonography is an effective method for diagnosing cranial hypertension in infants with open fontanelles
Laboratory tests are carried out: clinical analysis of blood and urine, biochemical blood test, toxicological analysis, etc.
It is possible to accurately measure intracranial pressure using invasive methods, but they are used only for cranial hypertension caused by severe brain pathology, for example, an extensive tumor.
Approach to the management of intracranial hypertension
The choice in favor of this or that treatment regimen depends, first of all, on the underlying disease that caused the development of cranial hypertension.
Intensive therapy is indicated when the intracranial pressure rises above 20 mm Hg. Art., before surgery to facilitate access, in case of dislocation syndromes, with cerebral edema (according to computed tomography or the presence of indirect signs), with a rapid increase in neurological symptoms.
Drug therapy consists in the use of diuretic (diuretic) drugs, which can quickly lower cranial pressure by removing fluid from the body. Substances in this group include furosemide, glycerol, mannitol, etc.
In order to support the functioning of nerve cells in cranial hypertension, neurometabolic drugs are prescribed. In some cases, corticosteroids, vasoconstrictors (vasoconstrictors) are indicated.
Therapy may include artificial ventilation of the lungs, the use of sedatives, normalization of the electrolyte composition of the blood and other measures depending on the existing symptoms.
The main treatment can be supplemented with physiotherapy, folk remedies (in this capacity, decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs of diuretic and restorative action are usually used).
Surgical treatment can be urgent or planned.
In some cases, shunting is carried out - the implantation of a special tube to create an artificial outflow of excess cerebrospinal fluid. The following types of shunting operations are performed: ventriculoatrial, ventriculoperitoneal and lumboperitoneal shunting.
In the presence of disorders on the part of the optic analyzer, it may be necessary to perform surgical fenestration of the optic nerve sheath. In this operation, the sheath that surrounds the optic nerve is opened to relieve pressure on the nerve and remove some fluid.
Lifestyle correction
In those cases when it is not about urgent conditions or especially severe pathology, but about moderate hypertension, correction of the lifestyle must be included in the treatment plan, i.e., its improvement. Without this, therapy will be ineffective, which means that the pathology will progress.
In some cases, especially in idiopathic cranial hypertension, changes in lifestyle to a healthy side may be sufficient to achieve a stable remission.
First of all, patients with cranial hypertension should stop smoking and drinking alcohol, since both of these bad habits are directly related to impaired blood circulation. Obese patients need to normalize their weight by following a rational diet and increasing physical activity, however, bearing in mind that extreme diets and excessive physical activity with increased cranial pressure are contraindicated.

A healthy lifestyle is an important condition for the effectiveness of the treatment of cranial hypertension
Physical activity should be moderate and regular. Physical therapy, swimming, Pilates, race walking are shown. It is optimal to combine physical exercise with being in the fresh air.
It is necessary to exclude excessive psychoemotional stress if the work is associated with them, it is desirable to change it or increase stress resistance, master relaxation techniques.
In case of visual impairment, especially progressive, one should limit the load on the visual apparatus - limit the time spent at the computer, watching movies, reading, take regular breaks to rest the eyes.
It is not recommended to use headphones, especially in the form of earbuds, listen to loud music, or be in noisy places.
Overheating should be avoided, visits to saunas, baths are contraindicated, beach vacations are undesirable (stay in the heat).
Proper nutrition is also important. The diet should include foods rich in magnesium and potassium (dried apricots, kiwi, seaweed, beans). It is necessary to limit the use of table salt, meat products, confectionery.
After a course of treatment, patients are recommended to have a medical examination at least twice a year in order to prevent relapse.
Forecast
The prognosis depends on the rate of increase in pressure inside the skull (rapidly progressive hypertension has the worst prognosis), the course of the underlying disease, as well as on the timeliness of diagnosis and the adequacy of treatment.
In uncomplicated cranial hypertension, the prognosis is generally favorable. Lifestyle correction and supportive therapy help keep intracranial pressure under control and avoid complications.
Often patients ask the question whether they will take a person with such a disease into the army. The answer to it depends on the cause of the increase in intracranial pressure and the severity of the patient's condition.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!