- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Intracranial pressure pills: drugs of primary and additional therapy
The content of the article:
- Approach to the therapy of intracranial hypertension
- Intracranial pressure pills for adults: main group
- Additional group drugs
- Non-drug therapy
- Video
What pills for intracranial pressure are effective and how effective are they? Can they be taken without a doctor's prescription? Let's try to figure it out.
The diagnosis of "intracranial hypertension" (increased intracranial pressure) can only be established by a specialist, and for this he will need an instrumental examination. After that, the patient is prescribed complex therapy, which is aimed not only at eliminating symptoms, but also, if possible, at removing the root cause of the disease. In practice, this means that the patient must take several drugs of different pharmacological groups, which together provide a complex effect. It is highly discouraged to take any medications for intracranial pressure on your own, without medical supervision, and also to change the prescribed therapy - the result may be the most unpredictable.

All medications for intracranial hypertension must be prescribed by a doctor.
Approach to the therapy of intracranial hypertension
Intracranial pressure medications act in two directions. The first is symptomatic, that is, their task is to relieve or alleviate painful symptoms, thereby improving the patient's quality of life. The second direction is pathogenetic, that is, the elimination of the primary cause of the pathological process. For effective treatment, it is necessary to combine these two groups, thereby providing a lasting result, and it is possible to reduce the cranial pressure for a long time. It should be noted that all drugs that lower cranial pressure are potent drugs that, if used incorrectly, can cause serious damage to the body, therefore they are prescribed only for medical reasons and should be drunk strictly according to the scheme prescribed by the doctor.
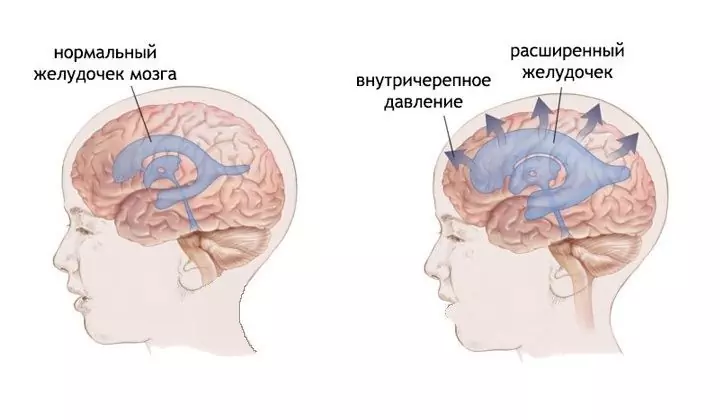
Intracranial pressure depends on the cerebrospinal fluid (cerebrospinal fluid, which is in constant circulation, produced in the ventricles of the brain), its quantity, movement, production and absorption, it is the production and circulation of cerebrospinal fluid that is the main link in the pathogenesis of cranial hypertension. Thus, treatment is aimed at improving the cerebrospinal fluid flow, cerebral circulation, or at reducing the amount of free fluid in the body (by diuresis), which will lead to a decrease in the amount of cerebrospinal fluid.
Why is it necessary to correct intracranial hypertension? Primarily because this condition causes excruciating and persistent headaches, a feeling of squeezing the head, nausea and vomiting, deterioration of vision and sometimes hearing, the appearance of pathological reflexes, especially the eyeballs and upper limbs. Patients become irritable, their ability to work decreases, sleep is disturbed, and chronic fatigue appears. Prolonged compression of the brain leads to its hypoxia and irreversible consequences from the nervous system; in the most severe cases, death can occur.
Intracranial pressure pills for adults: main group
How to treat high cranial pressure? Consider drugs for intracranial pressure for adults, since the approach to the treatment of this pathology in children will be different.
Diuretics are one of the main groups of pharmacological drugs that are used for high blood pressure as an ambulance. They are diuretics that stimulate the elimination of fluid from the body, thereby reducing the volume of circulating blood. Since the cerebrospinal fluid is formed by filtering blood, a decrease in its volume reduces its quantity, and, as a result, intracranial pressure.
According to the indications, the following diuretics are prescribed:
- Furosemide (Lasix) - this drug is prescribed when a massive, forced diuresis is needed, the effect occurs within half an hour after administration. It is usually prescribed in the morning, since urination will be frequent;
- Hypothiazide - like Furosemide, removes potassium from the body. A lack of potassium causes metabolic disorders, which can be very serious, therefore, when prescribing such drugs, an additional intake of potassium-containing agents is necessary;
- Diacarb is a loop diuretic that reduces the production of cerebrospinal fluid by blocking a number of transport systems and enzymes. The action occurs within a day, it reaches the maximum therapeutic effect for quite a long time. The drug is completely eliminated within 24 hours;
- glycerol and mannitol are osmotic diuretics that provide action within 10 minutes after ingestion. With frequent or improper use, micronutrient deficiencies and disturbances in water and electrolyte metabolism may develop.
The next group is vasodilator drugs, or vasodilators. Injection agents are used in the hospital, they include magnesia sulfate and nicotinic acid. More convenient to use are highly specific beta-blockers. Their list is extensive: Atenolol, Acebutolol, Anaprilin, Bisoprolol, Carvedilol, Coriol, Metoprolol, Nebilet, Nebivolol, Talinolol. Dosages of these drugs are indicated in special tables, taking into account the body weight and age of the patient.
Furosemide is a diuretic that allows you to quickly relieve increased intracranial pressure
Contraindications to their use are bronchial asthma, heart disease, renal failure and any systemic circulatory disorders, cerebrovascular accidents, stroke or heart attack. It is not recommended to use them during pregnancy and in children.
The list of the main group of tablets for intracranial pressure in adults is completed by neurometabolic stimulants, which increase cerebral blood flow, evenly distributing it, and also normalize metabolic processes in the tissues of the brain. The most popular names are Piracetam and Nootropil. This group includes Glycine, Cerebrolysin, Citrulline and others.
Additional group drugs
In order not only to relieve the existing hypertension, but also to minimize the risk of its formation in the future, additional drugs of the following groups are used:
- cerebroprotectors (neuroprotectors) - are necessary to increase the endurance of the nervous tissue and prevent brain injury in conditions of high blood pressure and prolonged hypoxia. Popular drugs in this group are Cerebrolysin, Cortexin, Gliatilin;
- vasoprotectors - serve to strengthen the walls of blood vessels, protect them from damage by free radicals, high pressure. Their reception prevents dangerous complications in the form of acute disorders of cerebral circulation, i.e., stroke. This group includes Cinnarizin, Cavinton;
- nootropic drugs - improve cerebral circulation, returning lost integrative functions. They contribute to the normalization of collateral blood circulation, that is, they increase the outflow through additional vessels, helping to eliminate cerebral edema. Helps restore cognitive abilities. The drugs in this group are Piracetam, Pantogam.
- glucocorticosteroids - powerful anti-inflammatory drugs, used in the fight against cerebral edema, perifocal inflammation;
- sedatives - have a calming effect, reducing the pathological excitability of the nervous system. These include preparations of valerian, Valocordin, etc.
Pain relievers can be prescribed to reduce headaches, but in this case they are not highly effective, and in addition, should be used only in a short course.
Non-drug therapy
Drug therapy will be ineffective in the long term if lifestyle adjustments are not made. It is necessary to revise the diet and exclude foods that affect blood pressure. These are spicy, spicy, pickled, salty dishes, tonic drinks, alcohol. The amount of salt consumed should be significantly reduced. It is recommended to completely quit smoking, as it destabilizes the vascular walls.
Mild sedatives reduce intracranial pressure
You need to pay attention to the daily routine. First of all, you should ensure a full night's sleep - try to go to bed and wake up at the same time. Also, do not overwork either mentally or physically. Shown are regular walks in the fresh air, physiotherapy exercises (exercises), head massage, water procedures.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Nikita Gaidukov About the author
Education: 4th year student of the Faculty of Medicine No. 1, specializing in General Medicine, Vinnitsa National Medical University. N. I. Pirogov.
Work experience: Nurse of the cardiology department of the Tyachiv Regional Hospital No. 1, geneticist / molecular biologist in the Polymerase Chain Reaction Laboratory at VNMU named after N. I. Pirogov.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.