- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
How to treat intracranial pressure: treatment in adults
The content of the article:
- How to treat intracranial pressure
- How to treat intracranial pressure with folk remedies
- Diet therapy
- What can cause increased intracranial pressure
- Signs of increased intracranial pressure
- Video
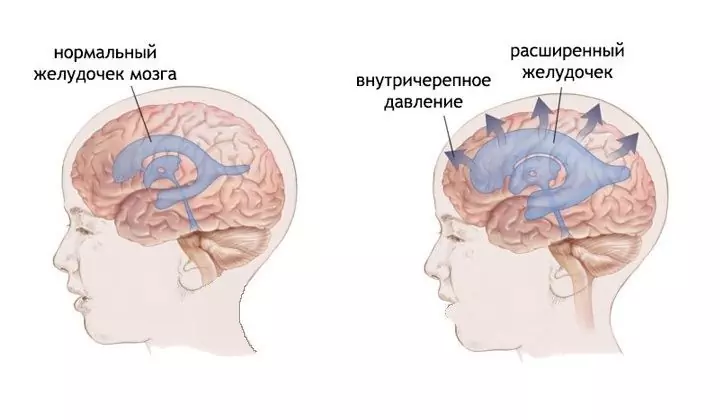
How is intracranial pressure treated? First, you need to have an idea - what is intracranial pressure, what is its rate and what can cause it to increase. Intracranial pressure is called the pressure exerted by the cerebrospinal fluid contained in the ventricles of the brain, as well as between the soft and arachnoid membranes of the brain. The intracranial pressure rate is 7.5-15 mm Hg. Art. With intracranial hypertension, it can exceed 30 mm Hg. Art.
Increased intracranial pressure (increased ICP, intracranial hypertension) is caused by impaired production or outflow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), this is a dangerous condition that can lead to adverse neurological consequences.
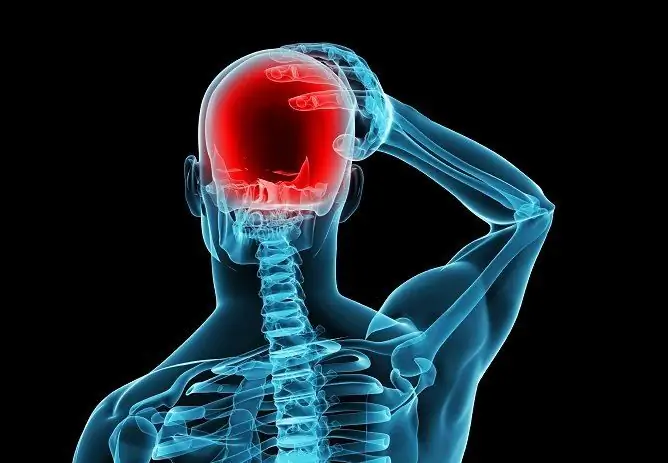
Increased intracranial pressure manifests itself mainly as a headache
Intracranial pressure can increase in healthy people, but in this case it quickly returns to normal. Long-term hypertension is usually not an independent disease, but one of the symptoms of another disease.
How to treat intracranial pressure
Can intracranial hypertension be treated at home? There is no definite answer to this question. In some cases, traditional medicine is enough, in others it is impossible to do without surgical intervention, it all depends on the primary disease. But even in cases where the patient is being treated at home, the doctor must control the course of therapy.
Drug therapy usually consists in the use of diuretics, that is, diuretics, which, by removing fluid from the body, help to reduce the amount of cerebrospinal fluid, and therefore its pressure on the cerebral structures. Also, vasodilators, sedatives are prescribed, in some cases, pain relievers are indicated.
As an additional treatment, physiotherapy, massage, physiotherapy exercises, diet therapy are used. Lifestyle improvement is an important element of therapy. Patients should be sure to normalize their work and rest regime, first of all, to ensure a full night's sleep. It is necessary to move more, be in the fresh air every day, and also quit smoking and drinking alcohol. Overweight patients should normalize it, since metabolic disorders affect, among other things, the cerebrospinal fluid.
Surgical treatment of intracranial pressure in adults consists in removing obstacles to the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. This is the removal of neoplasms (tumors, hematomas, cysts) or shunting - an operation that consists in creating an artificial drainage of excess cerebrospinal fluid using a shunt.
How to treat intracranial pressure with folk remedies
What folk remedies are most effective for intracranial pressure? Mainly, we are talking about home preparations from medicinal plants. It is generally accepted that, unlike pharmaceuticals, traditional medicines are completely harmless, and therefore preferable. This is not true. Folk remedies, just like pharmacy ones, can harm if they are not used for their intended purpose, in addition, they cause allergies much more often. They are usually milder, but for this reason they cannot replace drug therapy when required, but are used as a supplement. But even in this case, they may be incompatible with medications. That is why treatment with folk remedies should be agreed with the attending physician.
Below are a few easy-to-prepare home remedies for treating intracranial hypertension.
- Tea made from peppermint leaves, lemon balm, chamomile, linden flowers, mulberry - this tea is useful to replace ordinary black tea and coffee.
- Infusion of black poplar buds or corn stigmas - used as a diuretic.
- Alcoholic tincture of clover flowers - fill half a jar with dry clover, pour alcohol or vodka to the top and leave for two weeks in a cool dark place. Then drain the tincture, strain. Take ½ teaspoon 1-2 times a day.
- Lemon-garlic mixture - 2 lemons and 2 heads of garlic, grind into gruel, pour 2 liters of heated water (not boiling water!), Leave for a day in a dark place, then strain and take 30 ml in the evening before going to bed.
- Tincture of peppermint, motherwort, valerian, eucalyptus and hawthorn. All ingredients are mixed in equal parts, a tablespoon of the dry mixture is poured into 0.5 liters of vodka, insisted for a week in a dark place, then drained and filtered. Take 20 drops three times a day.
- A decoction of wild rosemary, motherwort and marshwormweed - mix dry raw materials in equal parts, pour a tablespoon of the mixture with a glass of water and boil for 5 minutes, then the broth is infused for 4 hours, then filtered. Take 0.5 cups before meals.
Rubbing some warmed lavender oil into your temples can help with headaches.
Diet therapy
With intracranial hypertension, diet is indicated. It is necessary to limit the use of products that can have an exciting effect on the nervous and cardiovascular system, cause fluid retention in the body, as well as those that are difficult to digest and cause the development of flatulence.
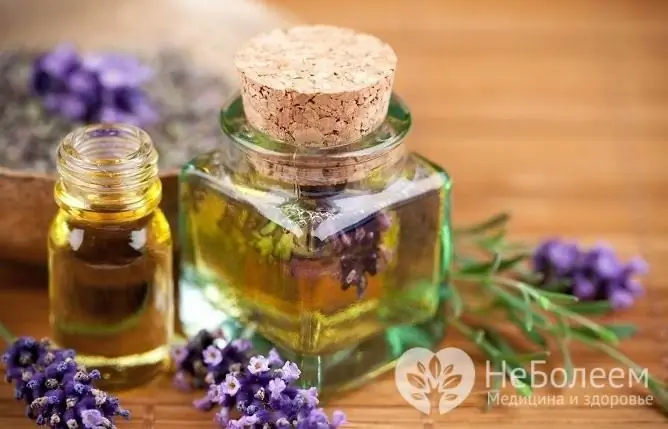

Rubbing lavender oil into whiskey sometimes helps relieve headaches
Food should be taken on schedule, observing approximately equal intervals between meals, at least 5 times a day in small portions. Dinner should be at least three hours before going to bed.
It is advisable to cook dishes using dietary methods - boil, bake, steam. It is imperative to include fresh vegetables and fruits in the diet, since the diet must provide the body's needs for vitamins and trace elements.
The diet should be based on the following foods:
- milk (if there is no individual intolerance) and dairy products;
- raw and cooked vegetables, especially cucumbers, tomatoes, pumpkin, potatoes, carrots, beets, zucchini, all types of cabbage, green peas, bell peppers, leafy greens;
- fresh and cooked fruits and berries;
- dried fruits;
- meat - it is recommended to give preference to veal, beef, rabbit, turkey, chicken;
- Fish and seafood;
- eggs;
- cereals;
- pasta;
- bread and unpalatable bakery products;
- butter and vegetable oils;
- fruit and vegetable juices, green, black, herbal tea, coffee with milk.
It is recommended to exclude baked goods, confectionery, strong meat, fish and mushroom broths, fatty meats, smoked sausages, caviar, fatty and salty cheeses, legumes, radishes, radishes, onions, garlic, mushrooms, horseradish, mustard, mayonnaise, black coffee, cocoa, alcohol, marinades, pickles and other canned food.
You should limit the consumption of table salt to 5 g per day.
If the patient is obese, it is necessary to reduce the daily calorie intake by 200-300 kcal while maintaining nutritional value. It is forbidden to adhere to strict low-calorie diets for patients suffering from intracranial hypertension.
What can cause increased intracranial pressure
The treatment of intracranial hypertension is carried out in two directions:
- Elimination of symptoms, first of all, a painful headache.
- Elimination of the cause of increased ICP.
What is the cause of intracranial hypertension? Its immediate cause is an increase in the volume of cerebrospinal fluid, either due to its impaired outflow, or due to increased production. An excess amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the closed space of the cranium increases the pressure on the brain, which leads to its hypoxia, and with prolonged compression it can destroy certain structures. In the latter case, the consequences of intracranial hypertension become irreversible, which is why this pathology requires mandatory pathogenetic treatment, and not just elimination of symptoms.
Excessive cerebrospinal fluid pressure can be caused by: hydrocephalus, stroke, meningitis, encephalitis, neoplasms of the brain (tumors, cysts, hematomas), congenital anomalies in the structure of cerebral vessels, metabolic disorders, intoxication, acute otitis media, malaria, craniocerebral trauma, excess sodium in blood, arterial hypertension, vitamin deficiency, taking certain medications, allergic reactions, obesity and some other conditions.
In rare cases, a primary disorder causing an increase in pressure within the skull cannot be detected. Then they talk about idiopathic intracranial hypertension.
Signs of increased intracranial pressure
The manifestations of increased intracranial pressure most often appear and increase gradually, but in some cases they can appear suddenly - for example, with a stroke. The most pronounced symptom of increased ICP is headache, which is pressing, bursting in nature (patients sometimes say that the pain literally makes them "eyes bulge their foreheads"). It is characteristic that such a headache is not eliminated by the use of conventional analgesics and is intensified if the head is lowered.
Pain syndrome is accompanied by nausea, up to vomiting. The peculiarity of vomiting in this case is that it is not associated with food intake, but is associated with a headache. Vomiting can be repeated, as a rule, the pain subsides after it.
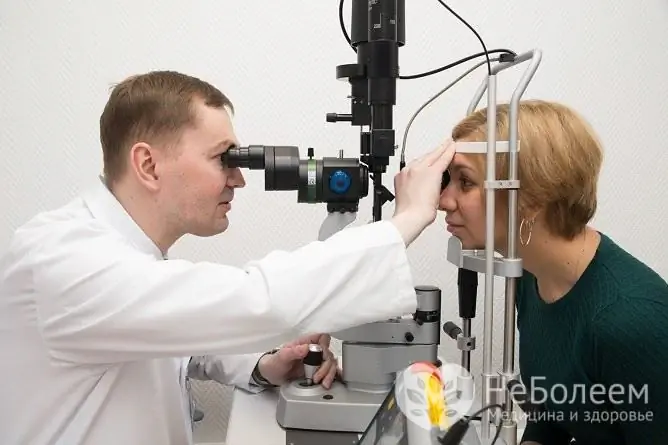
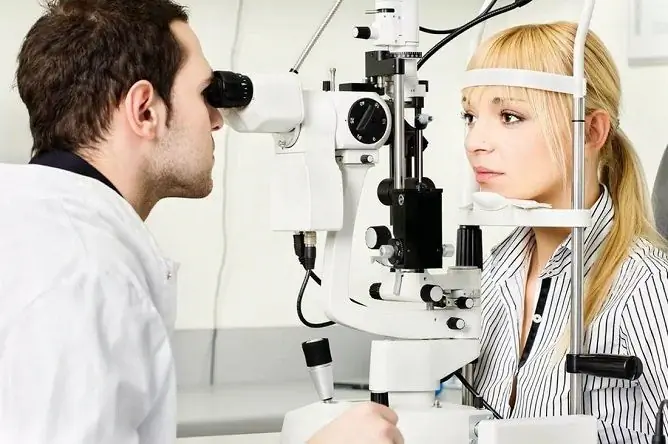
Ophthalmoscopy is used to diagnose intracranial hypertension.
The third characteristic sign of increased cranial pressure is visual impairment. This can be a decrease in visual acuity, loss of visual fields, light flashes or, on the contrary, black spots in front of the eyes, etc.
In addition, there are arrhythmias, palpitations, changes in blood pressure, dizziness, shortness of breath, nervousness, sleep disorders, decreased ability to work, and fatigue.
The diagnosis of intracranial hypertension is usually made on the basis of a characteristic clinical picture and is confirmed by the results of ophthalmoscopy (with an ophthalmological examination, the so-called stagnant fundus is found). To identify the primary disease, computed or magnetic resonance imaging, X-ray examination, ultrasound diagnostics, spinal puncture and a number of other studies may be required.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.