- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Brucellosis
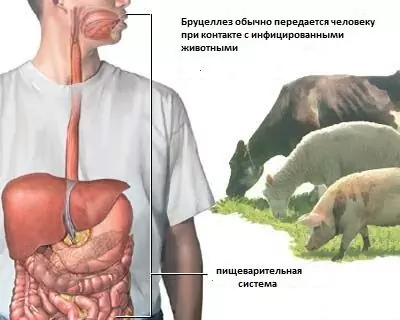
Brucellosis [brucellosis; brucella (Brucella, Ber - Bergey's manual of determinative bacteriology) + Greek -sis (word-form suffix) - disease; synonyms: melitococation, melitokokkosis, undulatory fever, Mediterranean fever, Brucella fever, Maltese fever, Maltese fever Banga disease] is an infectious disease, a member of the group of bacterial zoonoses, excited by microorganisms of the genus Brucella, transmitted by contact or alimentary means from sick animals to humans; usually proceeds as a chroniosepsis with relapses and exacerbations, a polymorphic clinical picture.
Allocate brucellosis:
- Goat-sheep type: excitable Brucella melitensis etiological variant of brucellosis; in humans, it has a severe course with various complications and multiple relapses;
- Bovine type: excitable Brucella abortus etiological variant of brucellosis; in humans, it differs in a relatively mild course of the disease;
- Acute (acuta): a clinical form of brucellosis characterized by profuse sweating, chills, fever, arthritis, polyadenitis, intoxication, enlarged spleen and liver, neuro-vegetative disorders and leukopenia;
- Porcine type: excitable Brucella suis etiological variant of brucellosis; in humans, it is rare and differs in a relatively easy course;
- Chronic (chronica): a clinical form of brucellosis, characterized by a prolonged course and a variety of symptoms that form in accordance with the predominant lesion of certain systems and organs against the background of an allergic organism.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.