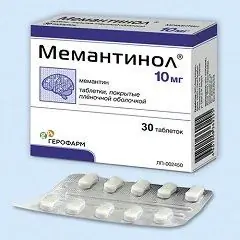
Memantinol
Memantinol: instructions for use and reviews
- 1. Pharmacological properties
- 2. Indications for use
- 3. Contraindications
- 4. Method of application and dosage
- 5. Side effects
- 6. Overdose
- 7. Special instructions
- 8. Application during pregnancy and lactation
- 9. Use in childhood
- 10. In case of impaired renal function
- 11. For violations of liver function
- 12. Use in the elderly
- 13. Drug interactions
- 14. Analogs
- 15. Terms and conditions of storage
- 16. Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
- 17. Reviews
- 18. Price in pharmacies
Latin name: Memantinol
ATX code: N06DX01
Active ingredient: memantine (memantin)
Manufacturer: GEROPHARM LLC (Russia)
Description and photo update: 2019-08-10
Prices in pharmacies: from 555 rubles.
Buy
Memantinol is a neurometabolic drug used to treat dementia. It is a blocker of glutamate NMDA receptors.
Release form and composition
Memantinol is available in the form of film-coated tablets:
- tablets with a dosage of 10 mg: biconvex, oblong, white, on each side with engraving "Ph" and "g" and a line between the letters; on the break, a white or almost white core is visible (10 pcs. in blisters, in a cardboard box 2, 3, 6, 9 or 12 blisters; 30 pcs. or 90 pcs. in polymer cans, in a cardboard box 1 can);
- tablets with a dosage of 20 mg: oval, from pink to pink with a brownish tint, on the one hand engraved "MEM", on the other - engraved "20"; on the break, a white or almost white core is visible (10 pcs. in blisters, in a cardboard box 3 or 6 blisters).
Each pack also contains instructions for the use of Memantinol.
Composition for one film-coated tablet:
- active substance: memantine hydrochloride - 10 mg or 20 mg;
- auxiliary components: microcrystalline cellulose, sodium starch glycolate (type A), magnesium stearate, lactose monohydrate, hydroxypropyl cellulose, colloidal silicon dioxide;
- film coating: for tablets 10 mg - Opadray II white OY-L-28900 (titanium dioxide, lactose monohydrate, macrogol 4000, hypromellose); for 20 mg tablets - Opadray 03B25482 Pink (titanium dioxide, macrogol 4000, hypromellose, yellow iron oxide dye, red iron oxide dye).
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
It is known that the manifestation and progression of symptoms of neurodegenerative dementia is facilitated by impairment of glutamatergic synaptic transmission, especially the function of NMDA receptors.
Memantine, the active ingredient of Memantinol, is a voltage-dependent and non-competitive inhibitor of ionotropic glutamate receptors that selectively bind N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA receptors). It has a moderate affinity for these receptors and has a modulating effect on the glutamatergic neurotransmitter system.
Memantinol improves cognitive processes and increases the daily activity of patients with dementia.
Pharmacokinetics
Memantine is rapidly and completely absorbed after oral administration of Memantinol. Its maximum plasma concentration is observed 3–8 hours after taking the pill.
Memantine pharmacokinetics are linear in the dose range of 10–40 mg.
As a result of the daily intake of a daily dose of 20 mg, an equilibrium plasma concentration is achieved, the value of which is 70-150 ng / ml. This pharmacokinetic parameter has pronounced individual variations. The volume of distribution is 10 l / kg. Approximately 45% of the active substance binds to plasma proteins. In patients with normal renal function, cumulation was not observed. Approximately 80% of absorbed memantine circulates in the blood unchanged.
The main metabolites of the drug: N-3,5-dimethyl-gludantane and a mixture of isomers of 1-nitroso-3,5-dimethyl-adamantane, 4-hydroxy-memantine and 6-hydroxy-memantine. Metabolites have no pharmacological activity. In vitro studies did not reveal the participation of enzymes of the cytochrome P450 system in memantine metabolism.
The main route of elimination is through the kidneys. T 1/2 is 60-100 hours. In the absence of renal dysfunction, the total clearance of memantine is 170 ml / min / 1.73 m 2. Partly renal clearance is achieved by secretion by the renal tubules. In addition, the elimination of memantinol by the kidneys occurs due to tubular reabsorption, which is probably mediated by cationic transport proteins. The rate of excretion of memantine under conditions of an alkaline urine reaction can decrease by 7-9 times. Alkalization of urine can be caused by changes in diet (in particular, a sharp transition from meat products to fruits and vegetables) or heavy use of alkaline gastric buffers.
When using Memantinol at a maintenance dose of 20 mg per day, the concentration of the drug in the cerebrospinal fluid corresponds to the inhibition constant (k i). For memantine, k i in the frontal cortex of the human brain is 0.5 μmol.
Indications for use
Memantinol is used in patients with severe to moderate Alzheimer's disease (Alzheimer's type dementia).
Contraindications
Absolute:
- pregnancy;
- lactation period;
- children and adolescents up to 18 years old;
- lactose intolerance, lactase deficiency, glucose-galactose malabsorption (since the tablets contain lactose);
- hypersensitivity to the main or auxiliary components of the drug.
Relative (Memantinol tablets are used with caution):
- renal and / or hepatic impairment;
- heart failure (III – IV functional class);
- a history of myocardial infarction;
- uncontrolled arterial hypertension;
- increased levels of thyroid hormones (thyrotoxicosis);
- severe infectious diseases of the urinary tract, the causative agents of which are bacteria of the genus Proteus;
- renal tubular acidosis;
- plentiful intake of alkaline gastric buffers, sudden changes in diet and other factors that contribute to alkalization of urine;
- predisposition to seizures (including a history);
- epilepsy;
- simultaneous administration of NMDA receptor antagonists (dextromethorphan, ketamine, amantadine).
Memantinol, instructions for use: method and dosage
Treatment with Memantinol should only be initiated and carried out under the supervision of a specialist experienced in the diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer's dementia. The doctor must establish a diagnosis in accordance with current guidelines. The drug should be used regularly, so treatment can only be started if the patient is under constant care. During the first three months, it is necessary to regularly assess the tolerance of memantine and, if necessary, change the dosage. After three months, the efficacy and tolerability of Memantinol is reviewed in accordance with clinical guidelines. If memantine is well tolerated by the patient and a positive effect is observed, maintenance therapy can be continued for a long time. The drug is stopped if there is no positive effect or intolerance to the treatment.
Memantinol tablets are taken orally, regardless of food. The drug should be taken at the same time, once a day.
To reduce the risk of unwanted adverse reactions, the dose of memantine is titrated by gradually increasing it by 5 mg weekly during the first three weeks of therapy:
- the first week of treatment (from the 1st to the 7th day): 5 mg per day (0.5 tablets 10 mg);
- the second week of treatment (from the 8th to the 14th day): 10 mg per day (one 10 mg tablet);
- the third week of treatment (from the 15th to the 21st day): 15 mg per day (1.5 tablets 10 mg);
- the fourth and subsequent weeks of treatment: 20 mg per day (2 tablets of 10 mg or 1 tablet of 20 mg).
The maintenance dose (also the maximum daily dose) is 20 mg per day.
In case of impaired renal function (creatinine clearance from 30 to 49 ml / min) at the beginning of treatment, it is not recommended to use the drug in a dose of more than 10 mg per day. If memantine is well tolerated within 7 days at a dose of 10 mg per day, it is possible to increase the daily dose to 20 mg (in accordance with the titration scheme). In severe renal failure (creatinine clearance from 5 to 29 ml / min) Memantinol should not be used in a daily dose of more than 10 mg.
In patients with mild to moderate liver dysfunction, dose adjustment is not required. There is no data on the use of memantine in persons with severely impaired liver function; therefore, memantinol is not recommended for such patients.
In patients over 65 years of age, Memantinol is used in normal doses, no dosage adjustment is required.
Side effects
- gastrointestinal tract: often - constipation; infrequently - vomiting, nausea; frequency unknown - pancreatitis;
- hepatobiliary system: often - an increase in liver function tests; frequency unknown - hepatitis;
- respiratory system: often - shortness of breath;
- cardiovascular system: often - arterial hypertension; infrequently - thromboembolism / venous thrombosis;
- nervous system and psyche: often - imbalance, drowsiness, dizziness; infrequently - confusion, gait disturbance, hallucinations (mainly in patients with severe dementia); frequency unknown - psychotic reactions;
- immune system: often - hypersensitivity to the components of Memantinol;
- parasitic and infectious diseases: infrequently - fungal infections;
- other reactions: often - headache; infrequently - increased fatigue.
In addition to the side effects listed above, during the post-registration use of Memantinol, the following adverse reactions were recorded: anxiety, increased excitability, impaired consciousness, suicidal thoughts, convulsions, depression, muscle hypertonia, increased libido, acute renal failure, cystitis, candidiasis, increased intracranial pressure, leukopenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, thrombocytopenic purpura.
Overdose
Data on drug overdose are limited.
When taking Memantinol in large doses (105 mg per day for three days or 200 mg once), symptoms of intoxication were absent or manifested by weakness, fatigue and / or diarrhea. In case of an overdose due to taking the drug at a dose of 140 mg or less (once), the patient experienced adverse reactions from the gastrointestinal tract (diarrhea, vomiting) and / or from the nervous system (dizziness, gait disturbance, drowsiness, agitation, confusion, excessive daytime sleepiness, hallucinations, aggression).
A single case of severe overdose was recorded when the patient survived after taking 2000 mg of memantine. He had nervous system side effects (10 days of coma followed by diplopia and restlessness). After plasmapheresis and symptomatic therapy, the patient recovered without any further complications.
There is no specific antidote for memantine. In case of overdose, symptomatic treatment is prescribed and standard therapeutic measures are carried out, which are aimed at removing Memantinol from the stomach and its early elimination from the blood (gastric lavage, intake of enterosorbents, forced diuresis, acidification of urine).
special instructions
Memantinol is not recommended to be used concomitantly with NMDA receptor antagonists (ketamine, dextromethorphan and amantadine), since they act on the same receptors as memantine and can increase the severity and frequency of unwanted side effects (especially from the central nervous system) …
The presence of factors in the patient that can increase the pH of urine requires careful monitoring. These factors include: increased intake of alkaline gastric pH buffers, abrupt changes in diet (eg, switching to vegetarianism), severe urinary tract infections (caused by Proteus spp.), Renal tubular acidosis. With an increase in urine pH, the excretion of memantine by the kidneys decreases and its plasma concentration increases.
Most often, Alzheimer's disease affects people 65 years of age and older, but there were no clinically significant differences in the main adverse events in patients under 65 years of age and patients 65 years of age and older.
Influence on the ability to drive vehicles and complex mechanisms
In patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's dementia, the ability to drive and operate other complex mechanisms is usually impaired. In addition, the drug itself can lead to a change in the reaction rate, so patients should refrain from any activity that requires increased concentration of attention and a quick reaction.
Application during pregnancy and lactation
Animal studies have shown that memantine can cause intrauterine growth retardation when used in doses that are similar to therapeutic doses for humans. During pregnancy, the use of Memantinol is contraindicated, unless absolutely necessary.
There are no data on the penetration of memantine into breast milk, but since this substance has lipophilic properties, excretion of the drug into milk is quite likely. If the use of Memantinol is necessary, breastfeeding should be discontinued.
Pediatric use
The efficacy and safety of memantine for children and adolescents has not been established, therefore memantinol is contraindicated in patients under 18 years of age.
With impaired renal function
With moderate renal failure, the initial dose of Memantinol should not exceed 10 mg per day, and patients with severe renal insufficiency should not be prescribed the drug in a dose of more than 10 mg per day throughout the course of the therapeutic course.
For violations of liver function
In patients with mild to moderate impairment of liver function, memantine is used in usual doses. In severely impaired liver function, the appointment of Memantinol is not recommended (there is no relevant experience).
Use in the elderly
Elderly patients do not need dose adjustment of Memantinol.
Drug interactions
Memantine can enter into drug interactions with the following substances and drugs:
- anticholinergics, dopamine receptor agonists, levodopa preparations: it is possible to enhance the action of these drugs;
- antispasmodics, baclofen, dantrolene: the therapeutic effects of these drugs can both increase and decrease (dose adjustment is required);
- antipsychotics, barbiturates: their effectiveness may decrease;
- amantadine, phenytoin, dextromethorphan and ketamine: increased risk of psychosis;
- hydrochlorothiazide: an increase in the excretion of hydrochlorothiazide and a decrease in its level in the blood are possible;
- ranitidine, quinidine, cimetidine, procainamide, nicotine: the plasma concentration of memantine may increase;
- oral indirect anticoagulants (for example, warfarin): an increase in the international normalized ratio is possible (it is necessary to regularly monitor this indicator or prothrombin time).
Analogs
Analogues of Memantinol are: Auraneks, Alzeim, Akatinol Memantine, Memantal, Memaneirin, Maruksa, Zemotin, Memikar, Memorel, Memantine, Memantin-TL, Memantin-Alvogen, Memantine Canon, Memantin-Richter, Memantin Sandoz, Tingrex, Noodzheron, Noodzheron …
Terms and conditions of storage
Store in a dark, protected from moisture place, out of reach of children, at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C.
The shelf life is 3 years.
Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
Dispensed by prescription.
Reviews about Memantinol
In the overwhelming majority of cases, reviews of Memantinol are positive. Patients themselves and people caring for patients with dementia note the effectiveness of the drug. It is known that Alzheimer's disease is incurable, but memantine slows down the course of the disease and improves the patient's quality of life (the emotional background stabilizes, depression decreases or disappears, mental abilities increase, memory strengthens). Memantinol is well tolerated (however, tablets should not be taken in the evening, as anxiety and sleep disturbances may occur). The drug is cheaper than some of the more expensive analogues.
Memantinol price in pharmacies
The price of Memantinol in the form of film-coated tablets with a dosage of 10 mg depends on the size of the package:
- film-coated tablets, 10 mg (30 pcs. in a package) - 730-870 rubles;
- film-coated tablets, 10 mg (90 pcs. in a package) - 1220-2115 rubles.
Memantinol: prices in online pharmacies
|
Drug name Price Pharmacy |
|
Memantinol 10 mg film-coated tablets 30 pcs. 555 RUB Buy |
|
Memantinol 10 mg film-coated tablets 90 pcs. 1419 RUB Buy |

Maria Kulkes Medical journalist About the author
Education: First Moscow State Medical University named after I. M. Sechenov, specialty "General Medicine".
Information about the drug is generalized, provided for informational purposes only and does not replace the official instructions. Self-medication is hazardous to health!