- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Medication for ovarian cysts
The content of the article:
- What medications for ovarian cysts can be prescribed
- Folk remedies
-
Other methods
When surgery is needed
-
Overview of Ovarian Cysts
- Symptoms
- The reasons
- Classification of cystic formations
- Video
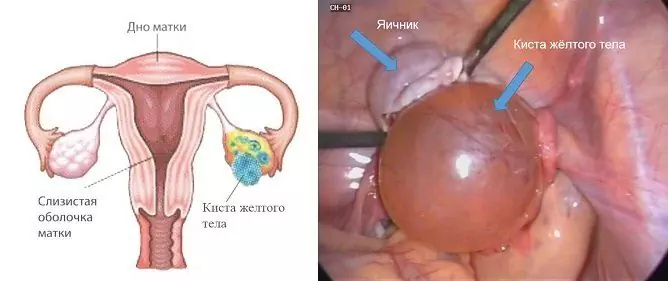
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled benign neoplasm most commonly seen in young women of reproductive age. As a rule, it is found by chance on an ultrasound scan during examination for another reason. Medication for ovarian cysts can only be prescribed by a doctor. The choice of a particular drug, first of all, depends on the type of neoplasm.

Drug treatment of cysts is not shown in all cases, its appropriateness and volume are determined by the doctor
When using ovarian cyst tablets, you must strictly follow your doctor's instructions. It is important not to complete the full course of treatment and not change the dosage of prescribed medications. It is not recommended to drink any medications uncontrollably (including numerous advertised dietary supplements with promising names), as this can worsen the condition. When trying to self-medicate, it is easy to miss the time when a neoplasm can be cured with conservative methods. In addition, it must be borne in mind that a number of cystic formations do not require treatment at all, while others are treated exclusively by surgery.
What medications for ovarian cysts can be prescribed
Different types of cysts require different treatment approaches. The most common drug groups and indications for their appointment:
| Group of medicines | Indications |
| Hormonal drugs (oral contraceptives) | They are prescribed when a cystic formation occurs against the background of a violation of hormone production. Progesterone drugs can stop the growth of the cyst, after which it can begin to shrink and disappear. Oral contraceptives not only can help resolve cystic formation, but also prevent pregnancy during treatment, and also normalize the hormonal cycle. |
| Antibiotics | Taking antibiotics for an ovarian cyst is indicated in the event of an infectious and inflammatory process. |
| Anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents | They are prescribed in a short course with significant pain syndrome, they allow to relieve pain, but they do not eliminate the problem, they are used as an adjunct to the main therapy. |
| Sedatives, vitamin and mineral complexes | They help to improve the general condition of the body. |
Folk remedies
It is ineffective to treat this disease with folk remedies. They can be used only as an adjunct to the main therapy, for example, motherwort decoction can be used to normalize sleep, and echinacea infusion can be used to strengthen immunity. It should be remembered that traditional medicine, like any other, requires prior agreement with the attending physician.
Other methods
In many cases, an ovarian cyst does not require treatment, its resorption occurs on its own. With small cysts and no complications, expectant tactics are chosen (several menstrual cycles). All that is needed in this case is regular medical supervision.
In addition to drug therapy, the following may be recommended:
- proper nutrition;
- physiotherapy;
- balneotherapy;
- quitting smoking and drinking alcohol;
- normalization of body weight;
- normalization of the regime of work and rest.
When surgery is needed
If the cystic formation does not involution on its own, and is also not cured by conservative methods, it may be necessary for a planned surgical intervention. Emergency indications for surgery arise in case of complications.
The main indications for surgical intervention are:
- a sharp increase in education;
- twist of the leg;
- rupture of cystic formation;
- the risk of malignant transformation.
The scope of the operation depends on the type and size of the cystic formation, it can be removal of only it (cystectomy), removal of the cyst with part of the ovary (resection) or complete removal of the affected ovary (oophorectomy).
Overview of Ovarian Cysts
Symptoms
A neoplasm usually does not manifest itself for a long time. Pathology is detected during diagnosis for another reason or a preventive medical examination.
Patients with large cystic lesions may experience:
- menstrual irregularities, dysfunctional uterine bleeding;
- pain in the lower abdomen (pulling pain, can radiate to the perineum), which can occur and / or intensify during physical exertion, at the beginning of the menstrual cycle, during intercourse;
- increased body temperature;
- headache;
- enlargement of the abdomen on one side.
The cystic formation can increase in size and put pressure on adjacent organs and tissues, while the patient may experience disorders of the urinary system (difficulty urinating) and intestines (constipation). Pathology can lead to the development of problems with conceiving and carrying a pregnancy.
The paraovarian cyst most often does not manifest itself in any way; in some cases, patients may experience pulling pains in the lower abdomen. With polycystic ovary disease, women may experience menstrual irregularities, acne, obesity, depression, constant pain in the abdomen and / or lower back, pelvic region.
In case of bleeding when the cyst ruptures, the following may occur:
- pallor of the skin;
- sharp pain;
- dizziness;
- disturbances of consciousness.
When a neoplasm ruptures, peritonitis and sepsis may develop.
The reasons
The reasons for the development of cystic ovarian formations are not fully understood.
Possible causes of the pathology include hormonal disorder. Cystic formation can also occur against the background of inflammatory processes in the organs of the genitourinary tract. There are also factors that affect certain types of neoplasms:
| View | Cause |
| Endometrioid cyst | Develops against the background of endometriosis (with proliferation of the endometrium) |
| Paraovarian cyst | It forms between the ovary, fallopian tube and uterine ligaments. Develops against the background of hormonal imbalance. |
| Dermoid cyst | It can be congenital, and its development can also occur against the background of injuries. |
The development of cystic ovarian formations can be facilitated by:
- excessive physical and mental stress;
- bad habits;
- overweight and underweight;
- chronic fatigue;
- early onset of sexual activity;
- artificial termination of pregnancy.
Classification of cystic formations
In gynecology, ovarian cystic formations are divided into congenital and acquired, complicated and uncomplicated, single and multiple, single-chamber and multi-chamber.
The table shows the main types of cystic formations.
| Type of ovarian formations | Explanation |
| Functional | Formed from the natural structures of the ovary, subdivided into follicular (occurs when ovulation is disturbed, when the follicle does not rupture, but continues to grow) and luteal (develops from the corpus luteum) |
| Endometrioid | These are cystic cavities filled with blood from the focus of endometriosis, which becomes thicker and darker over time |
| Cystic tumors | Subdivided into dermoid, serous and mucinous cystic formations |
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.