- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
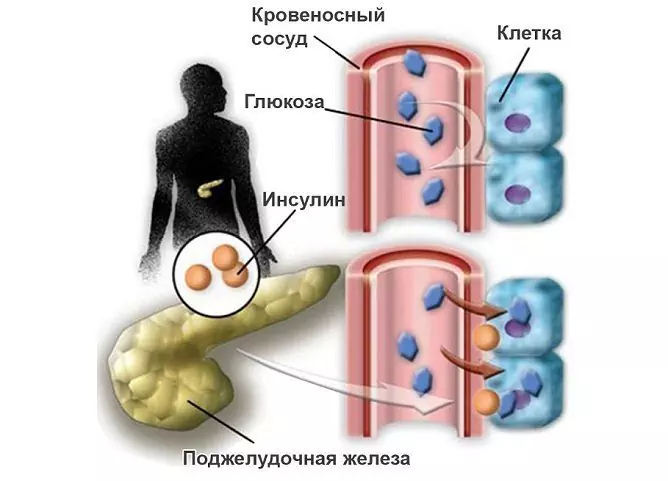
Glucose
Instructions for use:
- 1. Release form and composition
- 2. Indications for use
- 3. Contraindications
- 4. Method of application and dosage
- 5. Side effects
- 6. Special instructions
- 7. Drug interactions
- 8. Analogs
- 9. Terms and conditions of storage
- 10. Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
Prices in online pharmacies:
from 8 rub.
Buy

Glucose - a means for carbohydrate nutrition; has a detoxifying and hydrating effect.
Release form and composition
- solution for infusion 5%: colorless transparent liquid [100, 250, 500 or 1000 ml in plastic containers, 50 or 60 pcs. (100 ml), 30 or 36 pcs. (250 ml), 20 or 24 pcs. (500 ml), 10 or 12 pcs. (1000 ml) in separate protective bags, which are packed in cardboard boxes together with an appropriate number of instructions for use];
- solution for infusion 10%: colorless transparent liquid (500 ml in plastic containers, 20 or 24 pcs. in separate protective bags, which are packed in cardboard boxes together with the appropriate number of instructions for use).
Active ingredient: dextrose monohydrate - 5.5 g (which corresponds to 5 g of anhydrous dextrose) or 11 g (which corresponds to 10 g of anhydrous dextrose).
Excipient: water for injection - up to 100 ml.
Indications for use
Glucose is used:
- as a source of carbohydrates;
- as a component of anti-shock and blood-substituting fluids (for shock, collapse);
- as a base solution for dissolving and diluting medicinal substances;
- with moderate hypoglycemia (for prophylactic purposes and for treatment);
- with dehydration (due to diarrhea / vomiting, as well as in the postoperative period).
Contraindications
- hyperlactatemia;
- hyperglycemia;
- hypersensitivity to the active substance;
- intolerance to dextrose;
- hyperosmolar coma;
- allergic to foods containing corn.
Additionally for 5% glucose solution: uncompensated diabetes mellitus.
Additionally for 10% glucose solution:
- decompensated diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus;
- extracellular hyperhydration or hypervolemia and hemodilution;
- severe renal failure (with anuria or oliguria);
- decompensated heart failure;
- cirrhosis of the liver with ascites, generalized edema (including pulmonary and cerebral edema).
Infusion of 5% and 10% dextrose solutions is contraindicated within 24 hours after head injury. You also need to take into account the contraindications for medicinal substances added to the dextrose solution.
It can be used during pregnancy and lactation if indicated.
Method of administration and dosage
Glucose is administered intravenously. The concentration and dose of the drug is set depending on the age, condition and weight of the patient. The concentration of dextrose in the blood should be carefully monitored.
Usually, the drug is injected into a central or peripheral vein, taking into account the osmolarity of the injected solution. The introduction of hyperosmolar solutions can cause irritation of the veins and phlebitis. Whenever possible, when using all parenteral solutions, it is recommended to use filters in the solution line of infusion systems.
Recommended use for adults:
- as a source of carbohydrates and in isotopic extracellular dehydration: with a body weight of about 70 kg - from 500 to 3000 ml per day;
- for dilution of parenterally administered drugs (as a base solution): from 50 to 250 ml per dose of the administered drug.
Recommended use for children (including newborns):
- as a source of carbohydrates and with isotopic extracellular dehydration: with a body weight from 0 to 10 kg - 100 ml / kg per day, with a body weight from 10 to 20 kg - 1000 ml + 50 ml for each kg over 10 kg per day, with body weight from 20 kg - 1500 ml + 20 ml for each kg over 20 kg per day;
- for dilution of parenterally administered drugs (as a base solution): from 50 to 100 ml per dose of the administered drug.
In addition, a 10% glucose solution is used to treat and prevent moderate hypoglycemia and to rehydrate in case of fluid loss.
The maximum daily doses are determined individually depending on age and total body weight and range from 5 mg / kg / minute (for adults) to 10-18 mg / kg / minute (for children, including newborns).
The rate of administration of the solution is selected depending on the clinical condition of the patient. To avoid hyperglycemia, the threshold for dextrose utilization in the body should not be exceeded, therefore the maximum rate of administration of the drug in adult patients should not exceed 5 mg / kg / minute.
Recommended initial infusion rate for children according to age:
- premature and full-term newborns - 10-18 mg / kg / min;
- from 1 to 23 months - 9-18 mg / kg / min;
- from 2 to 11 years old - 7-14 mg / kg / min;
- from 12 to 18 years old - 7-8.5 mg / kg / min.
Side effects
The frequency of side effects cannot be determined based on the available data.
- immune system: hypersensitivity *, anaphylactic reactions *;
- metabolism and nutrition: hypervolemia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, dehydration, hyperglycemia, hypophosphatemia, electrolyte imbalance, hemodilution;
- skin and subcutaneous tissue: rash, increased sweating;
- vessels: phlebitis, venous thrombosis;
- kidneys and urinary tract: polyuria;
- pathological condition of the injection site and general disorders: infection at the injection site, chills *, phlebitis, fever *, local soreness, irritation at the injection site, extravasation at the injection site, fever, tremors, febrile reactions, thrombophlebitis;
- laboratory and instrumental data: glucosuria.
* These side effects are possible in patients with corn allergy. They can also manifest as symptoms of another type, such as cyanosis, hypotension, bronchospasm, angioedema, itching.
special instructions
Cases of infusion reactions have been recorded, including anaphylactoid / anaphylactic reactions, hypersensitivity reactions when using dextrose solutions. If symptoms or signs of a hypersensitivity reaction develop, the infusion should be stopped immediately. Appropriate therapeutic measures should be taken depending on the clinical findings.
Glucose should not be used if the patient is allergic to corn and corn products.
Depending on the patient's clinical condition, metabolism (dextrose utilization threshold), volume and rate of infusion, intravenous dextrose can lead to electrolyte imbalance (namely: hypomagnesemia, hypokalemia, hypophosphatemia, hyponatremia, overhydration / hypervolemia and, for example, congestive conditions, in including pulmonary edema and hyperemia), hypoosmolarity, hyperosmolarity, dehydration and osmotic diuresis.
Hypoosmotic hyponatremia can cause headache, nausea, seizures, lethargy, coma, cerebral edema and death.
With severe symptoms of hyponatremic encephalopathy, emergency medical attention is required.
An increased risk of hypoosmotic hyponatremia is observed in children, women, the elderly, patients after surgery, and those with psychogenic polydipsia.
The risk of developing encephalopathy as a complication of hypoosmotic hyponatremia is higher in children and adolescents under 16 years of age, premenopausal women, patients with central nervous system disease, and patients with hypoxemia.
Periodic laboratory tests are required to monitor changes in fluid balance, acid-base balance and electrolyte concentration during prolonged parenteral therapy and, if necessary, evaluate the dose or the patient's condition.
Glucose is prescribed with extreme caution in patients with an increased risk of water and electrolyte imbalance, aggravated by an increase in the load of free water, hyperglycemia, and the need for insulin.
The clinical indicators of the patient's condition are the basis for preventive and corrective measures.
Large-volume infusion is performed under close supervision in patients with pulmonary, cardiac, or renal insufficiency and hyperhydration.
When using a large dose of dextrose or long-term use, it is necessary to monitor the concentration of potassium in the blood plasma and, if necessary, prescribe potassium preparations to avoid hypokalemia.
To prevent hyperglycemia and hyperosmolar syndrome caused by the rapid administration of dextrose solutions, it is necessary to control the infusion rate (it must be below the threshold for dextrose utilization in the patient's body). With an increased concentration of dextrose in the blood, the infusion rate should be reduced or insulin administered.
With caution, intravenous administration of glucose solutions is carried out in patients with severe exhaustion, severe traumatic brain injury (administration of glucose solutions is contraindicated on the first day after receiving a head injury), thiamine deficiency (including in patients with chronic alcoholism), reduced tolerance to dextrose (to for example, in conditions such as diabetes mellitus, sepsis, shock and trauma, renal failure), water and electrolyte imbalances, acute ischemic stroke, and in newborns.
In severely malnourished patients, re-feeding can lead to the development of re-feeding syndrome, which is characterized by an increase in the intracellular concentration of magnesium, potassium, and phosphorus due to increased anabolic processes. Fluid retention and thiamine deficiency are also possible. In order to avoid the development of these complications, it is necessary to carry out careful and regular monitoring and increase the intake of nutrients gradually, avoiding excess nutrition.
In pediatrics, the rate and volume of infusions are determined by the attending physician experienced in intravenous infusion therapy in children and are dependent on the child's weight, age, metabolism and clinical condition, as well as concomitant therapy.
Newborns, especially those who are premature or low birth weight, are at high risk of developing hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, therefore, they need to closely monitor the concentration of dextrose in the blood. Hypoglycemia can cause prolonged seizures in newborns, coma and brain damage. Hyperglycemia is associated with delayed fungal and bacterial infectious diseases, necrotizing enterocolitis, intraventricular hemorrhage, retinopathy of prematurity, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, increased length of hospital stay, and death. Particular care must be taken in monitoring IV devices and other delivery equipment to avoid potentially fatal overdose in neonates.
Children, both newborns and older children, are at increased risk of developing hyponatremic encephalopathy and hypoosmotic hyponatremia. In the case of using glucose solutions, they need constant careful monitoring of the concentration of electrolytes in the blood plasma. Rapid correction of hypoosmotic hyponatremia is potentially dangerous due to the risk of serious neurological complications.
When using a dextrose solution in elderly patients, it is necessary to take into account the presence of cardiac diseases, liver diseases, kidneys, as well as concomitant drug therapy.
Glucose solutions are contraindicated to be administered before, simultaneously or after blood transfusion through the same infusion equipment, since pseudoagglutination and hemolysis may occur.
There are no data on the effect of the drug on the ability to drive vehicles and complex mechanisms.
Drug interactions
The simultaneous use of catecholamines and steroids reduces the absorption of glucose.
The influence on the water-electrolyte balance of dextrose solutions and the appearance of a glycemic effect cannot be ruled out when used together with drugs that affect the water-electrolyte balance and have a hypoglycemic effect.
Analogs
Glucose analogs are: solutions - Glucosteril, Glucose Bufus, Glucose-Eskom.
Terms and conditions of storage
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C, out of the reach of children.
Shelf life:
- solution for infusion 5%: 100, 250, 500 ml - 2 years, 1000 ml - 3 years;
- solution for infusion 10% - 2 years.
Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
Released for hospitals.
Glucose: prices in online pharmacies
|
Drug name Price Pharmacy |
|
Glucose (tablets) 0.5 g tablets 10 pcs. RUB 8 Buy |
|
Glucose tablets 500mg 10 pcs. RUB 10 Buy |
|
Glucose (for infusion) 5% solution for infusion 200 ml 1 pc. RUB 10 Buy |
|
Glucose 10% solution for infusion 100 ml 1 pc. 22 RUB Buy |
|
Glucose with natural fruit powders 2.33 g tablets with strawberry flavor or aroma 18 pcs. RUB 25 Buy |
|
Glucose (for infusion) 5% solution for infusion 200 ml 1 pc. RUB 26 Buy |
|
Reviews Glucose (for infusion) RUB 26 Buy |
|
Glucose (for infusion) 50 mg / ml solution for infusion 200 ml 1 pc. RUB 30 Buy |
|
Glucose (for infusion) 10% solution for infusion 200 ml 1 pc. 32 RUB Buy |
|
Glucose (tablets) 0.5 g tablets 20 pcs. 32 RUB Buy |
|
Glucose (for infusion) 5% solution for infusion 250 ml 1 pc. 34 rbl. Buy |
|
Glucose (for infusion) 5% solution for infusion 250 ml 1 pc. 35 RUB Buy |
|
Glucose (for infusion) 5% solution for infusion 400 ml 1 pc. 35 RUB Buy |
|
Glucose (for injection) 40% solution for intravenous administration 10 ml 10 pcs. RUB 36 Buy |
|
Glucose (for injection) 400 mg / ml solution for intravenous administration 10 ml 10 pcs. RUB 36 Buy |
|
Glucose (for infusion) 5% solution for infusion 200 ml 1 pc. RUB 38 Buy |
|
Glucose (for infusion) 10% solution for infusion 400 ml 1 pc. RUB 40 Buy |
|
Glucose (for infusion) 5% solution for infusion 250 ml 1 pc. 41 rbl. Buy |
|
Glucose (for infusion) 5% solution for infusion 200 ml 1 pc. 41 rbl. Buy |
|
Glucose (for infusion) 10% solution for infusion 500 ml 1 pc. RUB 42 Buy |
|
Glucose (for infusion) 5% solution for infusion 500 ml 1 pc. RUB 42 Buy |
|
Glucose (for infusion) 5% solution for infusion 500 ml 1 pc. RUB 42 Buy |
|
Glucose Brown 5% solution for infusion 250 ml 1 pc. RUB 42 Buy |
|
Glucose (for infusion) 5% solution for infusion 400 ml 1 pc. 43 rbl. Buy |
|
Glucose (for infusion) 50 mg / ml solution for infusion 400 ml 1 pc. RUB 48 Buy |
|
Glucose (for infusion) 5% solution for infusion 500 ml 1 pc. RUB 50 Buy |
|
Glucose (for infusion) 5% solution for infusion 400 ml 1 pc. RUB 51 Buy |
|
Glucose (for injection) 40% solution for intravenous administration 10 ml 10 pcs. RUB 51 Buy |
|
Glucose (for injection) 400 mg / ml solution for intravenous administration 10 ml 10 pcs. 52 RUB Buy |
|
Glucose (for injection) 400 mg / ml solution for intravenous administration 10 ml 10 pcs. 52 RUB Buy |
| See all offers from pharmacies |
Information about the drug is generalized, provided for informational purposes only and does not replace the official instructions. Self-medication is hazardous to health!