- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Blood glucose: the norm, types of research, how to prepare for the analysis
The content of the article:
-
Glucose tests: what is it, the norm and deviations
- Determination of blood glucose
- Glucose Tolerance Test
- Glucose tolerance test during pregnancy
- Analysis for glycated hemoglobin
- Determination of C-peptide
- Determination of lactate level
- Insulin antibody test
- Analysis of the level of fructosamine
- Rapid blood glucose test
- How to prepare properly and how to get tested
- Why is a glucose test prescribed?
The norm of glucose in the blood in women and men is 3.3-6.1 mmol / l. Significant and / or long-term deviations up or down may indicate the development of pathologies, primarily hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia.
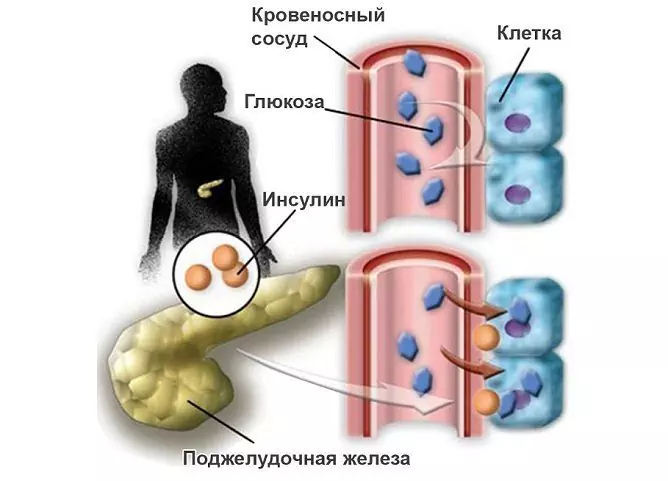
Glucose is the body's main energy substrate. Eaten carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars, which are absorbed by the small intestine and enter the bloodstream. With the blood, glucose is carried throughout the body, supplying energy to the tissues. Under its influence, insulin is produced - a hormone of the pancreas, which promotes the transfer of glucose into the cell, maintaining a certain level of glucose in the blood and its utilization. The liver, extrahepatic tissues, and some hormones are involved in maintaining the concentration of glucose in the internal environment of the body.

Glucose provides cells and tissues with energy, it is important that a certain amount of glucose is maintained in the blood
Glucose tests: what is it, the norm and deviations
Various studies are used to study the blood glucose content.
Determination of blood glucose
Determination of the level of glucose in the blood, like a complete blood count, is one of the most frequently prescribed laboratory tests. The glucose level can be tested separately or during a biochemical blood test. Blood for glucose can be taken from a finger or a vein. The norm of sugar in capillary blood in adults is 3.3-5.5 mmol / l, in venous blood - 3.7-6.1 mmol / l, regardless of gender. A glucose level of 7.8-11 is characteristic of prediabetes, an increase in the value above 11 mmol / l indicates diabetes mellitus.
Glucose Tolerance Test
Glucose tolerance test with exercise - three times measurement of glucose concentration with an interval after carbohydrate load. During the study, the patient takes the first sample of venous blood, determining the initial sugar level. Then they offer to drink a glucose solution. Two hours later, a blood sample from the vein is taken again. Such an analysis reveals impaired glucose tolerance and latent disorders of carbohydrate metabolism.
It is considered normal if no more than 5.5 mmol / l of glucose is determined in a portion of blood on an empty stomach, and after two hours - less than 7.8 mmol / l. Indicator 7.8-11.00 mmol / l after sugar load indicates impaired glucose tolerance and prediabetes. Diabetes is diagnosed if the amount of sugar in the first portion of blood exceeds 6.7 mmol / L, and in the second - 11.1 mmol / L.
Glucose tolerance test during pregnancy
The test is done to detect gestational diabetes. Physiological changes during pregnancy can lead to a violation of carbohydrate metabolism, as the placenta matures, insulin resistance increases. Normal average blood glucose levels fluctuate throughout the day during pregnancy in the range of 3.3-6.6 mmol / L.
The glucose tolerance test during pregnancy is carried out in two stages. All pregnant women undergo the first compulsory examination up to 24 weeks. The second study is carried out at 24-28 weeks of pregnancy. In the case of ultrasound signs of fetal abnormalities, in the presence of factors such as glucosuria, obesity, hereditary predisposition to diabetes, a history of gestational diabetes mellitus, the test is performed at an earlier date - at 16-18 weeks. If necessary, it is prescribed again, but no later than the 32nd week.
How to dilute glucose and how much solution should you drink? Glucose in powder form is diluted in 250-300 ml of water. If the test is a three-hour test, then take 100 g of glucose, for a two-hour test, its amount is 75 g, for an hour test - 50 g.
Pregnant women are characterized by a slight increase in blood glucose concentration after a meal, while on an empty stomach it remains normal. The rise in the blood glucose level of a pregnant woman who does not have diabetes mellitus, 1 hour after taking the load, should not exceed 7.7 mmol / l. Gestational diabetes is diagnosed if the glucose level in the first sample exceeded 5.3 mmol / L, after an hour it was above 10 mmol / L, after 2 hours - more than 8.6 mmol / L, after 3 hours it exceeds 7.7 mmol / L.
Analysis for glycated hemoglobin
Determination of glycated hemoglobin (designation in the test form - HbA1c) - determination of the average blood glucose level over a long period (2-3 months). The test allows detecting diabetes at an early stage, monitoring the effectiveness of therapy, and determining the degree of compensation for the disease.
The norm of glycated hemoglobin is from 4 to 6%. The higher the blood glucose concentration, the higher the hemoglobin glycation rate. If the blood sugar is in the range of 6 to 6.5%, then we are talking about prediabetes. An indicator above 6.5% indicates diabetes, its increase to 8% or more with confirmed diabetes mellitus indicates insufficient treatment effectiveness. An increased level of glycation is also possible with chronic renal failure, iron deficiency anemia, diseases of the pancreas, after splenectomy. A decrease in the glycated hemoglobin index below 4% may indicate insuloma, adrenal insufficiency, condition after blood loss, overdose of antihyperglycemic agents.
Determination of C-peptide
Blood test with determination of C-peptide - differential diagnosis of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus, assessment of the function of beta cells that produce their own insulin. The norm of C-peptide is 0.9-7.1 ng / ml. Its increase in the blood is observed in non-insulin-dependent type 2 diabetes mellitus, insulinoma, renal failure, cancer of the pancreatic head, after transplantation of pancreatic β-cells. A decrease in C-peptide in the blood may indicate type 1 diabetes mellitus, hypoglycemia due to the administration of insulin, alcoholic hypoglycemia, the presence of antibodies to insulin receptors.

Several methods are used to study blood glucose.
Determination of lactate level
Determination of the level of concentration of lactic acid (lactate) in the blood is carried out in order to assess the risk of developing lactic acidosis, complications of diabetes. The norm of lactate in the blood of an adult ranges from 0.5-2 mmol / l, in children this figure is higher. Only an increase in lactate concentration is of clinical importance. A condition in which the concentration of lactate in the blood exceeds 3 mmol / L is called hyperlactatemia.
Lactate levels can be increased in diabetes, heart attack, cancer, trauma, diseases that are characterized by strong muscle contractions, in case of impaired kidney and liver function. Alcohol and certain medications can also lead to lactic acidosis.
Insulin antibody test
A blood test for antibodies to insulin - detection of specific antibodies that interact with antigens of its own body, assessment of the degree of autoimmune damage to the beta cells of the pancreas, is used in the diagnosis of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. The norm for the content of autoimmune antibodies to insulin is 0-10 U / ml. An increase may indicate type 1 diabetes mellitus, Hirata's disease, an allergic reaction to exogenous insulin, and polyendocrine autoimmune syndrome. A negative result is the norm.
Analysis of the level of fructosamine
Determination of the concentration of fructosamine (a combination of glucose and albumin) - determination of the sugar level in 14-20 days. The reference values of the norm in the analysis for fructosamine are 205-285 µmol / l. With compensated diabetes mellitus, fluctuations in values can be in the range of 286-320 µmol / L, in the decompensated phase fructosamine rises to 370 µmol / L and above. An increase in the indicator may indicate insufficient renal function, hypothyroidism. An increased level of fructosamine may indicate the development of diabetes mellitus, renal failure, cirrhosis of the liver, trauma and brain tumors, decreased thyroid function, and impaired glucose tolerance. The decrease indicates the loss of protein by the body as a result of the development of diabetic nephropathy, nephrotic syndrome, hyperthyroidism. Evaluating the result of the analysis to determine the effectiveness of treatment, the tendencies to change in the indicator are taken into account.
Rapid blood glucose test
A rapid study of the determination of blood glucose concentration at home is used to control glycemia in insulin-dependent types of diabetes. For the procedure, home glucometers and special test strips are used, on which a drop of blood is applied from a finger. Diabetics need to keep sugar in the range of 5.5-6 mmol / L.
How to prepare properly and how to get tested
Most laboratory blood tests involve the delivery of material in the morning, after an 8-14 hour fast. On the eve of the study, one should not eat fatty, fried foods, avoid physical and psycho-emotional stress. Before the procedure, it is allowed to drink only clean water. It is necessary to exclude alcohol two days before the analysis, a few hours - to quit smoking. Before the study, with the knowledge of the doctor, stop taking medications that affect the result.
The analysis for glycated hemoglobin is easier to take, the result does not depend on the time of day when blood is donated, it is not necessary to take it on an empty stomach.
It is not recommended to test blood glucose after therapeutic procedures, operations, in acute infectious diseases, exacerbations of chronic pancreatitis, during menstruation.
Why is a glucose test prescribed?
Your glycemic level (blood glucose) can be normal, low, or high. With an increased amount of glucose, hypoglycemia is diagnosed, with a reduced amount, hyperglycemia.
Hyperglycemia is a sign of a violation of carbohydrate metabolism, indicates the development of diabetes mellitus or other diseases of the endocrine system. In this case, a complex of symptoms is formed, which is called hyperglycemic syndrome:
- headaches, weakness, increased fatigue;
- polydipsia (increased thirst);
- polyuria (increased urination)
- arterial hypotension;
- visual disturbances;
- weight loss;
- tendency to infectious diseases;
- slow healing of wounds and scratches;
- cardiopalmus;
- dry and itchy skin;
- deterioration of the sensitivity of the legs.
Long-term hyperglycemia leads to damage to almost all organs and tissues, and a decrease in immunity.
Hypoglycemia entails energy starvation of cells, disruption of the normal functioning of the body. Hypoglycemic syndrome has the following manifestations:
- headache;
- weakness;
- tachycardia;
- tremor;
- diplopia (double vision);
- increased sweating;
- convulsions;
- stunnedness;
- loss of consciousness.

For people with diabetes mellitus, it is convenient to carry out express diagnostics to control the rate of glucose in the blood.
Analyzing the above symptoms, the doctor prescribes a blood glucose test. In addition, glucose testing is indicated in the following cases:
- diagnosis and monitoring of diabetes mellitus or pre-diabetes condition;
- overweight;
- visual impairment;
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- heart pathology;
- diseases of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pituitary gland;
- liver disease;
- elderly age;
- pregnancy diabetes;
- burdened family history of diabetes mellitus.
Also, a glucose test is carried out as part of a clinical examination.
YouTube video related to the article:

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.