False croup in children
The content of the article:
- Causes of false croup in children
- Forms
- Symptoms of false croup in children
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of false croup in children
- Potential consequences and complications
- Forecast
- Prevention
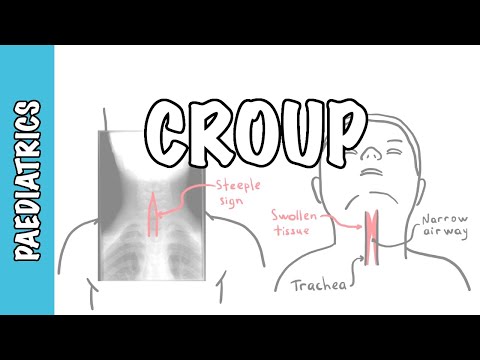
False croup in children is a syndrome characterized by a triad of clinical symptoms: stridor (wheezing) breathing, barking cough, hoarseness. The syndrome is formed in diseases accompanied by an acute inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the larynx and trachea.
With false croup, the inflammatory process is localized on the mucous membrane of the subglottic (subglottic) zone of the larynx.
The development of false croup is associated with three main mechanisms:
- the inflammatory process causes swelling of the space under the vocal cords, which narrows the lumen of the larynx;
- reflex spasm of the muscles of the larynx causes obstruction;
- the secretory activity of the glands of the mucous membrane of the larynx grows, and the already narrowed lumen of the larynx is clogged with a viscous inflammatory secretion.
False croup most often occurs in young and preschool children. This is due to the anatomical and physiological features of the children's larynx and trachea:
- small diameter of the lumen of the trachea and bronchi, short narrow vestibule, funnel-shaped (instead of cylindrical) shape of the larynx;
- relative weakness of the respiratory muscles;
- disproportionately short, high-positioned vocal folds;
- hyperexcitability of the adductor muscles that close the glottis;
- functional immaturity and susceptibility of reflexogenic zones;
- an abundance of lymphoid tissue with a weak development of elastic fibers in the mucous membrane and submucosa, prone to the development of edema.

Source: miksturka.info
Synonyms: acute stenosing laryngotracheitis, viral croup, pseudocroup.
Causes of false croup in children
The most common cause of false croup in children is a viral infection. The most typical causative agents of the disease are influenza viruses, parainfluenza, herpes, measles, chickenpox, whooping cough, and adenoviruses. The prevailing etiological factor is type I parainfluenza virus. The syndrome can also occur as a complication of adenoiditis, acute pharyngitis, chronic tonsillitis, measles, rhinitis, scarlet fever, influenza, chickenpox, ARVI.
Less common is a false croup of bacterial etiology. As a rule, the bacterial microflora (hemophilic bacillus, streptococci, staphylococci, pneumococci) joins the viral microflora with weakened immunity.
Non-infectious causes of false croup in children include trauma to the larynx, allergic edema, kidney and cardiovascular disease. Mechanical blockage of the laryngeal lumen can occur due to aspiration of foreign bodies.
Contributing factors are: decreased immunity, increased excitability of the nervous system, rickets, vitamin deficiency, a tendency to allergic reactions, exudative-catarrhal and lymphatic-hypoplastic diathesis, birth trauma, fetal hypoxia transferred during childbirth, paratrophy, post-vaccination period, artificial feeding, breastfeeding hypertrophy of the lymphadenoid ring.
Forms
Depending on the cause of the disease, viral and bacterial false croup are isolated.
According to the presence / absence of complications, false croup in children can be complicated or uncomplicated.
On the basis of clinical manifestations, four degrees of stenosis are distinguished:
- Compensated.
- Subcompensated.
- Decompensated.
- Terminal (asphyxia).
Symptoms of false croup in children
Symptoms of false croup in children depend on the degree of laryngeal stenosis. The syndrome usually develops on the second or third day of an acute infectious disease with damage to the upper respiratory tract, mainly in the evening or at night. The onset is sudden, acute. The child becomes restless, noisy breathing appears, an inspiratory type of shortness of breath, attacks of a rough, barking cough. The severity of the condition is determined by obstructive respiratory failure, the severity of toxicosis, the addition of complications.

Source: fantasyclinic.ru
With 1 degree laryngeal stenosis, there are:
- no signs of impaired external respiration at rest, inspiratory dyspnea during exertion and anxiety;
- shortening or loss of respiratory pauses between inhalation and exhalation;
- an increase in the depth and noise of breathing;
- the presence in the lungs of single wheezing rales that appear mainly on inspiration;
- bradycardia and compensated respiratory acidosis.
With stenosis of the 2nd degree, the clinical symptoms increase, the phenomena of stenosis can be permanent or paroxysmal. Signs of the 2nd degree:
- stenotic breathing at rest and during exertion, constant inspiratory dyspnea, heard at a distance;
- significantly hoarse voice;
- retraction of the compliant places of the chest (jugular fossa, supraclavicular and subclavian fossa, intercostal spaces, epigastrium) by increasing the work of the respiratory muscles;
- dry wheezing in the lungs;
- pallor of the skin and visible mucous membranes, perioral cyanosis (bluish coloration of the nasolabial triangle), aggravated during a coughing fit;
- tachycardia, anxiety, sleep disturbances;
- subcompensated respiratory or mixed acidosis.
Grade 3 stenosis is characterized by signs of respiratory decompensation and circulatory failure, a sharp increase in the work of the respiratory muscles. Symptoms of grade 3 stenosis:
- shallow, quiet cough;
- sharply hoarse voice;
- pronounced cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle, pallor of the skin;
- paradoxical breathing, inspiratory dyspnea with extremely difficult inhalation;
- an increase in breathing resistance, which leads to the activation of the respiratory muscles and a sharp retraction of the compliant places of the chest;
- maximum excursions of the larynx during inhalation and exhalation;
- rough rales of different sizes, and then a uniform weakening of breathing in the lungs on inhalation and exhalation;
- hypoxemia (low oxygen content in the blood);
- sticky cold sweat on the scalp and face;
- muffled heart sounds, arrhythmia, tachycardia, paradoxical pulse (loss of pulse wave or slowing of the pulse during inspiration);
- anxiety, feeling of fear or lethargy, drowsiness, confusion.
With stenosis of 4 degrees, a sharp deterioration in breathing is observed, the severity of inspiratory dyspnea and obstructive syndrome increases. Terminal degree symptoms:
- shallow, frequent, intermittent or arrhythmic breathing with recurrent apnea;
- the skin is pale with an earthy tinge, the nail phalanges are sharply cyanotic;
- atony of the diaphragm, vocal folds;
- threadlike pulse, difficult to determine;
- convulsive syndrome;
- sharpening of facial features, dilated pupils;
- drop in blood pressure, muffled heart sounds, bradycardia, then asystole;
- hypoxemia and hypercapnia, deep combined acidosis;
- confused consciousness, hypoxic coma is possible.
The child's condition is extremely difficult, he becomes indifferent, indifferent, does not ask for help. False croup with grade 4 stenosis has a high risk of death due to paralysis of the respiratory center.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of false croup in children is based on the presence of a characteristic triad of symptoms, data from auscultation, laryngoscopy.
On auscultation of the lungs, wheezing, stridor breathing are heard.

In order to visually assess the state of the mucous membrane, laryngoscopy is performed. During laryngoscopy, it is possible to detect swelling of the mucous membrane of the subglottic space, prolapse of the epiglottis.
Bacteriological analysis (smears from the surface of the palatine arches and the posterior wall of the pharynx, nose) is carried out in order to exclude diphtheria, to identify and identify the pathogen of a bacterial nature. The establishment of mycoplasma or chlamydial flora is performed by ELISA and PCR methods.
To assess the degree of oxygen starvation of the body, the gas composition of the blood and the acid-base balance are examined.
Diagnosis of complications, if necessary, includes pharyngoscopy, rhinoscopy, otoscopy, radiography of the lungs and paranasal sinuses.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with true diphtheria croup, epiglottitis, acute obstructive bronchitis, foreign body in the larynx or trachea, laryngeal papillomatosis, retropharyngeal abscess, and other diseases that may be accompanied by laryngeal stenosis.
Treatment of false croup in children
Treatment of false croup in children involves early hospitalization with full and timely etiopathogenetic therapy.
Before the arrival of the doctor, first of all, it is necessary to provide the child with access to fresh air, calm him down, and give him a warm alkaline drink.
You can apply reflex (distracting) therapy: prepare a foot bath to induce reflex vasodilation, press the child on the root of the tongue to provoke vomiting, tickle his nose, causing a reflex sneeze.
Further treatment is carried out in a hospital. The choice of methods is determined by a specialist and depends on the severity of the stenosis and the severity of the child's condition.
Etiotropic therapy involves taking antiviral drugs, interferons. In the case of bacterial complications and severe laryngeal stenosis, antibiotic therapy is prescribed. With subcompensated and decompensated laryngeal stenosis, parenteral administration of corticosteroids, inhalation of hydrocortisone is indicated. To influence the spasmodic component, drugs are used that reduce the contractile activity and tone of the muscles of the larynx and trachea.
Taking into account the possibility of participation in the development of false croup of the allergic component, antihistamines are included in the complex of therapeutic measures to eliminate edema.
Mucolytic and expectorant drugs help thin and remove phlegm from the respiratory tract, usually they are prescribed in the form of aerosols and inhalations, sometimes in the form of syrups, throat softening tablets for resorption.

Source: o-krohe.ru
To suppress a cough that does not stop against the background of inhalation therapy, in the event of signs of hypoxemia, an increase in the phenomena of acute stenosis of the larynx, steam-oxygen therapy is performed, however, placing the child in an oxygen tent is possible only if he is not afraid to be there.
For special indications, the administration of tranquilizers, neuroleptics is prescribed.
Hospitalization in the intensive care unit and intensive care unit is subject to children with false croup of the 3rd degree, as well as with the progression of stenosis of the 2nd degree against the background of ongoing therapy. For progressive airway obstruction that is resistant to drug therapy, nasotracheal intubation is used. It is carried out with a thermoplastic tube of small diameter. The duration of the endotracheal tube stay in children under 2 years does not exceed 2-3 days, in older children - weeks.
Potential consequences and complications
Complications of false croup can be:
- obstructive bronchitis;
- pneumonia;
- purulent laryngotracheobronchitis;
- bacterial otitis media;
- sinusitis;
- purulent conjunctivitis;
- lacunar angina;
- purulent meningitis.
Forecast
With an uncomplicated course, false croup in children, as a rule, ends in recovery. With appropriate supervision and restorative treatment, relapses can be avoided.
Prevention
Prevention of false croup in children consists in preventing the development of acute respiratory infections, and in case of illness - adequate and timely therapy.
To prevent upper respiratory tract infections, the child should be tempered, dress for the weather, eat well, and avoid contact with sick children.

Parents of children with a tendency to relapse of attacks of false croup should monitor the maintenance of the correct microclimate in the room where the child is located (moist cool air, regular ventilation of the room).
YouTube video related to the article:

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!