- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Hearing loss
Brief description of the disease

Hearing loss is a disease characterized by hearing loss, as a result of which the perception of spoken language becomes difficult. Hearing loss often manifests itself even in childhood. Congenital hearing loss affects one newborn in 1000. In general, 2 to 3% of the world's population has this problem.
Causes of hearing loss
The main cause of hearing loss in children is inflammatory diseases of the middle ear (mainly acute and chronic otitis media). Hearing loss occurs due to scars, perforations and adhesions in the eardrum. Infectious diseases such as influenza, measles, can lead to pathological changes in the inner ear and in the auditory nerve, which leads to a sharp decrease in hearing. Sometimes hearing loss is congenital. This hearing loss can negatively affect a child's speech development.
In adults, hearing loss occurs due to otosclerosis, after the use of certain medications, due to noise and vibration at work, in case of poisoning with industrial or household poisons. Also, hearing loss can develop against the background of atherosclerosis, since this disease disrupts the blood supply to the inner ear. There is such a thing as senile hearing loss, when hearing loss is caused by age-related changes in the inner ear and auditory nerves.
Degrees of hearing loss
There are three degrees of hearing loss.
With mild hearing loss (first degree), the patient distinguishes between a conversation in a whisper at a distance of 1 to 3 meters, and spoken speech at a distance of more than 4 meters. The patient cannot adequately perceive the conversation with extraneous noise or speech distortion.
Degree 2 hearing loss (moderate hearing loss) occurs if the patient perceives whispering speech at a distance of less than one meter, and hears spoken speech at a distance of 2 to 4 meters. Hearing loss of the 2nd degree is characterized by illegibility in the perception of all words in a normal setting, repeated repetitions of some phrases or individual words are required.
Severe hearing loss (grade 3) manifests itself in the inability to distinguish a whisper even at a very close distance, the patient hears spoken speech at a distance of less than 2 meters. This degree of hearing loss presupposes the presence of certain difficulties in communication. The patient must use a hearing aid to be able to communicate normally with others.
Types of hearing loss
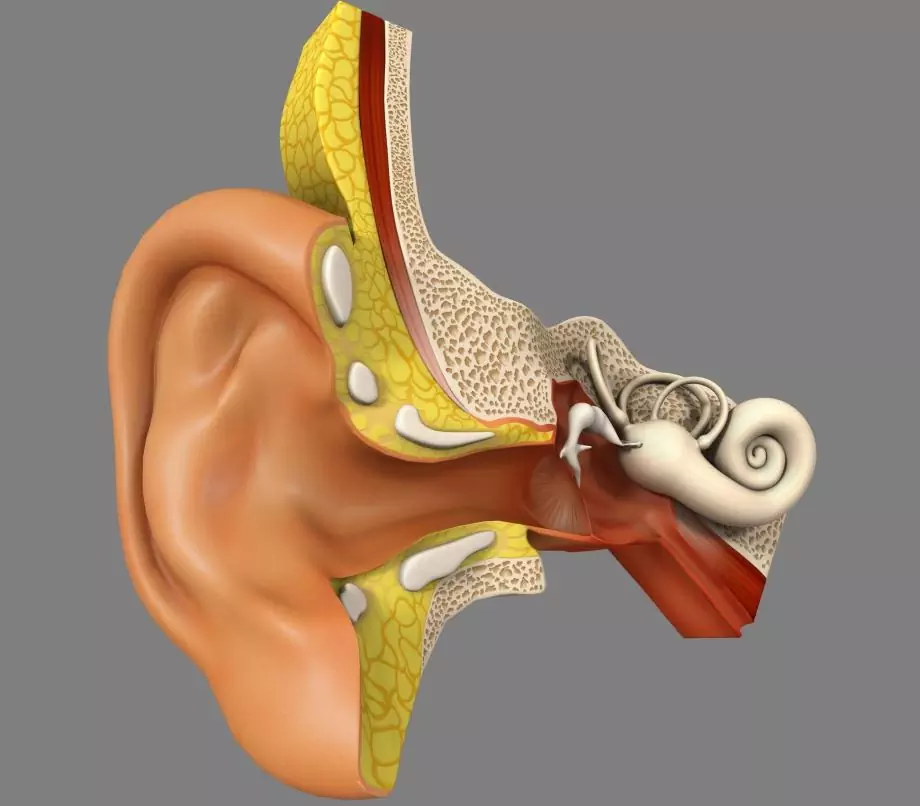
Distinguish between sensorineural hearing loss and conductive hearing loss.
Conductive hearing loss develops due to otitis media, adenoids, otosclerosis, pathological changes and dysfunction of the Eustachian tube. This type of hearing loss is characterized by changes in the eardrum and ossicles.
Sensorineural hearing loss - develops as a result of damage to nerve cells in the inner ear, the auditory nerve and the center of the auditory system. The causes of sensorineural hearing loss can be infectious diseases, stress, trauma to the inner ear, vascular disorders (atherosclerosis, hypertension), the negative effect of certain drugs and chemicals. The main symptoms of sensorineural hearing loss are hearing loss in combination with tinnitus, headache. Sometimes vomiting or nausea may occur.

Hearing loss diagnostics
For diagnostics, speech audiometry is used, which consists in the patient's recognition of whispering and speaking. Based on this research method, the degree of hearing loss can be determined.
It is possible to more accurately determine the presence and degree of hearing loss using tone audiometry - a hearing test for tones of the speech range. It is also possible to diagnose hearing loss using tuning forks. Their use is especially justified when it is necessary to make a diagnosis at home, although this method is also used in clinics.
Hearing loss in children
The main factors that can provoke the appearance of hearing loss in children are infectious or viral diseases of the mother during pregnancy, when the hearing organs are formed. Also, infectious diseases of a child at an early age can lead to the development of the disease. The hereditary factor also plays a role.
About 50% of children whose parents suffer from this disease have congenital hearing loss. The causes of the disease in children can be birth trauma, prematurity, newborn asphyxia, severe toxicosis during pregnancy, alcohol intoxication or other harmful substances during pregnancy.
Diagnosis of the disease at an early age is difficult, since the child cannot tell about his auditory sensations. Therefore, a special device is used to test the hearing in children. He makes sounds of a certain frequency, while the child's reaction is recorded. And the parents themselves can, observing the child, assess his hearing ability. To do this, you need to know the basic norms of the development of children. At the age of one month, the infant shudders or freezes at loud sounds, at four months it turns its head to the side where the sound is heard, humming appears, which turns into babbling, at the age of 8 to 10 months it begins to utter new sounds. If at any stage of the child's development his actions do not correspond to the norm, it is necessary to show the child to the doctor for a hearing test.
Hearing loss treatment

Treatment for hearing loss depends on the type of condition.
With conductive hearing loss, surgery is the only treatment. In case of contraindications to the operation, hearing aids are possible.
Sensorineural hearing loss is amenable to conservative treatment. They use medications that improve blood circulation in the inner ear (piracetam, cerebrolysin, etc.). Hearing loss treatment involves taking drugs that relieve dizziness (betahistine). Physiotherapy and reflexology are also used. For chronic sensorineural hearing loss, hearing aids are used.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!