Diseases
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Antibiotics are drugs with antibacterial action, which are of two types: bactericidal (destroys bacteria) and bacteriostatic (inhibits the growth of bacteria). The discovery of antibiotics was a milestone in human history. Antibacterial drugs save the lives of millions of people around the world every year. However, like any powerful remedy, they have side effects, and in case of abuse, the development of an overdose is possible
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Validol is used to relieve pain in the heart region that occurs against the background of cardioneuroses. Often, doctors recommend taking it for angina attacks, but only in conjunction with nitroglycerin. In addition, Validol has a good effect on motion sickness, and also finds application in the complex therapy of neurotic conditions
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
The use of Valocordin (Corvalol) in many countries of Western Europe is prohibited or allowed strictly according to the doctor's prescription. This is due to the fact that the drug contains phenobarbital, which can cause the development of drug dependence, and ethyl alcohol, which potentiates the effect of phenobarbital
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Aspirin (Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), salicylic ester of acetic acid) is a drug that has antipyretic, analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antiplatelet effects. Refers to the clinical and pharmacological groups of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), salicylic acid derivatives and antiplatelet agents
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Warfarin refers to indirect anticoagulants - substances that inhibit the coagulation link of hemostasis. Their reception prevents the formation of blood clots and stops the growth of already formed ones. This property of indirect coagulants has found active application in cardiology, neurology and surgical practice
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Vitamin A (retinol, A1, axeroftol) is a fat-soluble vitamin discovered in 1913. In 1931, the Swiss chemist Paul Carrer (awarded for the discovery of the Nobel Prize) for the first time fully described its chemical structure, and in 1937 vitamin A was able to crystallize
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
B vitamins are several water-soluble vitamins that were discovered in 1912 as a single substance. Later it turned out that this group includes 20 different nitrogen-containing compounds that have a similar effect on the body and received the appropriate designations - from B1 to B20
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) has pronounced antioxidant properties, takes part as a coenzyme in many biochemical reactions, is necessary for the normal functioning of bone and connective tissue, the immune system
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Vitamin D is the unified name for a whole group of fat-soluble biologically active substances formed under the influence of ultraviolet radiation in animal and plant tissues. Some of the vitamins of this group are synthesized in the cells of the human body, some come exclusively from the outside
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
An overdose of vitamin E occurs, as a rule, as a result of self-medication - many people mistakenly believe that vitamins are certainly useful, and the more they enter the body, the better
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Diphenhydramine is one of the earliest antihistamines. Has a pronounced antiallergic, hypnotic and soothing effect, available in the form of tablets, ampoules and syringe tubes
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Heroin is a hard opiate drug. Its use leads to the rapid development of addiction and is often accompanied by overdose phenomena. The release of heroin as an antitussive drug was launched in 1898 by the pharmaceutical company Bayer AG. In 1913, the company stopped producing the drug, as it was found that heroin is metabolized in the liver to morphine, causing the development of severe mental and physical dependence
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Donormil is a drug with a sedative, hypnotic and antihistamine (antiallergic) effect. It is most often taken for insomnia to improve the process of falling asleep and the quality of sleep. It is taken strictly according to the doctor's prescription. If the prescribed dosage is exceeded or the duration of the course of treatment is independently increased, an overdose of Donormil may occur
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
In order to prevent iodine deficiency conditions or eliminate them, it is recommended to take iodine preparations, in particular Iodomarin. It is especially important to do this in areas with low iodine content in the soil. It should be borne in mind that even with a diagnosed iodine deficiency, the abuse of iodine preparations, in particular, Iodomarin, leads to an overdose
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Ketanov is a drug from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). It has a pronounced analgesic (analgesic), moderate antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effect, and therefore is usually used to relieve pain syndromes of various origins, including postoperative
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Corvalol helps to relieve nervous tension, eliminate the effects of stress, and improve sleep. That is why it is often taken by many people, and often without a doctor's prescription. But this drug contains phenobarbital and long-term uncontrolled treatment with it leads to the formation of drug dependence, causes an overdose that is quite life-threatening
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Lyrics are often used by drug addicts to weaken withdrawal symptoms or to achieve a state of drug intoxication. Currently, this drug can only be purchased with a doctor's prescription. The drug is intended for use in pediatric practice
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Lidocaine is a local anesthetic and antiarrhythmic agent. It is used in the form of a solution of lidocaine hydrochloride for intramuscular and intravenous administration in ampoules (in 1 ml - 20 or 10 mg of the active substance) and in the form of a 10% metered spray (4.8 mg of lidocaine in 1 dose)
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Marijuana (cannabis, hashish, anasha) is a psychoactive drug derived from hemp. Its effects on the central nervous system are related to the cannabinoid content. Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol has the strongest intoxicating and analgesic effect. Once in the brain tissue, tetrahydrocannabinol increases the synthesis of serotonin. This leads to the development of euphoria, improved mood, feelings of happiness and joy
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Nitroglycerin is used both on demand, as an emergency aid for ischemic heart disease, and as a component of routine pharmacotherapy in a number of cardiological and gastroenterological pathologies
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Naphthyzine is a vasoconstrictor drug that relieves the symptoms of the common cold
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
No-shpa (drotaverine hydrochloride) is a drug with a pronounced antispasmodic effect. It relaxes the smooth muscles of the genitourinary organs, biliary tract and the digestive system. When taking tablets in a therapeutic dose, No-shpa has a slight effect on the state of the myocardium and the smooth muscle membrane of blood vessels
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Hawthorn tincture is a phytopreparation with moderate cardiotonic, antispasmodic and sedative effects. Despite the low toxicity of the drug, taking the tincture in high doses leads to the development of an overdose
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Nurofen is a drug with a pronounced anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and analgesic effect. Its active ingredient is ibuprofen from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The drug is widely used both for the treatment of adults and in pediatrics. If the recommended doses are accidentally or deliberately exceeded, an overdose of Nurofen may develop
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Despite the fact that in a therapeutic dosage, Paracetamol has extremely low toxicity, in the case of deliberate or accidental use of extreme doses of the drug through negligence, severe consequences for the body may develop. First of all, the liver suffers, and the kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, heart, central nervous system are also involved in the pathological process
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Remantadine is an antiviral drug with activity against influenza A viruses, as well as two types of herpes simplex virus, and also has an immunostimulating effect. The drug is widely used for the prevention and treatment of influenza, in this regard, cases of overdose are seasonal in nature - the largest number of them is observed in the autumn-winter period
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Fluoxetine (active ingredient of Prozac, Profluzac, Prodep, etc.) is a third generation antidepressant. Its action is to increase the concentration of serotonin in the tissues of the brain, which is called the "hormone of joy", and as a result, to improve mood and eliminate symptoms of a depressive state
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Motherwort is a plant widely used in both official and non-traditional medicine. As a medicine, two of its varieties are used: motherwort heart and motherwort hairy (five-lobed)
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Thyroxine (T3) is the main hormone of the thyroid gland, it accounts for 70-80% of the total mass of hormones produced. It has a weak biological effect, being in fact a prohormone. The activity acquires directly in peripheral tissues, being converted to triiodothyronine (T4)
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Phenibut is the commercial name for aminophenylbutyric acid (Acidum aminophenylbutyricum). By its chemical structure, Phenibut is a derivative of the natural inhibitory neurotransmitter, GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), which explains its physiological effects
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Fenistil is an antihistamine and antipruritic agent for external and internal use, the international non-proprietary name is dimetindene. Refers to drugs of the first generation, compares favorably with other drugs in this group by higher activity and the absence of side sedation
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Phenazepam is one of the most powerful tranquilizers of the benzodiazepine series. It is used in the treatment of hypochondriacal conditions, phobias, panic attacks, psychosis, neuroses, insomnia, alcoholic delirium, convulsive syndrome. Treatment with Phenazepam is carried out exclusively according to the doctor's prescription and under his supervision, since the unsystematic use of the drug can cause serious complications, one of which is an overdose
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Tramadol belongs to the psychotropic opioid analgesics. It is the most prescribed centrally acting analgesic in the world. Various sources classify it as both narcotic and non-narcotic. In accordance with the information provided on the website of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, Tramadol is defined as an opioid analgesic with a mixed mechanism of action
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Folic acid (vitamin B9) is a water-soluble substance that, like other vitamins, is not synthesized in the human body, but is necessary for the normal course of vital biochemical reactions. It is especially important that the body is provided with folic acid during pregnancy
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Coccyx fracture is a common injury, the severe consequences of which are fragments
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
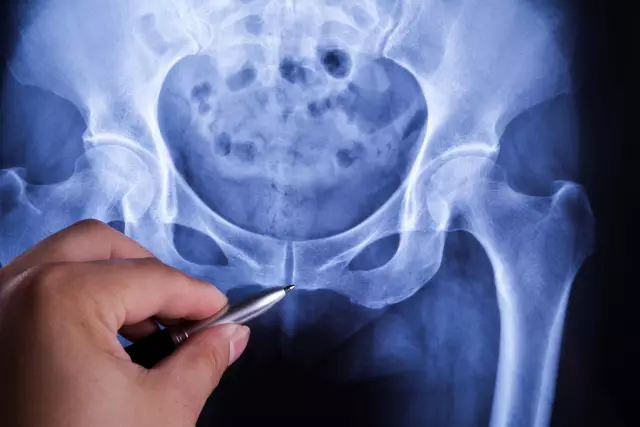
A fracture of the ischium is a complex injury to the musculoskeletal system. Usually due to squeezing of the pelvis or falling on the buttocks
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
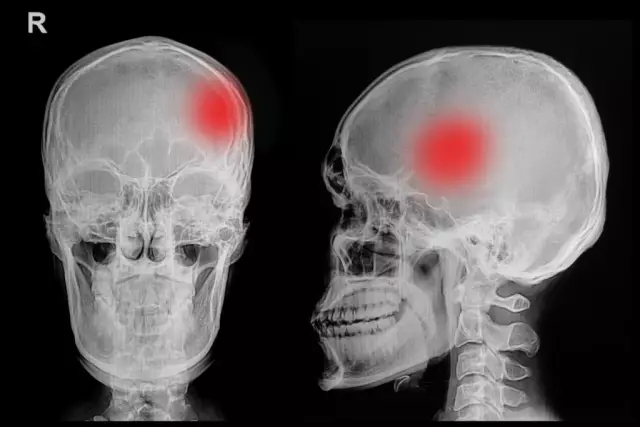
Fracture of the base of the skull - a severe injury that is fatal to the spinal cord and brain
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Furosemide (synonym Lasix) is one of the most powerful diuretics (diuretics). The drug is used more often as an emergency aid, it is systematically used only in the presence of pronounced congestion in the large, small, or both circles of blood circulation. The diuretic action of Furosemide is powerful, fast and short-lived
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Foot fracture - an injury that can cause diseases of the musculoskeletal system
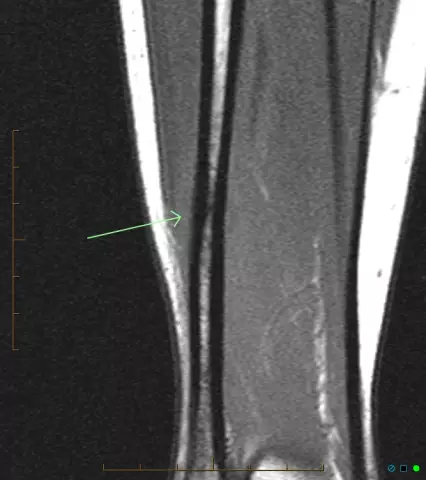
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
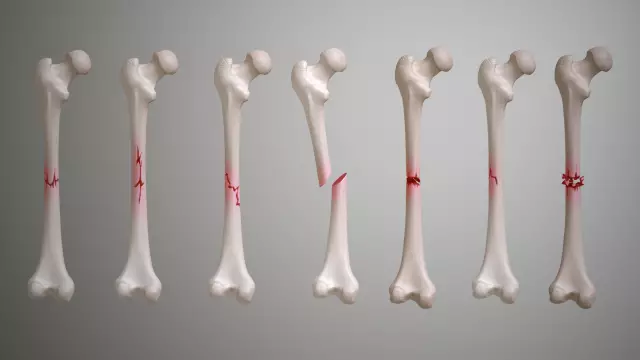
Fracture of the tibia - a common injury that often accompanies a fracture of the tibia