- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
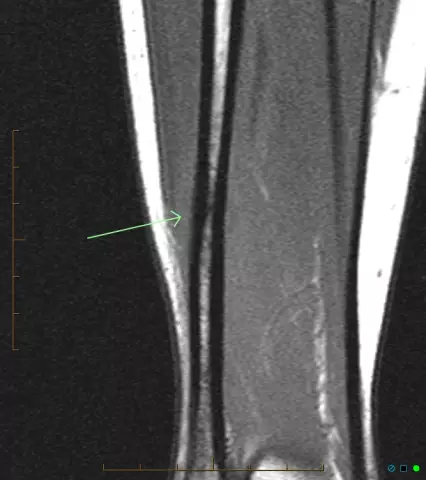
Fracture of the fibula
Shin fractures, in particular tibia and fibula fractures, are among the most common injuries to the lower extremities.

The tibia is a component of the lower leg. Depending on the directional blow and the type of injury, a fracture of the fibula is often combined with a fracture of the tibia. If we consider the nature of the fracture, then it can be divided into direct and indirect. A direct or bumper hit is considered to be more beneficial because it is much easier to treat. In addition, after a fracture of the fibula by means of a direct factor, there are no many fragments during crushing of the skeleton.
The indirect factor is more unfavorable. Such a fracture occurs when, when the damage is directed along the axis of the bone, rotation (traction) occurs. After a fracture of the fibula of the indirect factor, many fragments appear in the direction of the impact. The damage occurs in a spiral, involving large areas of the leg structure.
A tibia fracture can be caused by an elementary fall or impact. Such fractures are especially often observed in winter during the icy period. Often, these fractures occur together with the tibia. However, the tibia is stronger, and if it is not broken, treatment will be more reliable and faster. In addition, the possibility of developing various complications is significantly reduced: osteomyelitis, displacement of bone fragments, etc.
Tibia fracture symptoms
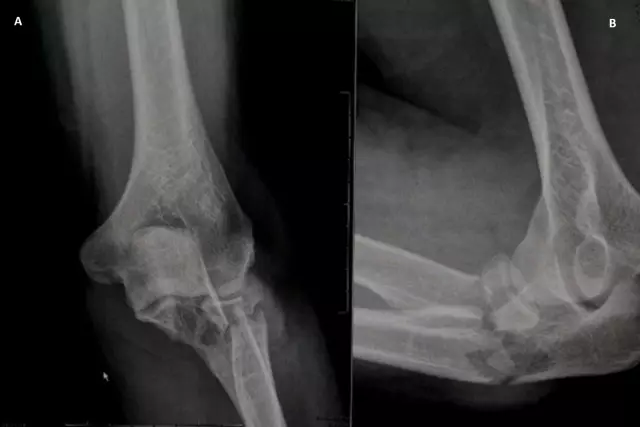
It is quite easy to identify a fracture of the fibula. First of all, a symptom of a tibia fracture is a visible displacement of the bones. The victim experiences severe pain when trying to lean on the affected leg. Due to the bruise, the leg swells a lot, hematomas occur. Visually, the leg may appear shorter, it may turn out in relation to the healthy leg. If the axis is not displaced during the fracture, then the victim can perform rotational movements. If only the fibula is fractured, the victim may even lean a little on the sore leg.
Fracture diagnosis
For the doctor to be able to accurately determine the nature of the fracture, the patient must tell how the injury occurred. The doctor assesses the force of the blow, how it was delivered, and in which direction the impact force was applied. The fracture properties directly depend on all these indicators.

To get a complete picture of what happened, the doctor takes an X-ray in two projections. As a rule, the diagnosis of a fibular fracture is not very difficult. The doctor may experience some difficulties if various complications have arisen, or when the fracture is localized in the tibiofibular joint. If the fracture happened in the upper third of the leg, then the doctor should take into account that this often affects the blood supply and innervation of this area.
Tibia fracture treatment
If the fracture has occurred without displacement, then the treatment of the fracture of the fibula is not particularly difficult. Even if there is a simultaneous fracture of the tibia, fractures without displacement are easier to treat. The doctor applies a cast from the tips of the toes to the point that needs to be immobilized. This is necessary to prevent the displacement of bone fragments.
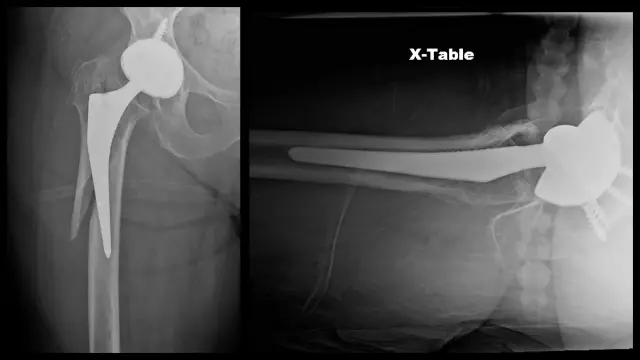
If, as a result of the impact, the displacement of bone fragments occurred, especially if both bones were displaced, then the doctor must first restore their correct position. For transverse impacts, bony plates may be required. If the displacement did not occur as a result of a transverse impact, then the introduction of the spokes is possible slightly above and below the fracture site. These needles fix and stretch the repair site.
The timing of the recovery of a fracture of the fibula depends on the complexity of the fracture. On average, recovery takes two to three months. Usually, callus does not develop until a month and a half after the fracture. If the fracture is complicated by the displacement of the bones, then rehabilitation may take about six months or more. The recovery period largely depends on the patient himself. He must clearly perform muscle exercises, attend massage and physiotherapy, and also take good care of the site of injury.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!