- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
How to treat dry cough in children at home
The content of the article:
-
Treatment of dry cough in children at home
- First aid for a cough attack
- Inhalation
- Drug treatment
- General recommendations
- Herbal medicine and folk recipes
- Treatment of the underlying disease
- Dry cough: how it manifests itself, features
-
Causes of dry cough
- ARI
- Postnasal flow syndrome
- Whooping cough
- Foreign body
- Video
How to treat dry cough in children at home? It depends on the cause of its occurrence. At home, you can use inhalations, lozenges, antitussives. However, before proceeding with therapeutic measures, you need to determine the cause of the symptom.

Prolonged dry cough ceases to function to clear the airways
Treatment of dry cough in children at home
A dry cough can be intrusive and intense, tire the child and disrupt their well-being. Therefore, treatment is aimed at softening the cough, and if impossible, at suppressing the cough reflex. Treatment must necessarily include the impact on the underlying disease, and not just on the symptom.
First aid for a cough attack
With a coughing fit, the child needs help quickly. How can you help:
- Drink warm tea. Getting warm fluids will help ease your cough.
- Give peppermint candy, cough candy (if the child is over 3 years old).
- Make a warm foot bath, then wrap the limbs in woolen socks.
After the intensity of the cough has decreased, you can begin a full treatment.
Inhalation
An effective method for easing a child's cough is inhalation (inhalation of medicinal substances).
At home, steam inhalation can be used to treat children over 7 years old. To do this, heat the solution, cover your head with a towel and breathe in the steam for 2-4 minutes. Inhalations are used 3-4 times a day. If you have a cough, your child should breathe in and out through the mouth, not through the nose.
A solution for steam inhalation can be prepared at home. For this, medicinal plants are used that have anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects:
- chamomile;
- mint;
- eucalyptus;
- cedar needles;
- St. John's wort.
Dry plant materials are poured with boiling water at the rate of 1 tbsp. for 1 glass of water, insist for 15-20 minutes. Older children who do not suffer from allergies can use essential oils - pine, eucalyptus, sea buckthorn. The solution is prepared at the rate of 3-4 drops of oil per liter of water.
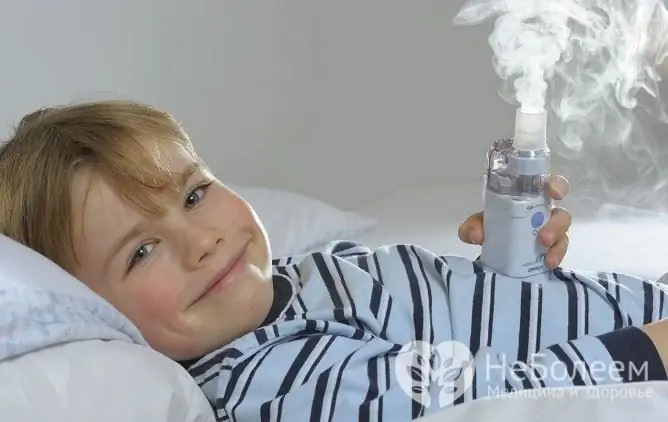

It is better for children to inhale with a nebulizer
For dry cough, alkaline solutions (water with soda, mineral water) are effective.
With steam inhalation, there is a risk of burning the upper respiratory tract. To avoid the consequences, you need to adhere to the rules:
- The water temperature should be 50-60 ° C. A hotter solution can harm the baby.
- The distance above the container should be 20-30 cm. If you lean below, the steam can damage the mucous membrane of the nose and nasopharynx.
- The duration of the procedure is no more than 5 minutes.
Steam inhalation can help with diseases of the upper respiratory tract (rhinitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis), but they are contraindicated at elevated temperatures.
If coughing is a symptom of bronchitis, steam inhalation will be ineffective. In such cases, you need to use a special drug - a nebulizer, which allows you to deliver medicinal substances to the small branches of the bronchi.
As a solution, weakly alkaline mineral waters, physiological saline, water with soda or medicines are used.
Drug treatment
To treat dry cough, antitussive drugs are used to suppress the cough reflex. Antitussive drugs are of two types:
- Central action - inhibit the cough center located in the medulla oblongata.
- Peripheral action - reduce the sensitivity of the cough receptors located in the respiratory tract.
Centrally acting antitussives are used only for the treatment of older children. In young children, they can depress the respiratory center, which is located next to the cough, which is dangerous by stopping breathing. Centrally acting antitussive drugs are prescribed for a painful cough, which is accompanied by vomiting or poor health. These drugs include Butamirate, Glaucin, Oxeladin. You can give them to a child only as directed by a doctor.
Libeksin belongs to antitussive drugs of peripheral action. Such drugs are used mainly for diseases of the lower respiratory tract.
Libeksin is an antitussive agent of peripheral action
Lozenges that contain menthol or local anesthetics can be used to soothe coughs. Local preparations are effective for pharyngitis, as they reduce sensitivity in the pharyngeal region. Reducing sensitivity leads to a softening of the cough.
General recommendations
General recommendations will help soften dry cough:
- Give your child more fluids to drink. Suitable green and fruit tea, a decoction of chamomile and rose hips, warm milk with honey, still mineral water. Frequent drinking reduces the number of coughing attacks, prevents drying of the mucous membranes.
- Provide clean air - ventilate the child's room frequently.
- Humidify indoor air. To do this, you can use a special humidifier or place containers with water around the room, and do wet cleaning daily.
- The room in which the child is located must be warm, as the cold air provokes a coughing attack.
Compliance with these recommendations will reduce the intensity of the cough, alleviate the child's condition.
Herbal medicine and folk recipes
Treatment of dry cough in children at home can be carried out using herbal medicine.
The following plants are shown to be used:
- polysaccharide-containing herbs. These are plants that have a pronounced enveloping and expectorant effect. This group includes marshmallow root, leaves of coltsfoot, flax seeds;
- plants with astringent properties - St. John's wort, horsetail, knotweed;
- plants with desensitizing properties - black elderberry, string, chamomile;
- herbs with antitussive action - thyme, oregano, angelica rhizomes.
Decoctions and infusions are prepared from plants; they can also be used for inhalation. Raw materials, or rather, the pomace that remains after straining, can be used to make compresses on the chest.
Herbal medicine must be approached wisely, plants are selected taking into account the existing symptoms and their causes.
Before using medicines, it is imperative to consult a doctor, since some herbs are highly allergenic or have the ability to cause poisoning. For example, wild rosemary (an antitussive plant) can cause hallucinations in children.
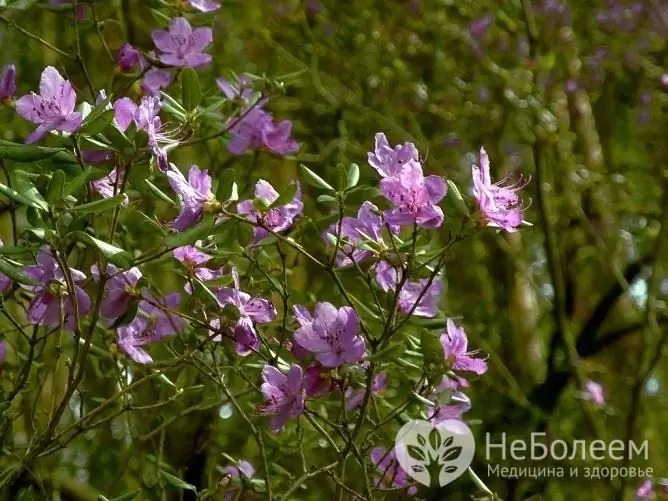

Ledum can not be used to treat children, although it has an antitussive effect
Treatment of the underlying disease
Cough is not a separate disease, but only one of the symptoms. It is ineffective to treat only the symptom and not treat the underlying disease.
Specific therapy depends on the cause of the cough:
| Disease | Etiotropic treatment |
| Whooping cough | Antibacterial agents from the macrolide group (Azithromycin). |
| ARVI | There are no specific drugs. |
| Flu | In the early days of the disease, antiviral drugs are used: Remantadin, Oseltamivir, Zanamivir. |
| Foreign body | At home, Heimlich's technique can help - a sharp press in the epigastric region. Further treatment is carried out only in a hospital (removal of a foreign body by surgery). |
| ENT pathology (postnasal drip syndrome) |
Complex treatment, consists of 3 components: Remediation of the focus of infection. It consists in rinsing the nose and nasopharynx, rinsing the throat. Topical preparations. Use drops with a decongestant effect (Nazivin). Systemic drugs. Herbal preparations are used (Sinupret). With a bacterial infection, antibiotics are prescribed from the macrolide or penicillin group (Amoxicillin, Azithromycin). |
| Allergy | First of all, you need to exclude contact with the allergen. Additionally, antihistamines and glucocorticoids are used. |
| Pleurisy | With bacterial pleurisy, antibiotics are prescribed, with fibrinous - glucocorticoids. With exudative pleurisy, pleural puncture is indicated (performed in a hospital). |
Dry cough: how it manifests itself, features
In most cases, coughing is a defense reflex that aims to clear the airways. There are two types of coughs: dry and wet.
Dry cough is not accompanied by sputum production. It is obsessive, intense, often disrupts the child's sleep and well-being.
Dry cough occurs when irritation of the cough receptors, which are located in the mucous membrane of the larynx, trachea, bronchi. Irritants can be dust, bacteria, viruses, allergens, mucus. In children, a foreign body can provoke a cough.
A dry cough can be acute (up to 3 weeks) and chronic. Acute cough can be effectively treated at home, chronic cough is difficult to treat.
Causes of dry cough
A dry cough occurs at the initial stage of airway inflammation, as well as with reflex irritation of the cough receptors.
The most common causes of dry cough include:
- acute respiratory diseases: viral and bacterial;
- pathology of ENT organs: rhinitis, tonsillitis, adenoids;
- whooping cough;
- ingress of a foreign body.
ARI
The most common cause of dry cough. The child can get sick several times a year. ARIs are caused by viruses or bacteria that are transmitted by airborne droplets. This can affect the nasal cavity, throat, larynx, trachea, or bronchi. In all cases, the cough is dry, but its nature may differ:
- with sore throat - obsessive, mainly in the morning;
- with inflammation of the larynx - rough, barking;
- with inflammation of the trachea - painful, painful;
- with inflammation of the bronchi (at 1 week of illness) - loud, sonorous.
It is possible to suspect ARI by characteristic clinical signs at home. In addition to coughing, the child will have fever, weakness, runny nose, and sore throat.

Acute respiratory illness is the most common cause of dry cough
Postnasal flow syndrome
With the pathology of the ENT organs, the appearance of cough is associated with the syndrome of postnasal flow. The mucus that is produced in the upper respiratory tract flows down the back of the pharynx. This leads to irritation of the receptors, which provokes a cough.
Postnasal flow syndrome is more common in children than in adults. This mechanism for the development of cough is typical for the following diseases:
- rhinitis - inflammation of the nasal mucosa;
- tonsillitis - inflammation of the tonsils;
- sinusitis - inflammation of the paranasal sinuses;
- adenoids and adenoiditis - hypertrophy and inflammation of the nasopharyngeal tonsil.
The cough with ENT pathology is not very strong, it worsens at night and in the morning.
Whooping cough
In children, whooping cough can be the cause of severe coughing. Mostly unvaccinated children are ill. Whooping cough is a bacterial infection that causes violent coughing attacks. Attacks occur 10-20 times a day, and may end with vomiting. This is a dangerous disease, as a complication of the disease can develop respiratory failure, convulsions, pneumonia and even death. If you suspect whooping cough, parents should definitely show the child to a doctor.
Foreign body
In children, a dry, sudden cough may be caused by a foreign body in the airways. Often this occurs in young children while playing with small details, while eating. The peculiarity of this pathology is the suddenness of its occurrence. In addition to coughing, the child is worried about breathing disorders. Help must be urgent.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.






