- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Scrotal edema: causes, signs and treatment
The content of the article:
- Causes and risk factors
-
Signs and accompanying symptoms
- Testicular torsion
- Varicocele
- Dropsy of testicles
- Epididymitis
- Orchitis
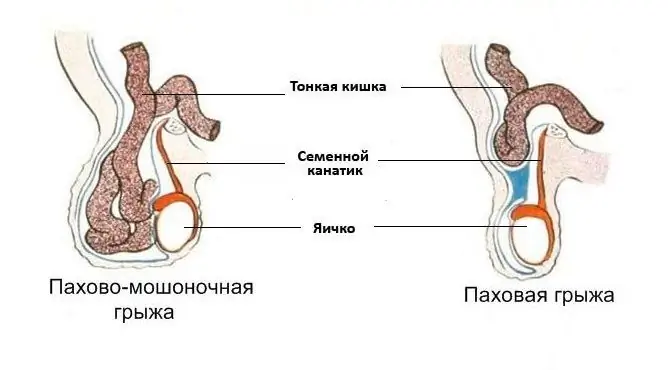
- Inguinal hernia
- Allergy
- Diagnostics
-
What to do if the scrotum is swollen
- Drug therapy
- Surgery
- General and rehabilitation measures
- Prevention
- Video
Scrotal edema is a condition that can be caused by both physiological and pathological causes. The diagnosis and treatment of genital pathologies in men is carried out by a urologist or andrologist.
The swelling can be unilateral or bilateral, localized, or involving the testicles and penis. The swollen scrotum can reach gigantic proportions, as seen in the photo, but this condition rarely happens, usually the swelling is less pronounced.

Scrotal edema can take on different sizes, even huge
Causes and risk factors
The scrotum is a musculocutaneous saccular formation, which contains the testes (testicles), epididymis and partially the spermatic cord in men. The reasons that cause swelling of the external genital organs in men are divided into infectious and non-infectious.
Infectious etiology is:
- orchitis - an inflammatory process in the tissues of the testicle;
- epididymitis - inflammation in the epididymis;
- epididymo -orchitis is a combined inflammation of the testicle and its epididymis.
In addition, swelling may appear if infection spreads to the scrotal tissue in acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, pneumonia, tuberculosis.
In newborns, inflammation can be caused by infection (often E. coli, staphylococcus) through the blood vessels of the umbilical cord. In older children, the infectious process can develop against the background of mumps.
The non-infectious causes of the development of pathology include:
- genital trauma (most often observed in adolescent patients);
- torsion of the testicle (torsion of the spermatic cord);
- surgical interventions on the organs of the genitourinary system;
- inguinal hernia;
- varicocele (varicose veins of the spermatic cord and testicle);
- dropsy of the testicle (hydrocele);
- benign and malignant neoplasms of the genital organs;
- heart failure.
The table shows various diseases that are common causes of the development of edema, distributed according to the frequency of occurrence in a particular age group.
| Pathology | Age group of patients |
| Testicular torsion | 10-20 years |
| Dropsy of the testicle | 1-10, 50-70 years old |
| Varicocele | 10-20 years |
| Testicular neoplasms | 20-50 years |
| Epididymo-orchitis | 30-60 years old |
Signs and accompanying symptoms
The main symptoms in the development of this pathology are swelling and pain in the groin. Also, patients may experience:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- nausea and vomiting;
- increased body temperature (usually no more than 38 ° C);
- dizziness;
- change in the color and transparency of urine;
- pathological discharge from the urethra;
- deterioration in general well-being.
In addition, chills, headache may occur, ulcers and seals may appear on the scrotum. The skin in the scrotum may be hyperemic, the skin may flake off. If the disease in which this pathology is observed proceeds in a chronic form, the patient's pain may be absent or weak, occurring sporadically.
Testicular torsion
One of the most common causes of swelling and pain. Pathology is dangerous because it can cause the development of necrosis in a short time.
Varicocele
With varicocele against the background of varicose veins, patients have venous congestion and swelling. This pathology can cause the development of infertility.
Dropsy of testicles
With dropsy of the testicles, an enlargement of the scrotum occurs, there is a feeling of a foreign body in the scrotum, pain, problems with erection and ejaculation. An adult patient may experience discomfort when wearing underwear. Dropsy of the testicles in newborns can go away on their own for 1 year.
Epididymitis
With epididymitis, which often develops against the background of sexually transmitted diseases, in addition to swelling, there are:
- intense pain that can radiate to the penis, diffuse pain may also appear (without clear localization);
- foreign body sensation;
- discharge from the urethra.
Orchitis
With orchitis, there is swelling on the side of the lesion, the patient complains of severe pain, which in some cases radiates to the penis, anal region, lower abdomen, lower back, as well as discomfort during urination.
Inguinal hernia
With an inguinal hernia, edema may occur in the postoperative period against the background of impaired lymph outflow. After some time, the patient's condition, as a rule, returns to normal.
Allergy
Puffiness with an allergic reaction often occurs when using contraceptives, lubricants. Also allergens can be food, cosmetics, household chemicals. Often, in addition to swelling, patients in the affected area have hyperemia, itching, and rash. Problems with urination and potency are usually absent.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, complaints and anamnesis are collected, with special attention paid to the following issues:
- when the tumor appeared, under what circumstances did it happen;
- the size of the swelling;
- the presence of atypical discharge from the penis.
They also carry out an objective examination, if necessary - ultrasound, diaphanoscopy, laboratory tests (general blood and urine analysis, biochemical blood test, examination of a smear from the urethra), puncture of the scrotum, biopsy.

Ultrasound of the scrotum - a method that allows you to diagnose the cause of its swelling
Diagnosis of volvulus in newborns can be difficult, since boys of this age group often have physiological swelling of the scrotum after childbirth.
What to do if the scrotum is swollen
Drug therapy
In most cases, conservative methods are used for treatment, treatment prescribed by a doctor is carried out at home, in some cases hospitalization may be required.
Depending on the cause, analgesic, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic drugs are prescribed. In the presence of allergies, patients should avoid contact with the causative allergen, antihistamines are indicated.
Surgery
Surgical treatment may be required if the patient has neoplasms, complicated orchitis, cryptorchidism, severe epididymitis.
General and rehabilitation measures
With the permission of the attending physician, you can apply a cold compress to the lesion site (no more than 1 day). Patients are shown wearing a special bandage, loose clothing that does not squeeze the body.
You may need to massage the testicles, sitz baths with decoctions or infusions of medicinal plants.
It is possible to apply any traditional and folk methods of treatment for this pathology only after consultation with the attending physician.
Prevention
In order to prevent the development of pathology, it is recommended:
- improve immunity;
- avoid various injuries of the genitals;
- avoid physical overload;
- eat properly;
- avoid stressful situations;
- avoid hypothermia.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.