- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Ear swelling: causes, treatment
The content of the article:
- Causes of ear swelling
-
Ear edema treatment
- Drug therapy
- Physiotherapy
- Surgery
- Folk remedies
- Prevention
-
Swelling of the ears with various diseases
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases
- Barotraumatic otitis media
- Tumor process
- Allergy
- Erysipelas
- Injury
- Diagnostics
- Video
Ear edema is often a symptom of various pathological processes of a traumatic, allergic, infectious and inflammatory nature and is often accompanied by pain, a feeling of congestion, and hearing loss.
If a person has swollen ear, it is recommended to see a doctor as soon as possible, as some diseases can be life-threatening for the patient. In addition, they can be complicated by hearing loss, involvement in the pathological process of the brain. Therefore, it is advisable to carry out treatment at home only after consultation and under the supervision of a doctor.
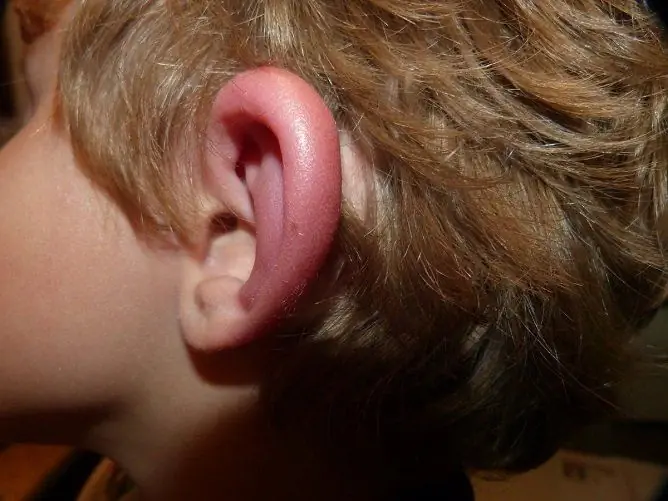
Edema of the outer ear is most often caused by injury or allergies
What to do with edema depends on why it developed.
Causes of ear swelling
The pathological condition can be observed in patients of different age groups. Both endogenous and exogenous factors can cause the development of edema:
| Endogenous causes | Exogenous causes |
| Otitis externa (inflammation of the ear canal or auricle) | Ingress of a foreign body (dust, insects, small objects) into the ear, infection of the auricle |
| Infectious and inflammatory processes in the throat | Mechanical damage |
| Acoustic neuritis | Wearing low quality jewelry or having a reaction to a particular metal |
| Pathology of fungal etiology | Improper hygiene procedures |
| Benign (more common) and malignant neoplasms, such as hemangioma | Long-term use of in-ear headphones |
| Allergic reactions (including Quincke's edema) | Hypothermia of the body |
The development of ear puffiness is more susceptible to people who are professionally involved in sports, especially in water sports, as well as those associated with increased injuries.
Puffiness can develop not only with injury, but also with strong stress, pressure drop (more often observed in divers, climbers). Ear swelling in a child may be the result of a ruptured eardrum (due to mechanical damage, loud sounds).
Acoustic neuritis can develop against the background of inflammatory processes, as well as when chemicals enter the ear. This pathology is dangerous by tissue atrophy and complete hearing loss for several hours.
In children, especially girls, the development of an infectious process, which is accompanied by edema, can occur when the earlobes are pierced. For this reason, during healing, you need to carefully look after the lobes, regularly treat the puncture site with an antiseptic solution.
The development of pathology can be facilitated by:
- some chronic diseases;
- injuries, scars;
- polyps;
- frequent cauterization of granulations.
Edema of the lobe can be observed with erysipelas, wen, atheroma, reactions to jewelry and costume jewelry.
Allergic reactions and the development of ear swelling are often observed in children. Also, in this category of patients, the pathological process often develops with hypothermia, against the background of acute respiratory diseases, tonsillitis.
Ultraviolet irradiation and radiation (including during radiation therapy, X-ray studies) can contribute to the development of pathology. Risk factors are a weakened immune system, a deficiency in the body of vitamins and minerals.
Ear edema treatment
In most cases, treatment is conservative, but sometimes surgery may be required. Some patients need to be hospitalized and treated in a hospital setting.
The choice of the treatment regimen depends on the cause of the development of the pathology, the presence of certain signs, contraindications. For example, during pregnancy, women are not prescribed drugs that can affect the fetus.
Drug therapy
Drug treatment is indicated for infectious and inflammatory diseases, allergies. Depending on the etiological factor, the patient may be assigned:
- antibiotics;
- antifungal agents;
- antihistamines;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- analgesics.
With slight suppuration, you can wash the affected area with hydrogen peroxide, boric acid. To relieve edema, injecting drugs into the ear, it may be necessary to blow through the Eustachian tube. The procedure is carried out in a medical institution.
An antibacterial ointment may be prescribed to treat injured areas, including the puncture site.
If the patient has an allergy, contact with the allergen should be excluded or minimized, and ears should be protected from external stimuli that can cause the development of pathology. In this case, combined ear drops, which include glucocorticosteroids, can be used. With angioedema, hormone therapy is performed.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods are prescribed:
- ultra high frequency therapy;
- magnetotherapy;
- electrophoresis;
- pulse electrotherapy.
Surgery
To remove a hemangioma, as a rule, a cryodestruction method is used. To remove atheroma, the method of radio wave destruction is often used. Removal of atheroma can be done with a laser (in the initial stages of pathology) or surgery (with advanced disease). Attempts to self-remove atheroma can lead to the development of an abscess.
Folk remedies
With swelling of the ears, after consulting a doctor, you can use the means and methods of traditional medicine:
- Compress from cabbage or plantain. You can apply plantain or cabbage leaf to the affected area. The compress is fixed with a bandage and left for several hours. After that, the sheet can be replaced and the procedure repeated.
- Compress with bay leaf infusion. Grind the bay leaf, pour a glass of boiling water and leave for 1 hour. After that, a cotton swab is moistened with the resulting product and injected into the affected ear.
- Compress with propolis. To relieve inflammation and puffiness, you can use propolis alcohol tincture, which is mixed with vegetable oil in a 1: 4 ratio. The prepared mixture is moistened with a gauze swab and placed in the ear for several hours.
- Compress with essential oil. Add 2-3 drops of essential oil (chamomile, rose, sage, tea tree or lavender) to half a glass of clean warm water. The resulting liquid is moistened with a cotton swab and placed inside the affected ear.
- Horseradish juice. In the presence of edema and inflammation, horseradish juice can be instilled into the ear 2 times a day, which improves blood circulation in the tissues and helps to eliminate puffiness. It should be borne in mind that this method in some diseases can, on the contrary, cause a burn and a sharp deterioration in the patient's condition.
Prevention
In order to prevent the development of pathologies that may be accompanied by ear swelling, it is recommended:
- To carry out hygiene procedures correctly (you cannot use ear sticks for cleaning, and even more so other objects that are not intended for this, it is enough to regularly wash the ear canals with your finger, the depth to which the finger penetrates is quite enough).
- Wear a hat that covers your ears in cold weather.
- Avoid frequent contact with water and other liquids (when visiting the pool, wear a special swimming cap).
- Avoid swimming in polluted waters.
- Timely treat diseases that may affect the ears.
Swelling of the ears with various diseases
Infectious and inflammatory diseases
Often, swelling of the outer ear is caused by inflammation. In this case, patients may experience:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- heat;
- almost complete loss of hearing in the affected organ;
- intense throbbing ear pain;
- violation of coordination of movements;
- sleep disorders.
The inflammatory process can occur in the outer, middle and inner ear. With otitis externa, the patient may experience pain when palpating the auricle, pressing on the tragus, there may also be prolonged pain inside the ear canal, purulent discharge is possible.

If the ears (or one ear) are swollen, consult a doctor, as the pathology may be serious
In the presence of an infection, in addition to swelling, the patient may experience:
- persistent hearing impairment;
- increased body temperature (usually up to 37-38 ° C);
- chills;
- ear congestion;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- sensation of fluid transfusion in the ear canal.
With diseases of fungal etiology, the patient may experience tinnitus, a feeling of pressure or fullness in the ear, hearing loss, inflammation of the skin around the ear, itching. There may also be a cheesy discharge, which may have a grayish tint.
Barotraumatic otitis media
With barotraumatic otitis media, which occurs with a pressure drop, in addition to edema, patients may complain of:
- weakness and fatigue;
- irritation and itching in the ear;
- discomfort when swallowing;
- hearing impairment.
With the progression of the pathology, severe pain occurs, spotting may be observed.
An inflamed ear can become hypersensitive to any stimulus. The pain in this disease often has a shooting character, it can radiate to the neck, head. In the absence of adequate treatment, otitis media can turn into a purulent form, and against the background of this pathology, the patient may develop mastoiditis, meningitis, and neuritis of the auditory nerve. Lack of timely, correctly selected treatment for barotraumatic otitis media can lead to complete hearing loss.
Tumor process
In the presence of a benign or malignant tumor, the ear may ache, swell inside, the patient may have a feeling of having a foreign object in the ear. With atheroma, palpation of the earlobe reveals a seal, which is a spherical cyst.
Allergy
With the development of an allergic reaction, the lobe may swell, there may also be hyperemia of the skin outside the ear, headache, discharge from the nasal cavity, lacrimation.
When Quincke's edema occurs, in addition to swelling of the ears, face, and other parts of the body, there may be:
- cough;
- nasal congestion;
- hives;
- nausea and vomiting;
- stomach ache;
- in severe cases, breathing disorder.
Erysipelas
With erysipelas, the affected area of the skin of the auricle is hyperemic, sharply swollen, it can get wet, itchy, hurt. A wet wound usually crusts over time. Later, peeling begins.
Injury
With trauma, in addition to edema and external damage, bleeding from the ear canal may occur, which may be associated with a ruptured eardrum. This condition requires immediate medical attention.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, it is carried out:
- collection of complaints and anamnesis;
- otoscopy;
- laboratory tests (bacteriological examination of ear discharge and / or scraping from the affected area, general and biochemical blood tests, allergological tests, etc.);
- computed and / or magnetic resonance imaging of the brain;
- X-ray examination.
To clarify the diagnosis, it may be necessary to consult an otorhinolaryngologist, infectious disease specialist, surgeon, oncologist, allergist.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.