- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
How to quickly remove a bruise: effective remedies
The content of the article:
- The reasons
- First aid
-
Treatment of bruises, including on the face
- Surgical and inpatient treatment
-
Pharmacological agents
- Medicines containing heparin
- Badiaga
- Troxevasin
-
Traditional methods
Warm compresses
-
Effects
- Favorable outcome
- Unfavorable outcome
- Video
How to quickly remove a bruise - this question is especially often interested in localizing damage to the face, since it brings discomfort, aesthetic dissatisfaction and sometimes temporarily deprives a person of working capacity.
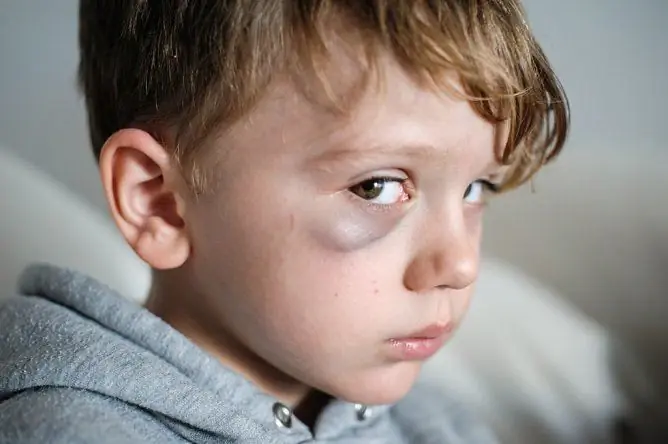
Hematomas are most often caused by trauma
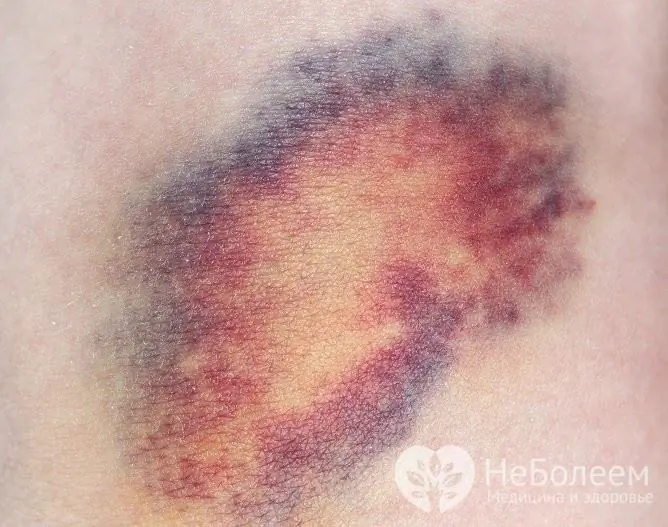
A bruise, or hematoma, is an area of blood accumulation limited to surrounding tissues, usually formed during traumatic injury and accompanied by rupture of blood vessels.
It is customary to call a bruise a subcutaneous hematoma because of its characteristic color - blue with a purple tint. However, hematomas are not only subcutaneous, but also intramuscular, subserous, subdural, etc.
All these types of hematomas require careful inpatient monitoring, and sometimes surgical treatment. Only mild subcutaneous hematoma can be treated on its own, since it usually does not threaten human life and health.
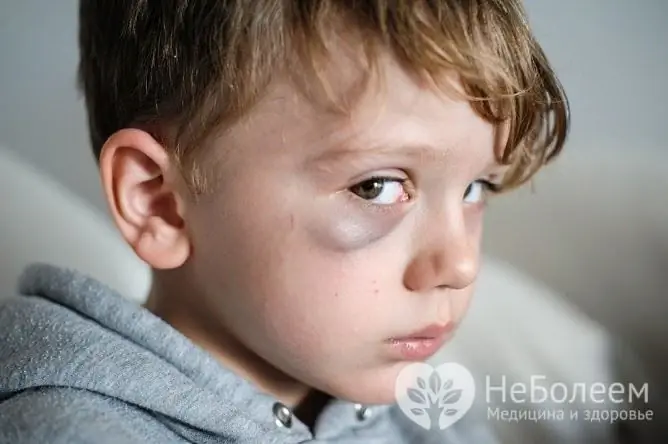
Subcutaneous hematoma is characterized by tenderness, swelling and discoloration of the area of injury
The following symptoms are characteristic of a subcutaneous hematoma:
- swelling and soreness: due to edema of the surrounding tissues;
- change in the color of integumentary tissues: from lilac-blue to yellow-green;
- local temperature rise.
The reasons
In most cases, bruises appear as a result of traumatic effects, namely, bruising, squeezing, infringement, blast damage.
Some drugs with anticoagulant properties (acetylsalicylic acid, warfarin, etc.) can contribute to their appearance, even with minor injuries.
Also, in women in the second phase of the menstrual cycle, just before the onset of menstruation, the likelihood of bruising increases.
Constantly appearing bruises on different parts of the body can be a symptom of several diseases, including:
- diabetes;
- von Willebrand disease;
- thrombocytopenic conditions.
Classification of soft tissue hematomas by severity:
| Severity | Description |
| Easy | A bruise occurs in a day or a little earlier from the moment of mechanical damage, is not accompanied by a violation of the functional activity of the limb and is manifested by mild soreness at the site of impact |
| Average | A hematoma appears 5-6 hours after a blow, if a limb is bruised, its functions may be partially impaired, the pain is moderate |
| Heavy | Hematoma is detected after 30-120 minutes, limb function falls out, pain is severe |
First aid
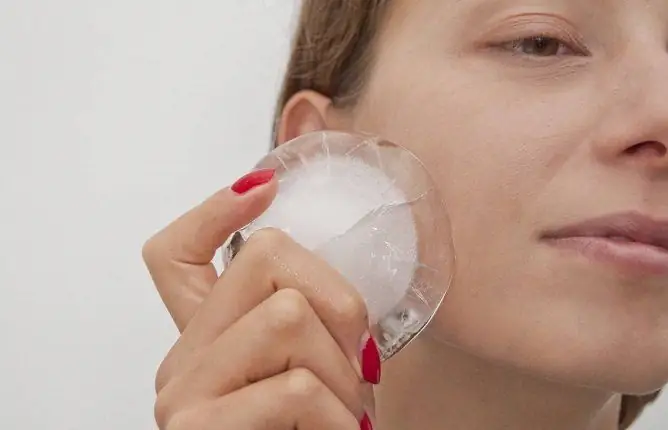
Immediately after the injury has been sustained, cold (cold object) must be applied to the injury site. If this happened at home, ice will do, if not, any product from the freezer or refrigerator.

First aid for injuries consists of exposure to cold
If you are injured on the street in winter, you can apply snow, if at other times of the year, use any metal object (metal ruler, coin, metal phone case, etc.). You can also attach a water bottle.
Treatment of bruises, including on the face
Therapy can be operative and conservative, inpatient and outpatient. It depends on the strength of the injury, the severity of the condition, and other factors.
Surgical and inpatient treatment
Such hematomas rarely heal on their own, and sometimes pose a threat to human life, therefore, this problem is solved by opening, removing the clot, sometimes suturing the vessel and other measures, depending on the clinical and laboratory picture.
Pharmacological agents
Usually, mild subcutaneous bruises are treated on an outpatient basis (at home). For this, there are a large number of drugs that can be purchased at the pharmacy.
Medicines for hemorrhage can be used for two purposes:
- anesthesia;
- acceleration of "flowering" of hematoma.
As pain relievers, you can use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in tablets, for example, Ibuprofen, Nimesulide, Diclofenac.
To quickly get rid of the blue-violet or yellow-green color of the damaged area of the skin, including on the face, means for local use in the form of gels, ointments and creams will help.
Medicines containing heparin
Topical heparin can be used to treat a bruise on the face or other area of the body.

For bruising, the use of drugs containing heparin, such as Lioton, is effective
Heparin, by reducing the inflammatory process and anticoagulant activity, promotes the early resorption of the bruise, has a weak analgesic effect.
Means for topical use, containing heparin, are represented by the following trade names: Heparin ointment or gel, Lyoton, Hepatrombin, Dioflan, Liogel, Lyothromb. Most often, drugs from this group can be found in the medicine cabinet for people suffering from varicose veins.
Apply ointments or gels with heparin daily, until symptoms are eliminated, 1-3 times a day. They are applied in a small layer to the affected area of the skin and gently rubbed.
It is forbidden to use these funds for people with pathology of the blood coagulation system, characterized by a tendency to bleeding (hemophilia, thrombocytopenia), with increased sensitivity to heparin. Do not use these drugs on gaping wounds and / or on wounds with signs of bacterial inflammation, bleeding wounds.
Badiaga
Badyaga will help you quickly remove the bruise. The main component of the preparation is a dried colony of inhabitants of freshwater reservoirs - badyag (sponges from the badyagovy family - Spongillidae). Their skeleton is represented by crystals of silica, which are needle-shaped. Thanks to this, the main effect of the drug is carried out - a local irritant.
Badiaga is available in two dosage forms - powder and gel.

Badyagu in powder form should be diluted in warm water before use
Before use, the powder must be diluted in warm boiled water. Such a mixture should look like a gruel, which is then applied with a swab to the damaged area of the skin, rubbing in circular motions. After application, the product is left on the skin for 15 minutes and then washed off.
The gel is applied in a circular motion, left for 10-20 minutes, and then washed off.
Contraindications to the use of the drug are:
- hypersensitivity to components;
- violation of the integrity of the skin at the site of application;
- dermatological (bacterial, fungal, etc.) skin lesions;
- peripheral nervous tissue tumors.
Do not use the drug in children under 12 years of age.
Troxevasin
Troxevasin gel contains an active ingredient - troxerutin. It has the following effects:
- improves vascular microcirculation;
- increases the resistance of erythrocytes to deformation, venous tone;
- reduces capillary permeability, erythrocyte aggregation, edema, pain.
All of these mechanisms help to quickly remove the bruise.
Troxevasin is applied to the affected area with a thin layer
The gel must be applied in a thin layer to the damaged area of the skin twice a day - in the morning and at night, rub in with massage movements until the drug is completely absorbed. How long treatment should be continued depends on the degree of injury and response to therapy.
Contraindications for use include troxerutin intolerance, open and / or infected wounds. Do not apply the medicine to the mucous membranes.
Traditional methods
Alternative medicine offers many solutions to how to quickly remove bruises at home. However, a large number of them are ineffective, and some are even dangerous.
For example, you can find advice to make an iodine mesh, lotions with vinegar solution, apply toothpaste, etc. These methods can reduce the severity of bruising, but often lead to other damage, in particular burns. Therefore, they should not be used, especially with hematomas localized on the face.
The use of cabbage and plantain leaves is considered effective. They must first be crushed, and then applied to the place of damage.
It is also recommended to mix salt with water and apply with a cotton pad to the bruise. Such a hypertonic solution can reduce swelling and soreness, but it must be remembered that this method can be used only after the final formation of the subcutaneous formation, that is, not earlier than 48 hours after the injury.
Warm compresses
Effective folk remedies are considered procedures with warm compresses, which can be applied two days after the appearance of the bruise, but not earlier. You can use coltsfoot, flax seed, arnica, etc.
But they are never applied immediately after injury, as this can aggravate the process.
Effects
Favorable outcome
As a result of a bruised injury, blood vessels rupture, the blood from which enters the intercellular space and is limited to neighboring tissues. After some time, this area is absorbed, passing through all the stages of "flowering", without the formation of residual phenomena. This is considered a favorable outcome.
Unfavorable outcome
An unfavorable outcome can be observed with massive hematomas. In this case, the formation of a cavity with clotted blood is possible, which is able to exist for a long time without a tendency to regress. This causes inconvenience, discomfort, can interfere with the normal life of a person.
In case of extensive injuries, in order to exclude the presence of a cavity with coagulated blood, it is necessary to consult a doctor and undergo the necessary examinations
Another unfavorable outcome is the addition of a bacterial infection (infection) with possible further suppuration.
Adequate therapy, including complex measures such as first aid, pharmacological agents for external use and traditional medicine, can significantly reduce the healing time of a hematoma. In severe cases, in order to quickly remove the bruise, you need to consult a doctor and follow his instructions.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.