- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Castor oil for constipation
The content of the article:
-
Description of the drug
- Group
- Composition
- Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
- Indications for use
- Contraindications
-
Method of administration and dosage
- Adults
- For children
- Side effect
- Overdose
- Interaction with other medicinal products
- Application features
- Storage conditions
- Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
- Analogs
- Video
Castor oil for constipation is an integral part of conservative therapy and is included in the scheme as a laxative. The clinical effect is somewhat weaker than that of other drugs (provides a laxative effect of moderate intensity). Helps in case of acute and uncomplicated constipation (positive feedback in 50-60% of cases).
The popular name is castor oil.
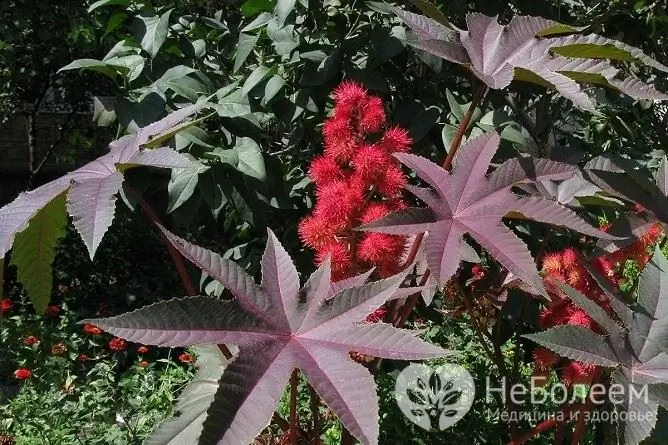

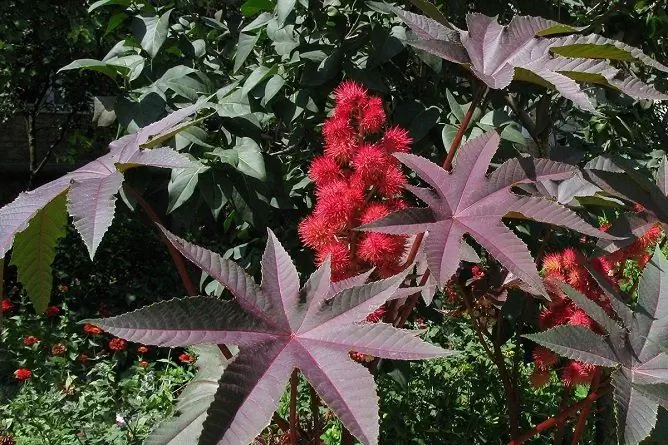
Castor oil is produced from the seeds of a poisonous plant - castor oil plant
Description of the drug
Group
Castor oil is a drug used for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (a subtype of laxative drugs that cause chemical irritation of the intestinal mucosa).
Composition
The drug is a thick transparent, sometimes yellowish liquid with an unpleasant taste.
It is an oil obtained from the seeds of the castor bean (Ricini communis semenis oleum), a family of Euphorbiaceae.
The main active ingredient is ricinoleic acid.
Produces in glass containers with a capacity of 30 g.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Refers to herbal preparations and is suitable for both external and oral administration.
It is broken down in the small intestine into its constituent elements under the action of an intestinal enzyme - lipase. Ricinoleic acid. It has a pronounced irritating effect on the receptor network of the small intestine. Due to its activation, a reflex increase in peristalsis occurs and, as a result, intestinal cleansing.
The drug is not absorbed into the bloodstream and only works in the intestinal lumen. The clinical effect occurs within 5-6 hours from the moment of administration.
Indications for use
Castor oil is used:
- In the treatment of acute constipation as a natural, fast acting laxative.
- In case of poisoning and intoxication in order to accelerate the evacuation of intestinal contents and reduce the absorption of hazardous substances.
- As a preoperative preparation or before carrying out a number of diagnostic procedures (irrigography, colonoscopy).
Often used in combination with other herbal medicines.
Contraindications
The drug has the following contraindications for use:
- Chronic constipation, since peristalsis is significantly stimulated, and tissue rupture may occur due to dense feces in the lower parts of the large intestine. Chronic constipation is often associated with organic lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, in which an increase in the peristaltic wave is not allowed.
- Acute inflammatory bowel diseases (dynamic or strangulated intestinal obstruction, acute appendicitis), since increased peristalsis will lead to a sharp deterioration in the course of the underlying disease (rupture, intussusception).
- Mechanical intestinal obstruction has been identified as a separate item due to partial or complete blockage of the intestinal lumen (tumors, foreign bodies, adhesions). In this case, stimulation of the intestine will also lead to rupture or the appearance of the phenomenon of reverse peristalsis.
- Abdominal pain of unknown origin (not prescribed until a specific diagnosis is established).
- Bleeding from various parts of the gastrointestinal tract, since it indirectly leads to an increase in blood flow to the intestine by increasing the work of muscle structures.
- Complete intestinal atony of unknown origin.
- Poisoning with fat-soluble substances such as phosphorus or benzene.
- Uterine bleeding, since by stimulating the contraction of the myometrium, blood flow to the organ can increase (increased blood loss).
Requires careful use during pregnancy and lactation.
Method of administration and dosage
It is permissible to use both in children and adults.
Adults
As a laxative inside, 15-30 g (1-2 tablespoons) 1 time per day for 3-5 days. In the case of use to prepare for diagnostic procedures, drink 15-30 g once 2-6 hours before the study.
For children
As a laxative for children aged 10 years and older, you need to drink 5-15 g (1-2 teaspoons) once a day. The specific dosage depends on age (1 teaspoon for a child aged 10-13, and then it is permissible to gradually increase the volume to the adult dose). To hide the unpleasant taste, lemon juice is sometimes mixed with castor oil (1: 1).
Side effect
There are the following side effects:
- Abdominal pain and nausea due to reflex intensification of the peristaltic wave.
- Digestive disorders like enterocolitis or intestinal atony after abrupt cessation of use (applies only to long-term use as part of complex therapy).
- Clinical manifestations of hypovitaminosis (lack of vitamins A and D). This is due to both a partial violation of the synthesis of vitamins in the intestine, and a violation of the normal absorption of nutrients.
It is not addictive because it is rarely used for a long time. Side effects are mild and rarely occur when used correctly.
Overdose
It may occur when taking more than 7 g / kg of body weight (some convention is important due to the lack of clinical studies). In connection with the extreme degree of stimulation, there are:
- diarrhea;
- sharp spasms of the intestines (paroxysmal acute pain in the abdomen without clear localization);
- dehydration of the body (rehydration therapy is required);
- dizziness and loss of consciousness.
In extremely rare cases, due to pronounced peristalsis, volvulus or dynamic intestinal obstruction may develop.
A specific antidote can be:
- atropine sulfate;
- loperamide.
In addition, symptomatic therapy is indicated to replace the loss of fluid and electrolytes.
Interaction with other medicinal products
The drug rarely causes pronounced cross-reactions, therefore it is permissible in the treatment of a number of concomitant diseases of other systems.
Interactions:
- Simultaneous reception with saline laxatives is not recommended, since the healing effect is layering.
- When taken simultaneously with multivitamin complexes, it reduces the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, K).
- When taken up to 4 g / day, the agent is able to slightly increase the absorption of fat-soluble drugs such as Mebendazole or Griseofulvin (enhances the effect of use).
- When taken simultaneously with M-anticholinergics (Atropine, Platifilin), the effective effect of castor oil decreases.
- Simultaneous reception with anticholinesterase agents (Neostigmine, Pyridostigmine) enhances the laxative effect of castor oil.
- Antispasmodics (Papaverine, Drotaverine) reduce the laxative effect of taking castor oil.
Castor oil helps with constipation for adults and children
Application features
In some cases, the use of castor oil requires some restrictions (the main points are presented in the table).
| States | Features: |
| Pregnancy and lactation | Since the drug can stimulate labor (contraction of the myometrium), it should not be used during pregnancy, especially in the third trimester. The risks of miscarriage or bleeding are moderate. |
| Pediatric practice | There is a high risk of developing dehydration in children under 10 years of age, as well as a high risk of colitis due to increased intestinal sensitivity to irritants. |
| Effects on concentration | Although the medication does not have a pronounced effect on concentration, it is not recommended to take it with the assumption of driving a vehicle. |
How long the course of therapy lasts is determined by the specialist depending on the individual characteristics and the specific disease that caused the constipation.
Storage conditions
It is required to be stored in a dark, dry place, protected from direct sunlight, at a temperature not exceeding 25 C.
Shelf life is 5 years.
Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
The drug does not require a prescription and is freely available (use strictly according to the attached instructions).
Analogs
Castor oil has a number of analogues that have similar properties, but are devoid of some negative characteristics (for example, unpleasant taste and a certain difficulty in using in children). Have a similar effect on the intestines: Senadexin, Alax, Radirex.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.