- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Ointments for warts
The content of the article:
- Ointment for warts on hands, face, soles: how to choose
- Antiviral agents
- Keratolytic agents
-
Cytotoxic drugs
- Vartek (podophyllotoxin)
- Fluorouracil
- Emollients
- Phytopreparations
- An integrated approach to therapy
- Features of warts and approach to their treatment
- Video
There are many ways to get rid of warts: medications, herbs, cryosurgery, electrocoagulation, surgical excision. Ointments for warts are one of the local treatments that are convenient to use at home. Topical medications are used to remove the wart and prevent recurrence.

Ointments with different mechanisms of action are used to treat warts.
Ointment for warts on hands, face, soles: how to choose
There are several groups of topical drugs that help get rid of warts: topical retinoids, antiviral, keratolytic (exfoliating), cytotoxic, emollients, and herbal remedies.
| Group name | What are they assigned for? | Mechanism of action |
| Antiviral and immunomodulators | Fighting the cause | Drugs from this group affect the cause of the disease - infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). Some ointments lead to the death of viral particles, while others activate the immune response. |
| Cytotoxic | Deleting | Cytotoxic drugs block cell division (destroy DNA), which allows you to get rid of a benign formation. |
| Keratolytic | Deleting | Keratolytics exfoliate dead skin cells. Their long-term use allows you to eliminate the build-up. |
| Local retinoids | Deleting | Local retinoids are able to stop the growth of epithelial cells, and also have an exfoliating effect. |
| Emollient | Skin restoration | Emollients speed up skin healing. |
You can use monotherapy or combine the use of several groups of drugs at once. For example, an exfoliator can be applied at the beginning of treatment, and an emollient can be applied after the wart has fallen off. It is contraindicated to combine the use of retinoids with other topical preparations.
Antiviral agents
Given the viral nature of the disease, the use of destructive and cytotoxic agents is far from always effective. Even after successfully removing the wart, it may reappear. To prevent relapse, local antiviral drugs and immunomodulators are prescribed. Antiviral ointments can be combined with other medications. Overview of Local Antivirals:
| Active substance | Tradename | How to use a wart ointment |
| Oxolin | Oxolinic ointment | Apply a thin layer to the affected area 3 times a day. The duration of treatment is 5 days. |
| Interferon | Viferon | The ointment is applied 3-4 times a day on the wart, rubbing gently. The duration of treatment is up to 7 days. |
| Imiquimod | Aldara cream, Ziklar, Keravort | The cream is applied 3 times a week. Apply the product directly to the wart before bedtime, leaving the cream to be absorbed for 8-10 hours. Treatment lasts until the lesions disappear, but the duration of the drug should not exceed 16 weeks. |

Oxolinic ointment belongs to the group of antiviral drugs
Antiviral agents cannot be applied to damaged skin areas, there are no other contraindications to use. Side effects are rare (discoloration of the skin, burning sensation, skin rashes).
Keratolytic agents
Salicylic ointment has a good exfoliating effect. The active ingredient is salicylic acid. For the treatment of the disease, 10% ointment is prescribed. How to use the medicine:
- Rinse and dry the skin.
- Apply ointment in a thick layer.
- Cover with a gauze bandage on top.
- Fix with a bandage or adhesive plaster.
- Remove after 6-8 hours (can be used at night).
The course duration is 14-21 days. The drug is used for flat and plantar warts. Also, keratolytic agents are used in the form of solutions for external use (Ferezol, Solkoderm).

Salicylic ointment has a keratolytic effect
Cytotoxic drugs
To remove the build-up at home, you can use cytotoxic drugs that block cell division. Such medicines include Vartek cream (podophyllotoxin) and 5-fluorouracil "Ebeve".
Vartek (podophyllotoxin)
Vartek is the drug of choice for the treatment of genital warts. The medicine is available in the form of a cream for external use. How to apply the cream:
- Wash with soap and dry the affected area.
- Apply the cream on the warts pointwise (for more convenient application, it is recommended to use a mirror).
You need to apply the cream 3 days a week, followed by a break for 4 days. The course of therapy lasts an average of 4 weeks (only 12 days of active treatment).
It is contraindicated to use the cream if there is a violation of the integrity of the skin. Side effects may occur:
- erosive and ulcerative skin lesions;
- redness, swelling at the site of application of the cream;
- pain and bleeding;
- skin rashes;
- itchy skin.
If side effects occur, stop using the cream and consult a doctor.

Vartek cream - a drug of cytotoxic action
Fluorouracil
Fluorouracil disrupts the synthesis of cellular and viral DNA. For the treatment of the disease, a 5% cream is prescribed. There are 2 drug prescription schemes:
- 1 time at night for 7 days.
- Once a week for 10 weeks.
The cream is applied in a thin layer to the affected area of the skin. The advantage of using Fluorouracil is its high efficiency - in 90% of cases, this treatment allows you to get rid of the disease.
The main drawback of the drug is the risk of serious side effects. Weeping erosions, up to severe contact dermatitis, are common.
Emollients
Emollients are prescribed at the second stage of the treatment of the disease, when the wart has disappeared, and a defect has appeared in its place. What medications are most often prescribed:
- Zinc ointment;
- balsamic liniment (according to Vishnevsky).
The use of these funds accelerates healing, prevents secondary infection.

Zinc ointment promotes skin regeneration after wart removal
Phytopreparations
At home, you can use pharmaceutical phytopreparations. They act mildly, rarely cause side effects. At the same time, their effectiveness is lower than from the use of cytotoxic or keratolytic agents.
Local remedies based on celandine are often used. How to apply the product:
- Steam the skin, remove keratinized areas.
- Squeeze a small amount of the ointment onto a cotton swab.
- Apply a thick layer to the wart.
- Cover with a gauze bandage on top.
- Leave on for 4 hours.
You need to use the medicine once a day for 5 days.

Celandine-based ointment can be used to get rid of skin growths
An integrated approach to therapy
For effective treatment, it is not enough to use only medications. Even after getting rid of the growth, relapses often occur, which is associated with the viral nature of the disease.
To prevent relapse, you must follow the recommendations:
- Use your slippers in the pool, sauna, gym, do not go barefoot.
- Choose comfortable shoes that do not squeeze the foot.
- Wash your hands often, especially after visiting public places.
- Use only personal hygiene products.
- Use only sterilized manicure accessories.
Features of warts and approach to their treatment
Warts are benign growths that appear on the skin. Any area of the skin can be affected: soles and toes, hands, face, genitals. The cause is a viral infection (human papillomavirus).
The choice of a therapy method depends on many factors:
- Localization. If the formation is localized on the face, laser therapy and cryodestruction are preferred, treatment at home is not recommended. If a build-up appears on the sole, you can use folk remedies and local medications.
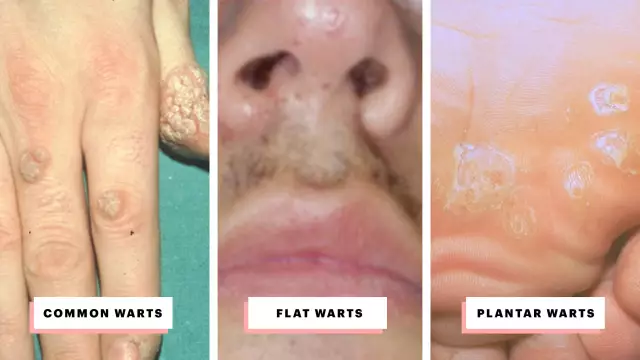
- Variety. Flat warts in most cases go away on their own, ordinary (vulgar) - can be treated with antiviral and keratolytic drugs. Warts are recommended to be treated with destructive methods (cryotherapy, laser therapy, electrocoagulation), or with the help of cytotoxic drugs.
- The patient's age. In children, such growths often go away on their own; with multiple formations, antiviral agents can be used. In adults, most lesions require medical or surgical treatment.
- Additional symptoms and complications. Ulceration, bleeding, and frequent damage to the wart are contraindications to home treatment.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.