- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
High blood sugar: symptoms, causes, diet
The content of the article:
- The reasons
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- What to do
- Diet
- How to prevent
Elevated blood sugar is not always a sign of diabetes. However, in order to rule out the disease or identify a prediabetic condition, it is recommended to undergo a medical examination.
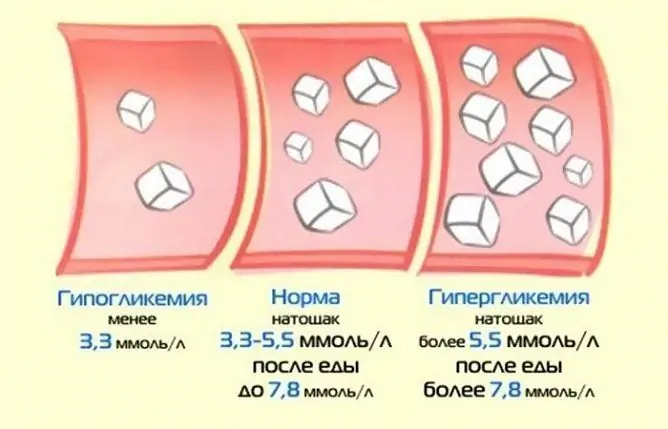
Sugar, or rather glucose, is the main source of energy in the human body. The normal level of glucose in capillary blood is 3.3-5.5 mmol / l, the glucose level in venous blood is 4-6 mmol / l. A condition in which there is high blood sugar is called hyperglycemia.
The maintenance of normal blood glucose levels is the result of many factors, among which hormonal regulation plays a key role. The main hormone that lowers the concentration of glucose in the blood is insulin, a peptide hormone produced in the pancreas (in the β-cells of the islets of Langerhans). Insulin promotes the absorption of glucose by cells, activates key glycolysis enzymes, stimulates the formation of glycogen in muscles and liver, and reduces the intensity of gluconeogenesis. Violation of the secretion of this hormone (absolute insulin deficiency) plays a significant role in the development of type 1 diabetes mellitus. In case of violation of the action of insulin on the tissues of the body (relative insufficiency of insulin), diabetes mellitus of the second type develops.
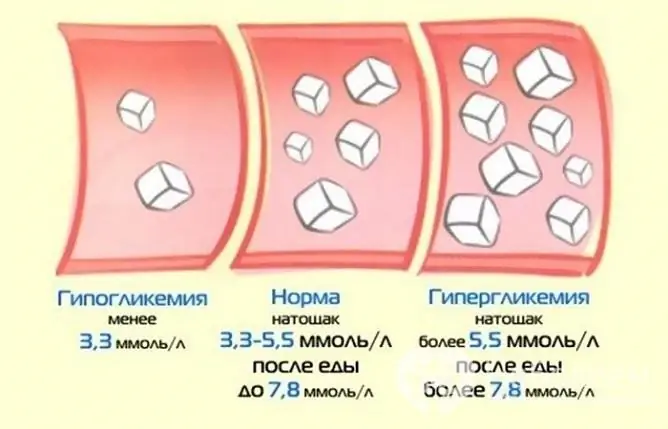
Increased blood sugar is called hyperglycemia.
Depending on the concentration, hyperglycemia is classified into three degrees:
- Light - 6-10 mmol / l.
- Average - 10-16 mmol / l.
- Severe - 16 mmol / L or more.
Allocate temporary, permanent hyperglycemia, fasting hyperglycemia and postprandial (after a meal).
If a person has high blood sugar on an empty stomach, this does not always indicate the presence of diabetes mellitus, however, in order to exclude the latter or determine a pre-diabetic condition, it is recommended to undergo a medical examination.
The reasons
Risk factors that can cause high blood sugar include:
- genetic predisposition;
- poor nutrition (especially the use of a large number of bakery products and sweets);
- irrational use of medicines;
- bad habits (especially alcohol abuse);
- profuse blood loss;
- deficiency of vitamins in the body (especially B 1 and C);
- excessive physical activity;
- poisoning with carbon oxides;
- frequent stressful situations.
Increased sugar levels are observed in diabetes mellitus, Itsenko-Cushing's syndrome, stroke, heart failure, epileptic seizures, some pathologies of the thyroid gland, stomach and intestines. The risk group includes women with polycystic ovary syndrome, as well as those with a low concentration of potassium in the blood.
In women, an increase in sugar can also be observed with premenstrual syndrome, during pregnancy. Hyperglycemia in pregnant women is caused by changes in hormonal levels and the associated low susceptibility of body tissues to the action of insulin. This condition is called gestational diabetes. Often it proceeds in the absence of any clinical manifestations, is detected only during laboratory diagnostics and passes after childbirth. With the development of gestational diabetes in early pregnancy, there is a risk of developing fetal pathologies, including serious ones: heart defects, cerebral palsy, congenital cataracts, etc. In some cases, gestational diabetes can turn into true diabetes. The risk group includes pregnant women with a family predisposition to diabetes, obesity, arterial hypertension,a history of repeated miscarriages.
Doctors note an increase in the detection rate of hyperglycemia in children. This phenomenon is associated with the regular consumption of large amounts of fast food, the early introduction of cow's milk and / or cereals into the diet, the use of drinking water with an excess of nitrates, and nervous disorders caused by an unfavorable psychological climate in the family. In addition, hyperglycemia in children is often observed after suffering from influenza or rubella.
Symptoms
The main signs of a long-term increase in sugar:
- constant thirst (even when drinking a lot of liquid), the inability to completely quench it;
- dryness of the mucous membranes of the mouth;
- frequent urge to urinate, increased urine output, nocturnal urination;
- decreased visual acuity;
- itchy skin;
- weakness, fatigue;
- irritability;
- arrhythmia;
- dyspnea;
- unreasonable weight loss (even with adequate nutrition);
- the smell of acetone from the mouth.
In addition, patients with hyperglycemia complain of numbness of the lips, numbness and coldness of the upper and / or lower extremities, unreasonable debilitating headaches, nausea, frequent constipation or diarrhea, dizziness, chills, flashing of flies in front of the eyes, susceptibility to infectious diseases.

Symptoms of hyperglycemia may indicate the development of type 2 diabetes.
In men, with high sugar, sexual dysfunction, inflammation of the foreskin are common.
These signs allow one to suspect hyperglycemia, but the final diagnosis is established after examination.
Diagnostics
In addition to laboratory determination of blood glucose concentration, if a pathological condition is suspected, a glucose tolerance test (glucose tolerance test) is performed. In this test, fasting blood glucose is measured, and then the patient takes glucose dissolved in water. After that, several successive measurements are taken at intervals of 30 minutes. Normally, the glucose concentration two hours after glucose load does not exceed 7.8 mmol / L. At a glucose level of 7.8-11.0 mmol / l, the result is regarded as impaired glucose tolerance; at higher rates, diabetes mellitus is diagnosed.
To avoid distorting the test results, it is recommended to adhere to certain rules for its preparation:
- blood must be donated on an empty stomach, the last meal should be no later than 10 hours before the study;
- the day before the study, you should stop playing sports, exclude heavy physical activity;
- you should not change your usual diet on the eve of the study;
- avoid stressful situations before taking the analysis;
- get a good night's sleep on the eve of the study.
If hyperglycemia is suspected, patients are prescribed a general blood and urine test (with the identification of ketone bodies), tests for the determination of C-peptide, glycosylated hemoglobin, antibodies to β-cells of the pancreas.
With prolonged elevated sugar levels, it is recommended to assess the function of the heart, liver and kidneys (ECG, ultrasound, etc.).
In order to exclude complications developing against the background of hyperglycemia, the patient, depending on the indications, is referred for a consultation with an endocrinologist, ophthalmologist, urologist or gynecologist, cardiologist, neurologist.
What to do
Physiological increase in sugar usually does not require special treatment; glucose levels, as a rule, normalize when the factor that caused it is eliminated.
Treatment of pathologically high sugar is complex and should be carried out under the supervision of the attending physician. It is important to remember that self-medication can aggravate the situation and lead to adverse consequences.
When a patient has diabetes mellitus, therapy is prescribed depending on its type. In addition to diet therapy, it may include subcutaneous injections of insulin, oral hypoglycemic drugs. In the absence of compensation for diabetes, there is a risk of developing hyperglycemic coma, which is a life-threatening condition.
In some cases, patients with hyperglycemia are shown vitamin and phytotherapy (blueberry tea, hibiscus, tea made from lilac leaves, sage).

Hibiscus helps to normalize sugar levels
Moderate physical activity (gymnastics, swimming, aerobics and water aerobics, badminton, tennis, golf, volleyball, basketball, cycling) contribute to the normalization of glucose levels. Walking, climbing stairs on foot, running at a moderate pace are also effective. Even half an hour of exercise therapy per day helps to normalize blood sugar. Among other things, regular physical activity refers to measures to prevent the development of type 2 diabetes.
Patients with hyperglycemia should exclude stress, physical and mental overload, up to a job change if necessary. It is necessary to get rid of bad habits and spend more time in nature.
Diet
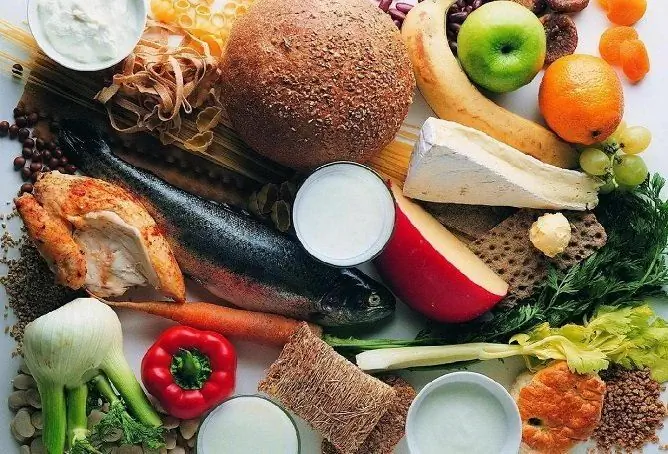
The main way to normalize blood glucose levels is through diet. Calorie intake is calculated based on physique and physical activity. Shown fractional nutrition - food intake 5-6 times a day in small portions at regular intervals. In addition to lowering blood sugar levels, the goal of diet therapy is weight loss. With increased body weight, the daily caloric intake should be reduced by 250-300 kcal from the daily intake recommended for a given age and lifestyle.
The basis of the diet is vegetable-protein, foods containing carbohydrates, only those with a low glycemic index are allowed. Recommended:
- vegetables in raw and thermally processed form (fresh vegetables should be eaten daily, their share should be at least 20% of all vegetables);
- lean meat, offal, fish, seafood;
- eggs (no more than two per day);
- natural dairy and fermented milk products;
- cereals (buckwheat, millet, barley, pearl barley, oatmeal);
- baked goods made from unleavened dough, whole grains, rye;
- legumes;
- berries, fruits, as well as fresh juices from them;
- black natural coffee, black, green, white, herbal tea, unsweetened compotes, fruit drinks;
- some sweets (marshmallow, marshmallow, marmalade, small amounts of honey, dark chocolate);
- vegetable oils.
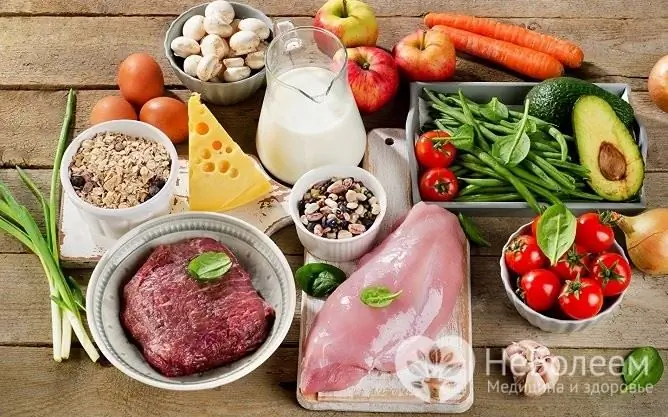

For hyperglycemia, you must follow a plant-protein diet that excludes high-carbohydrate foods
In case of hyperglycemia, it is recommended to consume at least 1.5-2 liters of water per day.
Confectionery products are excluded from the diet, with the exception of those permitted, pastries made from butter and puff pastry, rice, semolina, sausages, bacon, ham, rich meat broths, fatty, smoked and pickled products, pasta, fatty and spicy sauces, fast food, snacks. Sugar should be discarded, if it is difficult to do it right away, a small amount is left, gradually decreasing until it is completely removed from the diet. Alcohol is also banned, with the exception of a small amount (1-2 glasses) of natural dry red wine 1-3 times a week.
How to prevent
In order to prevent high blood sugar, it is recommended:
- healthy eating, avoiding the abuse of sugar, sugar-containing foods and alcohol, avoiding any unbalanced diets;
- maintaining a normal body weight;
- regular physical activity, while refusing excessive exertion;
- monitoring the concentration of glucose in the blood (especially for those who are at risk);
- development of stress resistance;
- rejection of bad habits;
- timely treatment of diseases that can lead to hyperglycemia.
YouTube video related to the article:

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.