- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Quentiax
Kventiax: instructions for use and reviews
- 1. Release form and composition
- 2. Pharmacological properties
- 3. Indications for use
- 4. Contraindications
- 5. Method of application and dosage
- 6. Side effects
- 7. Overdose
- 8. Special instructions
- 9. Application during pregnancy and lactation
- 10. Use in childhood
- 11. In case of impaired renal function
- 12. For violations of liver function
- 13. Use in the elderly
- 14. Drug interactions
- 15. Analogs
- 16. Terms and conditions of storage
- 17. Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
- 18. Reviews
- 19. Price in pharmacies
Latin name: Kventiax
ATX code: N05AH04
Active ingredient: quetiapine (quetiapine)
Manufacturer: KRKA d.d. (KRKA, dd) (Slovenia)
Description and photo update: 2018-21-11
Prices in pharmacies: from 457 rubles.
Buy
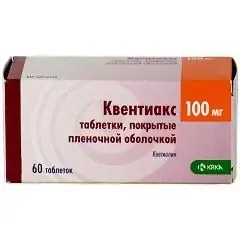
Quentiax is a neuroleptic drug with antipsychotic efficacy.
Release form and composition
Kventiax dosage form - film-coated tablets; at the break, white, rough (10 pcs. in blisters / blisters, in a cardboard box 3, 6 or 9 blisters / packages):
- dosage of 25 mg: biconvex, round, beveled, brownish-red shell;
- dosage of 100 mg: biconvex, round, light yellow shell;
- dosage 150 mg: biconvex, round, chamfered, white shell;
- dosage 200 mg: biconvex, round, white shell;
- dosage of 300 mg: biconvex, oval, white shell.
Composition for 1 tablet:
- active substance: quetiapine fumarate in the form of quetiapine hemifumarate - 28.78 / 115.13 / 172.69 / 230.26 / 345.39 mg, which corresponds to the content of quetiapine - 25/100/150/200/300 mg;
- auxiliary components: lactose monohydrate, povidone, calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate, sodium carboxymethyl starch (type A), magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose;
- film shell: titanium dioxide (E 171), hypromellose, macrogol-4000; for a dosage of 25 mg additionally - dye iron oxide yellow (E 172), dye iron oxide red (E 172); for a dosage of 100 mg additionally - a dye iron oxide yellow (E 172).
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
The active component of Quentiax, quetiapine, is an atypical antipsychotic drug that exhibits a higher affinity for serotonin 5-HT 2 receptors than for dopamine D 1 and D 2 receptors in the brain. Quetiapine has an affinity for α 1 - and histamine receptors, and to a lesser extent an affinity for α 2 -receptors. No significant affinity of quetiapine for muscarinic, cholinergic and benzodiazepine receptors was found. According to the results of standard tests, the manifestation of the antipsychotic activity of quetiapine is noted.
As a result of the study of EPS (extrapyramidal symptoms) in animals, it was found that quetiapine is capable of causing weak catalepsy at doses that effectively block dopamine D 2 receptors. It also selectively inhibits the activity of mesolimbic A10-dopaminergic neurons compared to A9-nigrostriatal neurons, which are involved in motor functions.
There were no differences in the incidence of extrapyramidal symptoms and the concomitant use of anticholinergic drugs when using therapeutic doses of quetiapine (75-750 mg / day) and placebo.
Kventiax does not cause a prolonged increase in the plasma concentration of prolactin.
Quetiapine is able to maintain clinical improvement for a long time, mainly in those patients whose positive effect developed from the very beginning of therapy.
The effect of quetiapine on serotonin 5-HT 2 and dopamine D 2 receptors after taking Quentiax is less than 12 hours.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of quetiapine do not differ between women and men and are dose-dependent linear.
Main pharmacokinetic parameters:
- absorption: quetiapine has a high absorption, food intake does not affect the bioavailability of the substance;
- distribution: 83% of the drug binds to plasma proteins;
- metabolism: quetiapine, actively metabolized in the liver, forms pharmacologically inactive metabolites under the action of cytochrome P 450 (isoenzyme CYP3A4). Quetiapine and its individual metabolites weakly inhibit cytochrome P 450 isoenzymes (1A2, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6 and 3A4), and only in concentrations exceeding 10-50 times, at least their content when used in the range of therapeutic doses of 300-450 mg per day. Based on the results of in vitro studies, it can be assumed that the appointment of quetiapine with other drugs will not cause a clinically pronounced inhibition of the metabolism of other substances, mediated by the cytochrome P 450 system;
- excretion: quetiapine is excreted mostly by the kidneys (73%) and intestines (21%). Less than 5% of the substance is not metabolized and is excreted unchanged. T 1/2 (half-life) is ~ 7 hours. Average clearance of quetiapine: elderly patients - 30-50% lower than in the age group 18-65 years; patients with severe renal impairment with creatinine clearance <30 ml / min / 1.73 m 2 and patients with liver damage (stabilized alcoholic cirrhosis) - a decrease of about 25%.
Indications for use
According to the instructions, Kventiax is recommended for the treatment of acute and chronic psychoses (including schizophrenia) and manic episodes in bipolar disorder.
Contraindications
Absolute:
- breast-feeding;
- children and adolescents up to 18 years old;
- hypersensitivity to quetiapine or ancillary components of tablets.
Relative contraindications (Kventiax should be used with caution): pregnancy, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and other conditions predisposing to arterial hypotension, hepatic / renal failure, congenital increase in the QT interval on the ECG (electrocardiogram) or the presence of conditions potentially capable of causing its increase (simultaneous use with drugs that prolong the QT interval, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, congestive heart failure), epilepsy, a history of convulsive seizures, old age.
Instructions for the use of Kventiax: method and dosage
The tablets are taken orally, regardless of food intake, 2 times a day.
Recommended dosage (daily doses):
- acute and chronic psychoses, including schizophrenia: 1st day - 50 mg, 2nd day - 200 mg, 3rd day - 200 mg, 4th day and then the therapeutic dose - 300 mg; depending on the individual tolerance and clinical efficacy of Quentiax, its dose can vary from 150 to 750 mg; the maximum allowable daily dose for the treatment of schizophrenia is 750 mg;
- manic episodes in bipolar disorder (as monotherapy or as an adjuvant to stabilize mood): 1st day 100 mg, 2nd day 200 mg, 3rd day 300 mg, 4th day 400 mg, a further increase in the dose by 200 mg per day is possible, by the 6th day of therapy, it can be 800 mg; depending on individual tolerance and clinical efficacy of Kventiax, its dose can vary from 200 to 800 mg; most often, the effective dose ranges from 400-800 mg; the maximum permissible daily dose for this disease is 800 mg.
Elderly patients and patients with renal / hepatic insufficiency are recommended to start treatment with a dose of 25 mg / day, which is gradually increased until an effective dose is achieved, daily by 25-50 mg.
Side effects
Classification of the incidence of side effects as recommended by the World Health Organization [very often (≥ 0.1); often (≥ 0.01 and <0.1); infrequently (≥ 0.001 and <0.01); rarely (≥ 0.0001 and <0.001); extremely rare (<0.0001), including isolated messages]:
- organs of hematopoiesis and the lymphatic system: often - leukopenia; infrequently - eosinophilia; extremely rare - neutropenia;
- metabolism and nutrition: often - an increase in body weight (most often in the first weeks of therapy); extremely rare - hyperglycemia / decompensation of diabetes mellitus;
- central and peripheral nervous system: very often - drowsiness, dizziness, headache; often - fainting; infrequently - agitation, insomnia, anxiety, akathisia, tremor, depression, convulsions, paresthesia; extremely rare - tardive (late) dyskinesia;
- cardiovascular system: often - orthostatic arterial hypotension, tachycardia, lengthening of the QT interval on the ECG;
- respiratory organs: pharyngitis, rhinitis;
- gastrointestinal tract: often - dyspepsia, dry mouth, constipation / diarrhea; rarely - nausea / vomiting, jaundice, abdominal pain; extremely rare - hepatitis;
- hypersensitivity reactions: infrequently - skin rash, allergies; extremely rare - Stevens-Johnson syndrome, angioedema;
- reproductive system and mammary gland: rarely - painful erection in men (priapism);
- other reactions: often - asthenia, peripheral edema; rarely - chest pain, low back pain, subfebrile condition, dry skin, myalgia, blurred vision, ZNS (neuroleptic malignant syndrome), manifested by hyperthermia, impaired consciousness, muscle rigidity, vascular disorders, an increase in the concentration of CPK (creatine phosphokinase);
- laboratory data: often - an increase in the level of hepatic transaminases [alanine aminotransferase (ALT) or aspartate aminotransferase (ACT)] in the blood serum; infrequently - hypercholesterolemia, increased serum gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) and triglyceride levels (not on an empty stomach); a decrease in the level of thyroid hormones (T - thyroxine): total T 4 and free T 4 - in the first 28 days of therapy, and total T 3 and reverse T 3 - exclusively when taking high doses of quetiapine.
Overdose
Data on Kventiax overdose are limited. There have been cases of taking the drug at a dose of more than 30,000 mg. In most of them, side effects were not noted or passed on their own. When taking quetiapine at a dose of 13 600 mg, a lethal outcome was recorded. Overdose leading to prolongation of the QT interval, coma, or death has been reported extremely rarely. The likelihood of side effects in patients with a history of severe cardiovascular pathologies due to taking high doses of Quentiax for a long time may increase.
Symptoms of a quetiapine overdose are drowsiness, excessive sedation, decreased blood pressure, tachycardia.
It is recommended to carry out symptomatic therapy, maintenance of the cardiovascular system, respiratory function, adequate oxygenation and ventilation of the lungs. There is no known specific antidote for quetiapine.
special instructions
Sudden withdrawal of high doses of antipsychotic drugs can cause withdrawal symptoms, symptoms of which are nausea / vomiting, and in rare cases, insomnia. It is known about cases of exacerbation of psychotic symptoms and the manifestation of involuntary movement disorders (dystonia, akathisia, dyskinesia) associated with the abolition of Quentiax, so it should be carried out gradually.
Taking quetiapine with drugs that prolong the QT interval requires caution, especially in elderly patients, in patients with congestive heart failure, hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia.
Given the effect of Quentiax on the central nervous system, it must be used with caution in combination with other drugs of similar action.
The appearance of symptoms of tardive dyskinesia indicates the need to reduce the dose or discontinue the use of quetiapine.
It is recommended to refrain from drinking alcohol during therapy with Kventiax.
According to controlled clinical trials, there were no differences in the incidence of seizures in patients taking quetiapine and in the placebo group. However, as with the use of other antipsychotics, it is recommended to prescribe Kventiax with caution to patients with a history of seizures.
ZNS can be a consequence of ongoing antipsychotic treatment. The clinical manifestations of the disease are hyperthermia, changes in mental status, muscle rigidity, instability of the autonomic nervous system, and increased CPK levels. If this syndrome develops, it is necessary to stop taking quetiapine and carry out appropriate treatment.
Influence on the ability to drive vehicles and complex mechanisms
Patients taking Kventiax are advised to perform with caution the types of work that require concentration of attention and speed of reaction, including driving a vehicle.
Application during pregnancy and lactation
Due to the fact that the safety and efficacy of using Quentiax during pregnancy have not been established, the drug is recommended to be taken only if the expected benefit exceeds the potential risks.
There are no reliable data on the degree of excretion of quetiapine in breast milk, therefore, breastfeeding should be discontinued during therapy.
Pediatric use
In pediatric practice, Kventiax is contraindicated for use up to 18 years of age due to the lack of reliable data on its effectiveness and safety for the treatment of children and adolescents.
With impaired renal function
Kventiax is taken with caution in case of impaired renal function.
For violations of liver function
Kventiax is taken with caution in case of liver dysfunction.
Use in the elderly
In elderly patients, the plasma clearance of quetiapine is reduced by 30-50%, therefore, Quetiax should be taken with caution, especially at the beginning of the course.
Drug interactions
Reception of Kventiax with carbamazepine, phenytoin (potential inhibitors of hepatic enzymes), as well as rifampicin and barbiturates can reduce plasma concentrations of quetiapine. It may be necessary to increase the dose of the drug depending on the observed clinical effect. This must also be taken into account when canceling inducers of the liver enzyme system or replacing them with drugs that do not induce liver microsomal enzymes (for example, valproic acid).
Quetiapine does not induce hepatic enzymes involved in the metabolism of lithium and phenazone.
Cimetidine (inhibitor P 450), fluoxetine (inhibitor of CYP3A4 and CYP2D6), antidepressant imipramine (inhibitor of CYP2D6) do not alter the pharmacokinetics of quetiapine.
The simultaneous use of quetiapine and systemic use of CYP3A4 inhibitors (antifungal agents of the group of azoles and macrolide antibiotics) requires caution, since it may increase plasma concentrations of quetiapine. In such cases, it is recommended to use lower doses of quetiapine, especially in elderly and debilitated patients.
Antipsychotics such as risperidone or haloperidol do not significantly affect the pharmacokinetics of quetiapine, but thioridazine increases its clearance.
Central nervous system depressants and ethanol in combination with Kventiax increase the likelihood of developing negative side effects.
Analogs
Quentiax analogs are: Viktoel, Gedonin, Quetiapin Canon, Quetiapin, Quetiapin San, Quetiapin-Vial, Quetiapin Stada, Ketiap, Quetitex, Ketilept, Kumenthal, Nantarid, Laquel, Seroquel, Servitel, etc.
Terms and conditions of storage
Store at 30 ° C. Keep out of the reach of children.
The shelf life is 5 years.
Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
Dispensed by prescription.
Reviews about Quentiax
Most of the reviews about Quentiax are positive. With depression, quetiapine helps to fall asleep almost immediately after taking it and sleep soundly until the morning, the next morning there is a slight drowsiness that passes during the day. The mental state is normalized, mood improves, irritability is relieved.
In one of the reviews, a patient with alcoholism shares his experience of using Quentiax when getting out of a binge, in his case, taking the drug helped to normalize sleep and made it easier to quit alcohol.
Many patients consider an increase in appetite, which results in weight gain, as a negative aspect of therapy.
Price for Kventiax in pharmacies
Estimated price of Quentiax, film-coated tablets, for 60 pcs. in the package: dosage 100 mg - 1517 rubles, dosage 200 mg - 2789 rubles, dosage 300 mg - 3874 rubles.
Kventiax: prices in online pharmacies
|
Drug name Price Pharmacy |
|
Kventiax 25 mg film-coated tablets 60 pcs. 457 r Buy |
|
Kventiax tablets p.p. 25mg 60 pcs. 466 r Buy |
|
Kventiax SR 200 mg film-coated tablets of prolonged action 60 pcs. 1145 RUB Buy |
|
Kventiax 100 mg film-coated tablets 60 pcs. 1150 RUB Buy |
|
Kventiax tablets p.p. 100mg 60 pcs. 1383 RUB Buy |
|
Kventiax SR 300 mg film-coated tablets of prolonged action 60 pcs. 1680 RUB Buy |
|
Kventiax 200 mg film-coated tablets 60 pcs. 2113 RUB Buy |
|
Kventiax tablets p.p. 200mg 60 pcs. RUB 2175 Buy |
|
Kventiax 300 mg film-coated tablets 60 pcs. RUB 2790 Buy |
|
Kventiax tablets p.p. 300mg 60 pcs. 2808 RUB Buy |
| See all offers from pharmacies |

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Information about the drug is generalized, provided for informational purposes only and does not replace the official instructions. Self-medication is hazardous to health!