- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
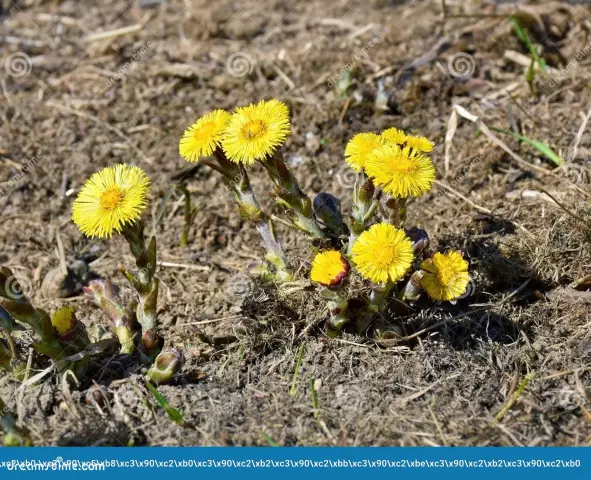
Mother and stepmother
Instructions for use:
- 1. Chemical composition
- 2. Useful properties
- 3. Indications for use
- 4. Contraindications
- 5. Home remedies

Mother-and-stepmother is a medicinal plant with anti-inflammatory, disinfectant and expectorant effects. Since ancient times it has been used as an antitussive agent.
Chemical composition
For medicinal purposes, inflorescences and leaves of coltsfoot are used. They differ somewhat in their composition.
The leaves contain the following substances that determine their beneficial properties: glycosides (tussilyagin and sitosterol), organic acids (malic, gallic and tartaric), carotenoids, tannin, mucus, tannins, inulin, saponins, flavonoids, dextrin, vitamin C, essential oils …
Inflorescences of coltsfoot are composed of: phytosterols, arnidol, firadiol, triterpene alcohols, carotenoids (taraxanthin), sterols (sitosterol, stigmasterol), rutin, heptacosan, tannins, complex carbohydrates.
Beneficial features
Mother-and-stepmother has long been known for her ability to alleviate coughs and increase the secretion of phlegm by stimulating the bronchial glands. It also has expectorant, anti-inflammatory, antiseptic properties, is capable of having a diaphoretic and antispasmodic effect. These properties make coltsfoot the number one medicinal plant in the treatment of broncho-pulmonary diseases.
Indications for use
Mother and stepmother is successfully used in the treatment of the following conditions and diseases:
- Whooping cough;
- Stomatitis;
- Laryngitis;
- Pharyngitis;
- Tracheitis;
- Acute and chronic bronchitis;
- Pneumonia;
- Bronchiectasis;
- Bronchial asthma;
- Pulmonary tuberculosis;
- Smokers' cough;
- ARI and ARVI, accompanied by cough, including influenza;
- Inflammatory diseases of the kidneys and bladder;
- Diathesis in children;
- Mastitis;
- Erysipelas;
- Hair loss of various etiologies;
- Abscesses, boils and other manifestations of purulent inflammation of the skin;
- Varicose veins in the legs;
- Gastritis;
- Enterocolitis;
- Lack of appetite.
Contraindications
Despite the extremely wide range of uses as a medicine, coltsfoot has some limitations. So, the plant and preparations from it are not recommended to be taken orally for more than 4 weeks, since in addition to useful substances, it contains some types of alkaloids that can accumulate in the body and, as a result, have a toxic effect.
Contraindications to the use of mother and stepmother are:
- Children under 2 years old;
- Pregnancy;
- Breast-feeding;
- Liver disease.
Home remedies from mother and stepmother
Homemade medicines from a mother-and-stepmother are not difficult to prepare. We offer you several recipes:
- Mother-and-stepmother juice with milk is a good remedy for bronchitis, bronchial asthma, smokers' coughs. For the medicine, take fresh, spring leaves of the mother-and-stepmother, using a juicer or manually, rubbing and squeezing through cheesecloth, squeeze out fresh juice - 2-3 teaspoons. Dissolve this amount in a glass of warm milk and drink immediately. Take once a day. This medicine is not stored, it must be prepared immediately before use.
- Cough tea. 1 teaspoon of dried flowers of mother-and-stepmother pour 250 ml of boiling water, leave for an hour. Strain, take 4 times a day, dividing the resulting amount of tea into 4 servings.
- External remedy for boils and boils. Grind a few fresh leaves of mother-and-stepmother, apply the resulting gruel directly to the sore spot. Apply several times a day until improvement occurs. Leaves of coltsfoot can simply be applied to wounds, abscesses and sores on the skin without rubbing, but in this case their effect is somewhat weaker.
Information about the drug is generalized, provided for informational purposes only and does not replace the official instructions. Self-medication is hazardous to health!