- Author Rachel Wainwright [email protected].
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Bimatan
Bimatan: instructions for use and reviews
- 1. Release form and composition
- 2. Pharmacological properties
- 3. Indications for use
- 4. Contraindications
- 5. Method of application and dosage
- 6. Side effects
- 7. Overdose
- 8. Special instructions
- 9. Application during pregnancy and lactation
- 10. Use in childhood
- 11. For violations of liver function
- 12. Drug interactions
- 13. Analogs
- 14. Terms and conditions of storage
- 15. Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
- 16. Reviews
- 17. Price in pharmacies
Latin name: Bimatan
ATX code: S01EE03
Active ingredient: bimatoprost (Bimatoprostum)
Manufacturer: Sentiss Pharma Pvt. Ltd. (Sentiss Pharma Pvt. Ltd.) (India)
Description and photo update: 2020-16-06
Prices in pharmacies: from 457 rubles.
Buy

Bimatan is an antiglaucoma drug, a synthetic analogue of prostaglandin F2-α.
Release form and composition
Dosage form - eye drops: colorless transparent liquid (in a cardboard box, 1 polyethylene bottle with a dropper stopper and a turquoise screw cap with first opening control, containing 2.5 ml, as well as instructions for using Bimatan).
Composition of 1 ml eye drops:
- active substance: bimatoprost - 0.3 mg;
- auxiliary components: water for injection, hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide, sodium hydrogen phosphate heptahydrate, citric acid monohydrate, sodium chloride, benzalkonium chloride.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Bimatoprost is one of the powerful ophthalmic antihypertensive agents. It is a synthetic analogue of prostamide, linked to prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α) at the structural level and does not act through its known receptors. The drug selectively mimics the effects of recently discovered biosynthesized substances - prostamides. However, the structure of the receptors of the latter has not yet been identified.
Due to an increase in the outflow of aqueous humor through the trabecular network and an increase in uveoscleral outflow, bimatoprost reduces intraocular pressure. This effect begins approximately 4 hours after its first application and lasts for at least 24 hours. The maximum effect is achieved after a period of 8 to 12 hours.
The available information on the effectiveness of the substance in the treatment of pigmentary and pseudoexfoliative glaucoma, as well as the experience of its use in the treatment of angle-closure glaucoma in patients who have previously received laser iridotomy, are limited.
According to the data of ongoing clinical studies, Bimatan does not have a significant effect on blood pressure and heart rate.
The safety and efficacy profile of bimatoprost in children and adolescents under the age of 18 has not been studied.
Pharmacokinetics
According to in vitro data, bimatoprost penetrates well into the cornea and sclera of humans. Its systemic exposure after instillation in adult patients is very small, no accumulation of the substance was noted. The maximum plasma concentration after the introduction of 1 drop of the drug into each eye once a day for 14 days was reached after 10 minutes. For 1.5 hours, this indicator was below the detection level (0.025 ng per 1 ml).
On average, the maximum plasma concentration and the area under the concentration-time curve of the substance from 0 to 24 hours are almost identical on days 7 and 14 (0.08 ng per 1 ml and 0.09 ng per 1 ml, respectively). This confirms that a stable drug level was achieved during the first 7 days of instillations.
Bimatoprost is characterized by a moderate distribution in body tissues. Its systemic equilibrium volume is 0.67 liters per kg. In human blood, it is mainly found in plasma and binds to its proteins at a level of 88%.
The drug reaches the systemic blood flow for the most part unchanged. Further, its oxidation, N-deethylation and glucuronization occurs with the formation of a number of metabolites.
Excretion of the substance mainly occurs through the kidneys. When administered intravenously to healthy adult volunteers, up to 25% of the dose was excreted from the body with feces, most (up to 67%) - with urine. The plasma half-life is approximately 45 minutes, the total clearance is 1.5 liters in 1 hour per 1 kg.
Indications for use
Bimatan eye drops are prescribed to reduce increased intraocular pressure in adult patients with ophthalmic hypertension and open-angle glaucoma (as monotherapy or in combination with β-blockers).
Contraindications
Absolute:
- age up to 18 years;
- pregnancy;
- period of breastfeeding;
- established hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Relative (the use of Bimatan requires special care and careful medical supervision):
- hepatic failure of moderate and severe degree;
- established risk factors for macular edema (for example, against the background of rupture of the posterior lens capsule, pseudophakia and aphakia);
- a history of severe eye infections (eg, caused by herpes simplex virus or iritis / uveitis);
- concomitant disturbances in the function of external respiration;
- heart block worse than first degree, uncontrolled congestive heart failure;
- a predisposition to low blood pressure or low heart rate;
- inflammatory pathologies of the organ of vision, narrow-angle, neovascular, congenital, inflammatory or angle-closure glaucoma;
- dry eye syndrome, corneal injury;
- combination therapy with several types of eye drops containing benzalkonium chloride.
Bimatan, instructions for use: method and dosage
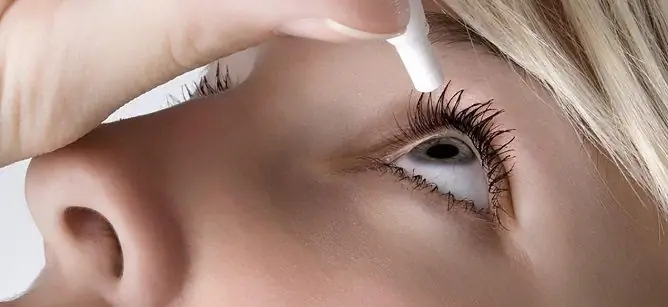
Bimatan eye drops are used by instillation into the conjunctival sac.
The drug is instilled once a day in the evening at a dose of 1 drop into the affected eye / eye. The recommended dose cannot be exceeded, since more frequent use can lead to a decrease in the hypotensive effect of the drug.
In patients with a history of mild liver dysfunctions, increased levels of aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase and / or bilirubin, no pathological effect of Bimatan on the functional state of the liver was observed for 24 months of therapy.
In cases of using eye drops as part of a combination treatment, it is required to observe an interval of 5 minutes between their instillation and the use of other drugs.
When skipping the next use of a drug, it is important to apply it as soon as possible in the recommended dose.
Side effects
Possible side effects of Bimatan [> 10% - very common; (> 1% and 0.1% and 0.01% and <0.1%) - rarely; <0.01% - very rare; frequency cannot be established from the available data - with an unspecified frequency]:
- nervous system: often - headache; infrequently - dizziness;
- organ of vision: very often - eyelash growth, itchy eyes, conjunctival injection; often - darkening of eyelashes, increased pigmentation of the iris, blurred vision, discharge from the eyes, lacrimation, photophobia, eye pain, dry eyes, foreign body sensation in the eye, conjunctival edema, asthenopia, decreased visual acuity, blepharitis, allergic conjunctivitis, eye irritation, burning in the eyes, corneal erosion, superficial punctate keratitis; infrequently - periorbital erythema, eyelid retraction, blepharospasm, iritis, cystic macular edema, uveitis, retinal hemorrhagic disorders; with an unknown frequency - enophthalmos;
- vessels: often - hypertension;
- skin and subcutaneous tissues: infrequently - hirsutism;
- general disorders and disorders at the injection site: infrequently - asthenia;
- laboratory and instrumental studies: often - deviation from the norm of biochemical parameters of liver function; very rarely - corneal calcification when using phosphate-containing eye drops against the background of concomitant significant damage to the cornea.
Overdose
With local application of Bimatan, no development of an overdose of bimatoprost was noted.
If intoxication is suspected, symptomatic and supportive treatment is recommended.
special instructions
Before starting therapy, the patient should be made aware of a possible increase in pigmentation of the iris, darkening of the eyelid skin and eyelash growth. Some of these phenomena can be permanent and can lead to differences in appearance between the eyes when only one eye is treated.
The change in the pigmentation of the iris may not be noticeable for several months or years because it is slow. Most often, the color change in the iris is permanent. To a greater extent, it is associated with an increase in the concentration of melanin in melanocytes than with an increase in the number of the latter. The long-term effects of increased iris pigmentation have not been established. In most cases, there is a spread of brown pigment from the area around the pupil to the root of the iris, causing the entire iris or parts of it to turn brownish.
Bimatan does not affect iris lentigo and nevi. In some patients, the pigmentation of the periorbital tissue is reversible.
Since there have been reports of the possibility of cystoid macular edema occurring during the period of use of drops (the frequency of this undesirable phenomenon is ≥ 1 / 1,000 to <1/100, infrequently), the drug for the treatment of persons with risk factors for macular edema should be used with caution.
Bimatan contains a preservative benzalkonium chloride, which can be absorbed by soft contact lenses. For this reason, discoloration of soft contact lenses and eye irritation can occur. Before instillation, it is important to remove contact lenses and put them back on no earlier than 15 minutes after the procedure. Benzalkonium chloride can also cause toxic ulcerative keratopathy and / or punctate keratopathy.
It is important to be careful when prescribing the drug in combination with several types of eye drops containing benzalkonium chloride, as well as with dry eye syndrome and corneal damage. Monitoring the state of the cornea in this group of patients is required under the condition of a long course of treatment with bimatoprost.
There have been reports of the risk of bacterial keratitis associated with the use of reusable eye drop vials.
Dropper bottles were unintentionally contaminated by persons with concomitant pathologies of the organ of vision. The likelihood of bacterial keratitis was higher in violation of the integrity of the corneal epithelium. Patients should be made aware of the need to avoid contact of the tip of the dropper bottle with the surface of the eye and other surfaces in order to avoid bacterial contamination of the substance and damage to the organ of vision.
Influence on the ability to drive vehicles and complex mechanisms
During the period of Bimatan therapy, undesirable phenomena may occur that affect the ability to drive vehicles, as well as perform other work associated with increased attention. In this regard, if after instillation of the drug there is a temporary blurred vision, before engaging in such activities, it is important to wait until the clarity of visual perception is restored.
Application during pregnancy and lactation
The use of Bimatan during pregnancy in the absence of strict indications is not recommended, since the results of clinical studies of its use in such cases are not available.
According to animal studies, reproductive toxicity of bimatoprost was noted when used in high doses for the mother's body, as well as its excretion into breast milk. It has not been established whether the drug is excreted in human breast milk. If necessary, its appointment during lactation, breastfeeding is stopped.
There is no information on the effect of Bimatan on fertility in women.
Pediatric use
Bimatan eye drops are contraindicated in children and adolescents under the age of 18, since the safety and efficacy profile has not been studied.
For violations of liver function
Hepatic insufficiency of moderate and severe severity is a relative contraindication to the use of Bimatan.
Drug interactions
Special studies of the interaction of bimatoprost with other drugs have not been conducted.
Since the systemic concentrations of the substance after topical use in ophthalmology in the human body are extremely low (<0.2 ng per 1 ml), no interactions are expected.
In clinical trials, eye drops were used in combination with several different β-blockers for topical use in ophthalmology, but no mutual influence of the drugs was noted. Combined treatment with bimatoprost with other antiglaucoma agents, in addition to ophthalmic β-blockers, has not been studied in the course of studies of the efficacy and safety of simultaneous therapy.
With the combined use of Bimatan with other analogs of prostaglandins in the treatment of ophthalmic hypertension or glaucoma, its hypotensive effect decreased.
Analogs
Bimatan's analogues are: Latisse, Bimoptik Rompharm, Bimikombi Antiglau ECO, Bimoptik Plus, Ganfort, Tizoptan, etc.
Terms and conditions of storage
Store at temperatures up to 25 ° C. Keep out of the reach of children.
The shelf life is 3 years.
After opening the bottle, eye drops should be used for 30 days (no more).
Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
Dispensed by prescription.
Reviews about Bimatan
There are few reviews about Bimatan, indicating its effectiveness when used to reduce intraocular pressure. But there are also frequent discussions about the use of the drug as a means to enhance growth and increase the density of eyelashes. In the instructions, these properties of the drug are described in the "Side effects" section. The girls claim that the eyelashes really grow and become thicker, but after using Bimatan, their original length and density return, and some complain of severe eyelash loss.
Doctors warn that this drug is a drug, so it should be used strictly according to medical indications, in accordance with the instructions. It can be used for a short time, as drops can affect eye pressure and impair vision. In addition, in some cases, Bimatan causes an irreversible discoloration of the iris of the eye, especially if it is initially light in color.
Price for Bimatan in pharmacies
The approximate price for Bimatan (1 bottle in the package containing 2.5 ml of eye drops) is 510 rubles.
Bimatan: prices in online pharmacies
|
Drug name Price Pharmacy |
|
Bimatan eye drops 0.03% fl. 2,5ml 457 r Buy |
|
Bimatan 0.03% drops for topical application 2.5 ml 1 pc. 458 r Buy |

Maria Kulkes Medical journalist About the author
Education: First Moscow State Medical University named after I. M. Sechenov, specialty "General Medicine".
Information about the drug is generalized, provided for informational purposes only and does not replace the official instructions. Self-medication is hazardous to health!