- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
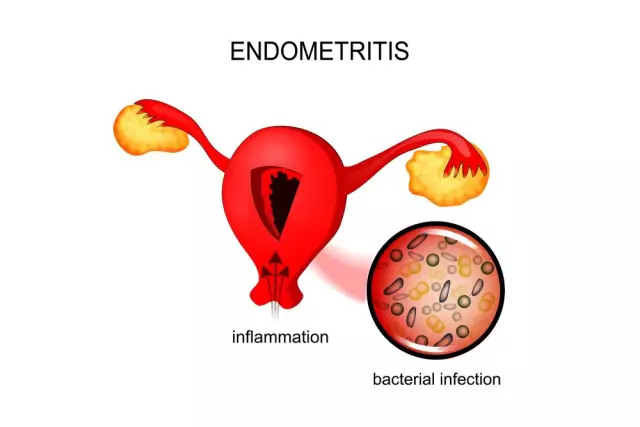
Endometritis
General characteristics of the disease
Endometritis is an inflammation of the lining of the inside of the uterus.

The factors that provoke the onset of endometritis include stress, vitamin deficiency, chronic diseases, intoxication and other phenomena that cause a decrease in immunity.
The probability of the appearance of the first symptoms of endometritis after trauma to the cervix during abortion, the introduction of an intrauterine device, diagnostic or therapeutic curettage or childbirth is high.
Acute endometritis
Acute endometritis develops as a result of the primary inflammatory process of the mucous epithelium of the uterus. It is caused by infection of the ascending type: through the broken cervical barrier deep into the uterus.
In acute endometritis, inflammation may spread to the muscular layer of the organ. In this case, the disease turns into a complicated form of acute endometritis - endomyometritis. In the most severe cases of the spread of infection to all layers of the walls of the uterus, panmetritis develops.
Chronic endometritis
Chronic endometritis most often occurs as a consequence of acute endometritis not cured in time. In about half of cases, childbirth complicated by deep ruptures of the cervix, without adequate follow-up treatment, ends with chronic endometritis.
Other possible causes of chronic endometritis are repeated curettage of the uterus, remnants of suture material after childbirth by caesarean section. Vaginal dysbiosis caused by an increase in the number of opportunistic bacteria in the vaginal environment significantly aggravates the course of chronic endometritis.
Endometritis symptoms
Acute endometritis begins with a sharp rise in temperature. Among the symptoms of acute endometritis, severe pain in the lower abdomen and a feeling of chills are also called. Signs of this type of endometritis include also abundant purulent or purulent-purulent vaginal discharge.

The duration of acute endometritis is 7-10 days. Without treatment, the disease turns into chronic endometritis or ends with generalization of the process:
- parametrite,
- peritonitis,
- thrombophlebitis of the pelvic veins,
- pelvic abscess
- or sepsis.
A relapse of the disease is characterized by the following signs of chronic endometritis: menstrual irregularities, pulling pains in the lower abdomen, abundant serous-purulent vaginal discharge.
In the history of patients with symptoms of chronic endometritis, spontaneous miscarriages are frequent. An increase in temperature does not apply to signs of chronic endometritis. The patient's state of health, as a rule, is not strongly disturbed.
Endometritis diagnostics
In the diagnosis of endometritis, an important role is played by the collection of anamnesis - the regularity of the menstrual cycle, the presence of intrauterine interventions in the patient's history, the use of intrauterine contraceptives, cases of unprotected sex with a non-permanent partner.
During a physical examination, the following signs of endometritis may be found:
- an increase in the size of the uterus,
- organ seal,
- special sensitivity of the lateral walls of the organ on palpation.
In laboratory blood tests of patients with symptoms of acute endometritis, leukocytosis, increased ESR levels and C-reactive protein are diagnosed, indicating inflammation in the body. Vaginal smear microscopy also plays an important role in the diagnosis of acute and chronic endometritis. To confirm the signs of endometritis, ultrasound of the pelvic organs and histological examination of scrapings of the endometrium of the uterus are additionally used.
Endometritis treatment
In the treatment of acute endometritis, the use of antibiotic therapy is mandatory, since the cause of the primary inflammation of the uterine mucosa in most cases of infectious etiology.
After the relief of the acute process, the treatment of endometritis is supplemented by the use of anti-inflammatory and physical therapy, fortifying vitamin preparations and immunomodulators. To prevent the exacerbation of the process, the patient is recommended to take oral contraceptives, at least for 3-5 menstrual cycles.

It is advisable to start treatment of chronic endometritis on the first day of the menstrual cycle. If the disease is no longer infectious, but functional in nature, caused by the remoteness of the process, cyclic hormonal therapy is used in the treatment of endometritis.
Surgical treatment of endometritis is used in case of complications of the disease with polyps and intrauterine contractions. Removal of polyps and curettage of the endometrium of the uterus with numerous signs of scarring contributes to tissue renewal, restoration of the menstrual cycle and safe bearing of the fetus.
Prevention of endometritis
Endometritis is a common cause of pregnancy-related problems in women. It can also lead to placental insufficiency and massive postpartum hemorrhage. For the prevention of endometritis, it is recommended to exclude casual sex without barrier methods of contraception.
It is advisable to use the same type of contraceptive for the prevention of pregnancy in order to prevent the use of medical abortion. Therefore, such gynecological diseases as endometritis, it is necessary to start treating as early as possible, and be sure to bring the treatment to the end.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!