- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Stomatitis

Stomatitis is a lesion of the oral mucosa.
General information about stomatitis
The name "stomatitis" comes from the Greek word "stoma", which means "oral cavity".
Stomatitis in some cases is an independent lesion, and in some it is one of the symptoms of another disease. For example, with diseases such as chickenpox, adenovirus infection and some blood diseases, damage to the oral mucosa should be regarded as one of the signs of the underlying disease.
Stomatitis is not a contagious disease, but with herpes, which is a highly contagious disease, mucosal lesions will be one of its symptoms.
Stomatitis is quite common, especially in childhood. It must be distinguished from leukoplakia, which is characterized by local thickening and keratinization of the epithelium.
Types of stomatitis
If the entire mucous membrane of the mouth is affected, then they speak of stomatitis. But if there is a defect in the mucous membrane only in some separate area, then the lesion is called by its name. For example, if the sore is on the tongue - glossitis, on the lip - cheilitis, in the palate - palatinitis.
The origin of stomatitis is viral, bacterial, fungal, traumatic, allergic. According to the characteristic symptoms, stomatitis is divided into catarrhal, ulcerative and aphthous.
Causes of stomatitis
There are many opinions about the mechanisms of development and causes of stomatitis, but until the end a single scheme of its origin (pathogenesis) remains unclear. The role of the immune system in the development of lesions is reliably known. When local immunity encounters unknown foreign substances, it cannot determine them, this provokes an attack of leukocytes (protective immune cells) and damage to the mucous membrane. With reduced immunity, stomatitis recurs regularly.
The appearance of stomatitis is caused by such factors as a violation in the oral cavity of the constant composition of the microflora, the activation of opportunistic fungi of the genus Candida, diseases of the digestive tract - gastritis, colitis, helminthic invasions (it is they that first of all provoke dysbiosis in the mouth).
Stomatitis in adults can be a symptom of general diseases of the body, for example, with cardiovascular problems or metabolic disorders.
Stomatitis is accompanied by burns, mechanical damage to the oral mucosa, dental problems (including tartar, dentures that do not fit in size).
Disease manifestations
Stomatitis in adults and children has an approximately similar picture, and the main thing in making this diagnosis is the patient's complaints and the appearance of changes in the oral cavity.
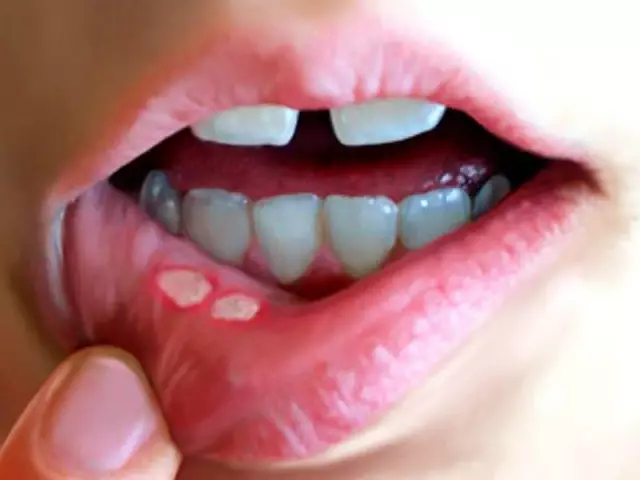
Pain and discomfort are the very first and unpleasant symptoms of stomatitis, they appear even before the redness visible to the eye during a catarrhal process or ulcers and aphthae in ulcerative and aphthous stomatitis. The pain is worse with eating, especially rough, too hot, hot, or sour.
The mucous membrane of the mouth becomes edematous, hyperemic. As a symptom of stomatitis, a whitish, yellowish or brownish coating may appear, sometimes with an unpleasant odor. This is due to a decrease in the protective and cleansing properties of saliva. The surface of the gums becomes loose, easily bruised and bleeding. Salivation increases - hypersalivation.
Ulcerative stomatitis in children is more severe than in adults. Most often, they have a transition to an ulcerative form from catarrhal, that is, if the treatment of stomatitis is not started on time. In this case, single or multiple defects of the mucous membrane in the form of ulcers can be found on the surface of the oral cavity.
If the edges of the ulcers are somewhat raised, with a bright red border, and a plaque has formed at the bottom of the ulcers, and the size of the lesion is not larger than a lenticular grain, then such stomatitis is called aphthous. Stomatitis in children can be accompanied by fever, severe local pain and impaired general well-being.
Stomatitis treatment

First of all, when treating stomatitis, it is necessary to eliminate the immediate cause that caused it, if possible, of course (for example, with tartar, diseased teeth). Only warm, mechanically sparing food can be eaten in order to injure the inflamed mucous membrane as little as possible.
The oral cavity is treated with antiseptics several times a day. As antiseptic agents in the treatment of stomatitis, you can use water infusions of chamomile, calendula in a warm form, 0.05% aqueous solution of chlorhexidine or miramistin or methylene blue, a pale pink solution of potassium permanganate.
Ulcers heal well if they are treated with a dilute solution of 3% hydrogen peroxide. In case of viral stomatitis in adults and children, interferon solutions can be applied topically up to 4-6 times a day. With stomatitis as a specific process (with syphilis, tuberculosis), the appointment of etiotropic antibacterial drugs is required.
With stomatitis in children, it is important to eliminate the pain factor. Therefore, they are often additionally prescribed local anesthetics (for example, Kamistad, Kalgel, Cholisal gels).
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!