- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Bronchitis without fever: symptoms in an adult and a child, causes, treatment
The content of the article:
- Symptoms of bronchitis without fever in adults and children
- Causes and risk factors
- How to treat bronchitis without fever
- Patient care recommendations
- Traditional methods of treating bronchitis
- Prevention
- Video
The question of whether there can be bronchitis without fever is of interest to many patients, since inflammation of the bronchial mucosa is one of the most common pathologies of the respiratory system. It can be difficult to identify acute bronchitis without an increase in body temperature, since a cough after an infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract (against which bronchitis often develops) often persists for another 1-1.5 weeks.
The course of bronchitis without fever, especially in children, often leads to the transition of the disease into a chronic form. The disease is especially dangerous for children under 2 years of age with reduced immunity. If you find symptoms of bronchitis without fever in children, you should consult a doctor immediately.
Acute bronchitis, not accompanied by an increase in temperature, is characteristic of debilitated patients
Symptoms of bronchitis without fever in adults and children
The main symptom of bronchitis without fever in a child and an adult is usually a chest cough, which at the onset of the disease is most often dry, and as the inflammation develops, the patient begins to sputum. Coughing fits are most severe in the morning, often accompanied by pain in the chest. Cough is aggravated by changes in temperature and / or humidity in the environment.
Bronchitis can occur both with a cough and (much less often) without it, which complicates the diagnosis.
It should be noted that bronchitis without fever is more common in adult practice than in children.
Bronchitis is manifested by rapid and more shallow breathing, which is characteristic of the onset of the inflammatory process in the bronchi. Patients with acute bronchitis have discomfort in the throat and along the trachea, nasal discharge, shortness of breath (especially with a deep breath), shortness of breath, headache, increasing weakness, lethargy. With obstructive bronchitis with respiratory failure, the patient has cyanosis of the face and neck.
During auscultation, hard breathing is determined, as well as dry wheezing. The radiograph shows an increase in the pulmonary pattern and / or expansion of the bronchial tree.
Launched acute bronchitis becomes a chronic form, in addition, bronchopneumonia, pneumonia, pulmonary inflammation, pulmonary emphysema, bronchial asthma, and cardiovascular disorders can develop against its background.
Causes and risk factors
Lack of temperature is most often observed in acute obstructive bronchitis of non-infectious etiology. Bronchitis often occurs without fever in immunocompromised patients. In pediatric practice, this form of the disease often develops in premature babies or in infants with perinatal heart or respiratory system disorders.
In some cases, cough is also absent in the clinical picture of bronchitis without fever. This may indicate an early stage of the disease, significant damage to the bronchioles, a non-standard course of the disease.
One of the leading risk factors for developing bronchitis without fever is the uncontrolled use of antibacterial drugs during the treatment of respiratory infections.
Bronchitis caused by microscopic fungi usually occurs without fever, but is rare. Usually, this form of the disease is diagnosed in debilitated patients, especially after treatment with antibacterial drugs.
How to treat bronchitis without fever
Treatment of bronchitis with normal body temperature in a patient practically does not differ from that proceeding with an increase in temperature. The only difference is that antipyretic medications are not prescribed.
Treatment of bronchitis without fever in children under 3 years old is usually recommended to be carried out in a hospital setting, where it is possible to provide the child with emergency assistance in case of sudden suffocation. In other cases, treatment is carried out at home.
Whether antibiotics are needed for bronchitis depends on the form of the disease. Antibacterial drugs are prescribed for infectious bronchitis of bacterial etiology or with the addition of a secondary bacterial infection.
With the development of bronchitis against the background of viral diseases, antiviral drugs may be prescribed to patients. In some cases, antihistamines are required to prevent the transition of the disease to an obstructive form. If it is difficult to discharge sputum, mucolytics are prescribed, drugs that facilitate the discharge of sputum.
A therapeutic massage has a good therapeutic effect for bronchitis.
In some cases, physiotherapy and massage are indicated.
Inhalations are effective, which promote sputum discharge and speedy tissue regeneration. For this purpose, solutions of anti-inflammatory and mucolytic drugs, salt, soda solutions, essential oils (in the absence of allergies), decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs are used.
Inhalation is recommended for 10-15 minutes 1-3 times a day, but no more than 5 times. It is important to note that hot steam inhalation is contraindicated for children; the procedure is carried out using a nebulizer.
Patient care recommendations
In the first week of the disease, it is recommended to stay at home, to observe bed or semi-bed rest. After that, with normal health, a person can go outside, avoiding, however, excessive physical activity, since with bronchitis it is recommended to spend more time in the fresh air.
People with bronchitis should drink more fluids than usual. An adult patient is recommended to drink up to 2-3 liters of water per day. Berry teas, mint, lime tea, juices are useful. During illness, it is advisable to limit the use of drinks containing caffeine. The patient needs to eat more vegetables and fruits, dairy products, as well as cereals and broths. Spicy and salty foods are excluded from the diet.
The room in which the patient with bronchitis is located must be well ventilated. Dr. Komarovsky recommends maintaining the room humidity at least 60% and making sure that the patient does not overheat (the air must be cool).
Patients who have undergone bronchitis are shown sanatorium treatment, a visit to salt mines.
Traditional methods of treating bronchitis
With bronchitis, you can make a compress under a scapula of honey, vegetable oil, vodka (1 tablespoon each) and mustard powder (4 tablespoons), while placing the compress on the kidney area should be avoided. Keep the compress for about 30 minutes.
From herbal remedies that have an expectorant effect, breast fees are effective, which are sold ready-made in the pharmacy. In addition, you can independently prepare an infusion from a mixture of marshmallow, wild rosemary and licorice root, taken in 1 part, and 2 parts of coltsfoot, which is taken 3 times a day for ¼ glass.
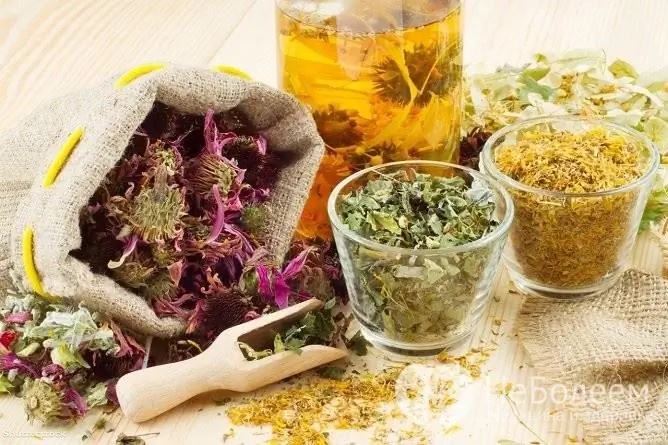

Herbs can be used to relieve bronchitis symptoms
Prevention
For the purpose of prevention, it is recommended to treat acute respiratory infections in a timely manner, increase immunity, eat right, lead an active lifestyle, avoid physical and mental overstrain, hypothermia of the body, observe the rules of personal hygiene, especially with regard to hygienic treatment of hands, carry out all the necessary vaccinations in accordance with the official vaccination calendar … Quitting smoking and alcohol abuse is very important.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.