- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Paraovarian cyst
The content of the article:
-
How does a paraovarian cyst arise?
- Formation mechanism
- Development reasons
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
-
Treatment
- Laparoscopic method
- Laparotomic operative access
- Forecast
- The presence of paraovarian education and pregnancy
- Video
A benign cavity formation that develops from the periobital appendage and has an embryonic origin is called a paraovarian cyst. It is often asymptomatic and is found on pelvic ultrasound. Complaints arise with a significant size of the neoplasm and the development of complications. The paraovarian ovarian cyst does not dissolve on its own, the treatment is operative.
How does a paraovarian cyst arise?
Both men and women have organs that are laid during embryonic development but do not develop fully. They are rudimentary, or have lost their meaning. In women, near each ovary, both on the right and on the left, in the wide ligament of the uterus there is a formation related to the rudimentary organs - this is the perio-ovarian appendage, or paraophoron. It is represented by a network of thin, disconnected tubules that end blindly. It is from the tubules of the paraophoron that when the processes of embryonic development are disturbed, paraovarian cysts arise.
Formation mechanism
The growth of true cystic tumors occurs due to the division of epithelial cells that line the inner surface of their capsule. These cells are capable of pathological degeneration. The paraophoron cyst is not true, since it is formed in a completely different way: the tubules produce fluid that has nowhere to go, it accumulates, forming a cavity. The increase in volume occurs due to the stretching of the walls by the liquid content. As a result of this mechanism of occurrence, education does not become malignant.
Development reasons
The basis for the appearance of cystic formation of paraophoron is a violation of tissue differentiation at the stage of embryonic development. Contribute to its occurrence:
- menstrual irregularities;
- premature puberty;
- endocrinological diseases (hyperfunction, hypofunction of the thyroid gland, etc.);
- chronic inflammatory processes of the female genital area;
- uncontrolled intake of hormonal contraception;
- spontaneous miscarriages;
- artificial termination of pregnancy;
- prolonged sunbathing, passion for artificial tanning;
- excessive thermal procedures (hot baths, warming applications);
- sudden weight loss;
- obesity.
Symptoms
Cavity formation can be completely asymptomatic and detected by a gynecologist during routine preventive examinations or ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs for another reason. Clinical manifestations are usually due to the large size of the formation and complications in the form of:
- twisting of the legs;
- rupture of the capsule;
- suppuration.
In this case, complaints come to the fore, signaling a catastrophe in the abdominal cavity. These include:
- cramping abdominal pain;
- weakness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness;
- feeling of fear;
- chills;
- drop in blood pressure;
- decreased intestinal peristalsis;
- hyperthermia.
When the formation of the perio-ovarian appendage reaches a significant size, and in some cases its diameter can reach 20 centimeters, the symptoms of compression of neighboring organs are in the foreground.
| Compressed organ | Clinical manifestations |
| Bladder, ureter | Frequent urination, often accompanied by pains of varying intensity, false desires, a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. |
| Colon | Bloating, discomfort, pain during bowel movements, a tendency to constipation, or increased stool frequency. |
| Ovary | Pain in the right or left iliac region, depending on the localization of the formation, often aggravated by intercourse, physical exertion; violation of the rhythm of the menstrual cycle. |
The cavity formation of the perio-ovarian appendage does not respond to fluctuations in the level of sex hormones, its characteristic feature is the absence of dependence of the intensity of pain on the phase of the menstrual cycle.
Diagnostics
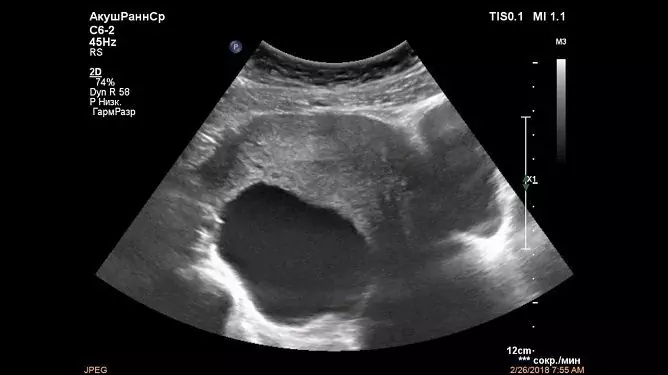
A doctor can detect a cyst of the perioral appendage during a gynecological examination: a rounded formation of a dense elastic consistency is determined along the edge of the uterus or above it, limitedly displaceable, often painless. But the final diagnosis is established after an ultrasound scan. Modern devices make it possible to obtain a three-dimensional image and demonstrate it to the patient both on the screen and in the form of a photo handed out to the hands along with the conclusion.
In ultrasound examination, the paraovarial cyst usually looks like a single-chamber, round or oval, anechoic thin-walled formation, enclosed between the leaves of the wide ligament of the uterus. Its size varies from a few millimeters to 15-20 centimeters. Visual identification of a separate ovary is a characteristic feature of the pathology. It is often possible to separate the cyst from the genital gland during an ultrasound scan using the device's sensor.
There are no specific echoes that distinguish the cyst of the peri-ovarian appendage from other tumor-like formations of the female genital glands. It is the presence of an ovary adjacent to the surface of the cavity formation that is considered a diagnostic sign when establishing the final diagnosis. In other cysts, it is not separately visualized.

Paraovarial cystic formation is well visualized on ultrasound
Treatment
If there are no complaints in the presence of a cavity formation of the paraophoron, and its size does not exceed two centimeters, then dynamic observation is possible. In the case of cyst growth, it is necessary to resort to surgery, since the formations of paraovarian origin do not dissolve on their own, and it makes no sense to treat them conservatively.
Laparoscopic method
In women of childbearing age, removal of the cyst by laparoscopy is optimal. This type of surgical treatment is gentle. When using it, the trauma of the anterior abdominal wall is minimal, the period of postoperative rehabilitation is short, and the ability to work is restored quickly.
During the operation, the ovary and fallopian tube on the side of the lesion are always tried to be preserved, and the scope of the intervention is limited by the removal of the cavity formation. If the operation is performed as planned, and not for torsion or suppuration of the paraovarian cyst, then this is technically possible. The fallopian tube is able to return to its original shape, even with significant deformation and elongation. The good retraction, or contractile ability of its muscle layer allows this to be done. This tactic helps to preserve the menstrual and reproductive function of patients.
Attention! Photo of shocking content.
Click on the link to view.
Laparotomic operative access
If during laparoscopy an optical system is introduced through small incisions into the abdominal cavity, allowing to display the "picture" on a large screen, and special instruments, controlling which, the surgeon performs the necessary manipulations, then with laparotomy the incision of the anterior abdominal wall is more significant. This access is used in cases of large cysts and their complicated course.
This technique expands the capabilities of the operating physician during the examination and revision of the pelvic organs, allows for a thorough sanitation of the abdominal cavity, and helps to avoid difficulties during the removal of cavity formation and tissue suturing.
Forecast
Removal of the cyst of the perio-ovarian appendage provides a favorable prognosis. During surgical treatment, the tubules of the paraophoron, which are the basis for the emergence of cavity formation, are removed along with it, which means that the possibility of relapse is excluded.
The rhythm of the menstrual cycle does not change: the expected menstrual bleeding occurs on time, since the sex gland on the affected side remains. Only in rare cases, with significant volumes of cysts, complicated by suppuration, twisting of the legs with tissue necrosis, this cannot be done.
The presence of paraovarian education and pregnancy
In the presence of cystic formation of paraophoron, it is necessary to decide what to do with it, and only then plan a pregnancy. If the cyst is 1-2 cm in size, it is possible not to perform the operation, if it is larger, laparotomy is indicated. It is better to plan conception no earlier than 3 months after surgery.
Detection of a paraophoron cyst in a pregnant woman is not a contraindication to gestation. It is necessary to regularly visit the antenatal clinic and adhere to the recommendations of the obstetrician-gynecologist.
The small diameter, the lack of growth of cavity formation allow us to limit ourselves to ultrasound control during pregnancy and with the exception of:
- excessive physical exertion;
- sexual intercourse in the presence of discomfort, pain during or after intimacy;
- thermal procedures (saunas, hot baths, etc.).
It is necessary to observe the mode of work and rest, wear a bandage in late gestation.
The rapid growth of the cyst, the development of complications are not compatible with conservative tactics. Modern technologies allow operations to be performed without disrupting the course of pregnancy.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!