- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Lymphoma
Brief description of the disease

Lymphoma is a malignant disease of the human lymphatic system. Lymphoma is characterized by the presence of tumors in the lymphatic system or in internal organs.
Lymphoma symptoms
Usually an early symptom of lymphoma is swollen lymph nodes in the armpits, groin, or neck. The nodes do not shrink over time and do not respond to antibiotic treatment. Lymph nodes are not painful. If the internal organs (liver, spleen) are enlarged, there may be distension in the abdomen, respiratory failure, pain in the lower half of the back.
Also, symptoms of lymphoma are weakness, sweating, severe fever, susceptibility to infectious diseases, indigestion, and weight loss.
Types of lymphomas
There are two groups of tumors: Hodgkin's lymphoma and non-Hodgin's lymphomas.
Hodgkin's lymphoma is characterized by the presence in the body of a special type of cells, which are also called Sternberg-Read cells. These cells can be identified by examining the lymphoid tissue under a microscope. Treating Hodgkin's lymphoma is different from treating non-Hodgkin's lymphomas, so getting it right is essential.
Hodgkin's lymphoma is most common at a young age. Until now, the exact cause of the disease has not been identified.
Risk factors for the development of Hodgkin's lymphoma is a decrease in immunity, infection with the Epstein-Barr virus, which causes infectious mononucleosis.
The main symptom of Hodgkin's lymphoma is swollen lymph nodes in the groin, neck, and armpits. In addition, there is a high fever, night sweating, cough, weight loss, itching, and fatigue.
Non-Hodgins lymphomas
Non-Hodgins' lymphomas include a fairly large group of lymphomas. They have subspecies that differ in the course of the disease and prognosis.
Indolent lymphomas are characterized by a long course and a favorable prognosis. These types of tumors do not require treatment, but require constant monitoring by a doctor.
Aggressive lymphomas are the exact opposite of indolent lymphomas. This type of tumor requires immediate treatment due to the rapid progression and increasing symptoms.
Extranodal lymphomas are characterized by the development of the disease not in the lymph nodes, but in the internal organs: intestines, spleen, lungs, stomach, and brain.
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma accounts for 30-40% of all non-Hodginian lymphomas. Large cell lymphoma is most common in older people, but children can also. The main symptom of large cell lymphoma is the rapid growth of the tumor. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is an aggressive form of lymphoma and requires immediate treatment.
Classification of lymphomas
The classification of lymphomas is quite extensive and includes a large number of types. All lymphomas can be conditionally divided depending on the following factors:
- appearance;
- mutations;
- grouping of cells: some lymphomas form clusters - groups of cells, others are scattered around the lymph node or organs of the body;
- the type of cells that caused the tumor;
- the type of protein on the surface of the lymphoma cell;
- which organ is affected by lymphoma.
Stages of lymphoma
There are four stages of lymphoma.
The first stage is characterized by damage to one area of the lymph nodes.
The second stage is characterized by lesions of two or more areas on one side of the diaphragm.
The third stage is characterized by damage to the lymph nodes on both sides of the diaphragm.
The fourth stage is characterized by the generalization of the process.
Diagnosing lymphoma
Various methods are used to diagnose lymphoma. The main diagnostic method for lymphoma is biopsy. This method allows you to determine the presence of tumor cells in the tissue.
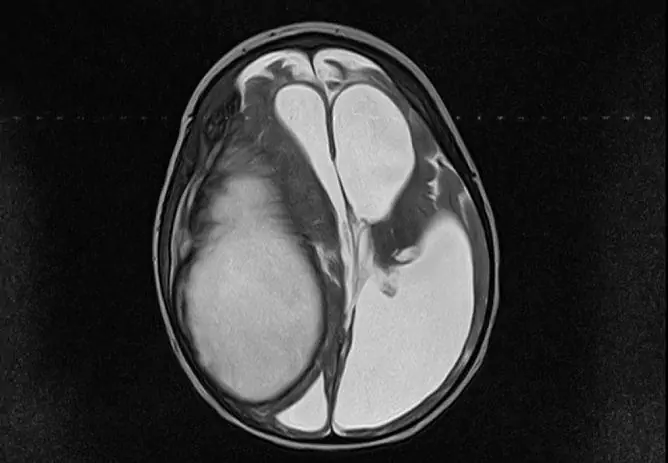
In addition, X-ray, CT or MRI are used, which allow not only to identify the presence of a tumor, but also to determine the stage of lymphoma.
A bone marrow test is also done to determine the presence of lymphoma cells in the bone tissue.
Lymphoma treatment

Treatment for lymphoma depends on the stage, shape, and symptoms of the disease. Indolent forms of lymphoma in the absence of symptoms and development of the disease do not require treatment. But when signs of growth appear, treatment for lymphoma begins. If the tumor is localized, radiotherapy is used. With a more severe and extensive course of the disease, chemotherapy is used.
Treating aggressive lymphomas requires a quick response to the situation. The most effective treatment for this type of lymphoma is chemotherapy with several courses, and if it fails, bone marrow or stem cell transplantation. Among the drugs for the treatment of lymphoma in an aggressive form, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, rituximab, chlorbutin and others are prescribed. The main goal of treating aggressive lymphoma is to improve the patient's well-being, since a complete cure is unlikely.
Lymphoma prognosis
The prognosis for Hodgkin's lymphoma is good. Modern treatments for lymphomas have been shown to have good results. The five-year survival rate after treatment for Hodgkin's lymphoma is 80 to 90%.
The prognosis of non-Hodginsky lymphomas with timely initiation of treatment and the use of modern methods and drugs is about 55% for adults and 80% for children.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!