- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
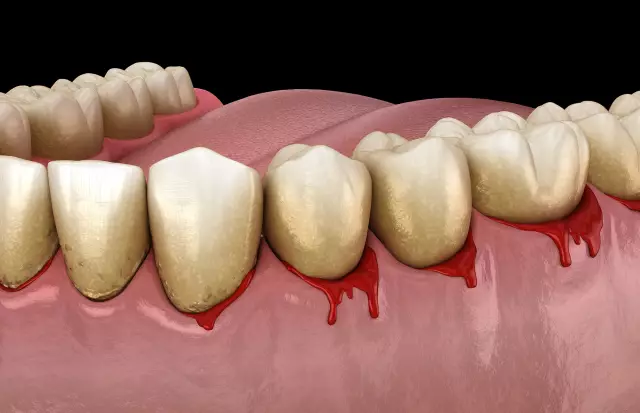
Bleeding
Bleeding is the most dangerous post-traumatic complication that threatens the life of the affected person. The degree of possible risk depends on the specific characteristics and location of the damaged vessels.
Types of bleeding

There is the following classification of types of bleeding:
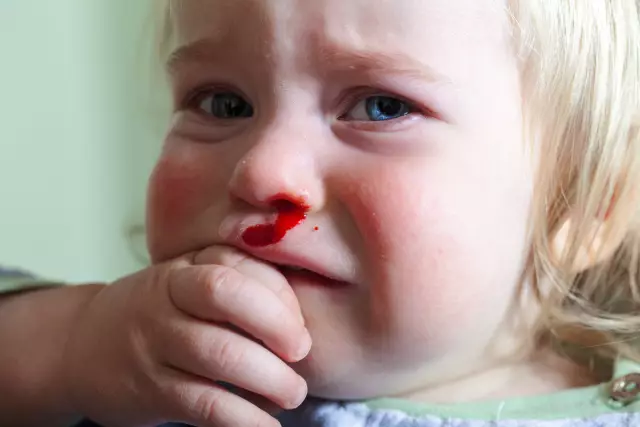
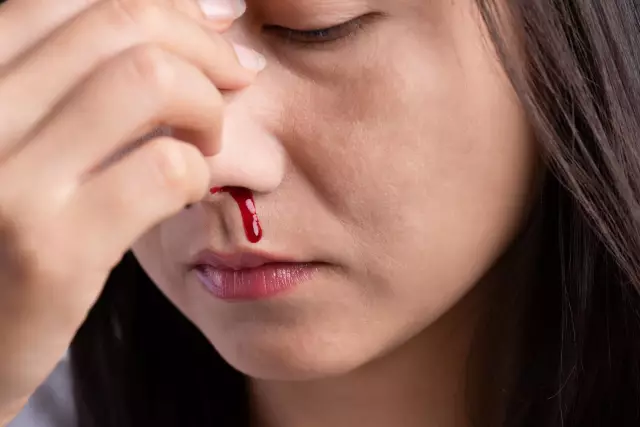
- Capillary bleeding. This type of bleeding occurs when the smallest vessels are injured in the mucous membranes, muscle tissues, and skin. Signs of bleeding from the capillaries are: a dark red color of blood, bleeding in a small trickle (with superficial cuts) or even blood flow over the entire surface of the wound (with abrasions). Capillary bleeding extremely rarely threatens the life and health of the affected person (if there is no hemophilia disease and blood clotting problems) and, as a rule, stops on its own.
- Venous bleeding. The main symptom of bleeding from a vein is a slow but continuous bleeding from the wound. The blood is dark red in color. In case of venous bleeding of significant strength, to prevent the loss of a large amount of blood, it is urgent to squeeze the damaged vessel using any available means (even with a finger).
- Parenchymal bleeding. Refers to internal bleeding. It is typical for wounds and injuries of the lungs, liver, spleen and other internal organs. With this type, blood of various colors (depending on which internal organ is damaged) may leak - dark red and bright scarlet. When blood comes out, it appears evenly over the entire wound surface. The most dangerous option is when parenchymal bleeding is hidden. The patient runs the risk of losing a lot of blood without waiting for first aid, because diagnosis of internal bleeding is extremely difficult.
- Arterial bleeding. A characteristic sign of bleeding from the arteries is a pulsating jet outflow of blood from the wound, the color of the blood has a bright scarlet hue. This species poses a particular danger to the life of the victim, because rapidly leads to the onset of complete exsanguination of the body. The development of acute anemia with arterial bleeding is accompanied by the following, the most obvious, signs: a drop in pulse and blood pressure, progressive pallor of the skin and mucous membranes, nausea, vomiting, darkening of the eyes, dizziness, loss of consciousness.
- Mixed (combined) bleeding - occurs with extensive trauma and combines various types of bleeding described in the previous paragraphs.
Bleeding treatment
First aid measures for bleeding should be initiated as soon as possible after injury. They consist primarily in stopping bleeding and preventing significant blood loss. If we are talking about arterial bleeding, the necessary measures to stop the bleeding must be taken immediately, since with this type of bleeding for a short period of time, a significant volume of blood flows from the wound injury. Rapid and sudden blood loss (more than two liters) can lead to death of the victim, especially if bleeding is combined with combined traumatic injuries.
For obvious reasons, first aid for bleeding is usually performed outside the walls of a medical facility. Therefore, this procedure is temporary, and consists in stopping bleeding for the speedy transportation of the injured person to the conditions of a medical hospital.

Ways to temporarily stop bleeding:
- Pressure bandage. Used to press the immediate bleeding site. A sterile gauze bandage is applied to the wound surface (if not, a piece of any pure natural fabric) and bandaged tightly (in the absence of material for bandaging, simply press the bandage to the wound with your hand). Applied for capillary, venous and mixed bleeding of moderate intensity.
- With insignificant bleeding in case of wound injuries of the feet, lower leg, fingers, etc. use the method of giving the injured limb a raised position. It is good to combine this method with applying a pressure bandage.
- In the case of arterial bleeding and the need to immediately stop bleeding (when there is no time to search for suitable means), use the method of pressing the bleeding artery with a finger. The arteries are pressed at specific anatomical points where they can be pressed tightly against the bones and thus temporarily stop bleeding.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!