- Author Rachel Wainwright [email protected].
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
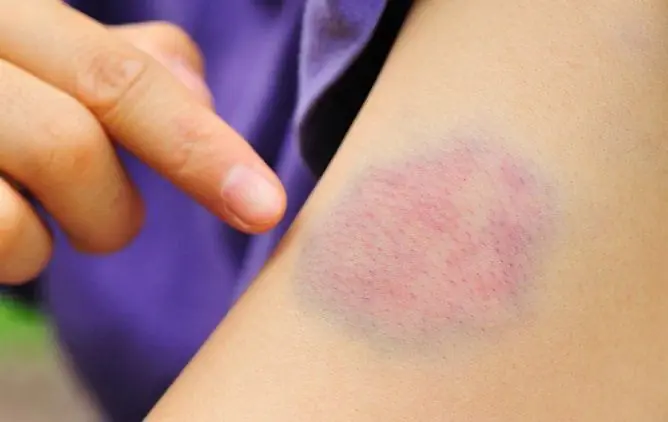
Hematomas

As a result of internal bleeding in the tissues of organs or muscles, cavities filled with blood are formed in some cases. In medicine, this phenomenon is called hematomas, and it actually has little to do with ordinary superficial bruising. This fact is connected with the fact that complications arising after hematomas (depending on the place of their localization) can be very serious and rather unpredictable. Regularly occurring extensive hematomas, formed even as a result of minor blows and bruises, can indicate, for example, such serious diseases as vascular atherosclerosis or hemophilia. Therefore, it is extremely important not to leave constantly appearing hematomas without proper attention and to have time to seek qualified medical help in time to establish the exact cause and treatment.
Distinguishing a hematoma from an ordinary bruise is quite simple:
- in the area of hematoma formation, there is a sharp soreness;
- a tumor at the site of the injury;
- local temperature rise (skin surface is hot to the touch);
- limitation of mobility and normal muscle function.
Causes of hematomas
The causes of hematomas most often include traumatic effects on soft tissues - bruises, blows, pinching, squeezing, etc. The main mechanism for the formation of hematomas lies in the ruptures of the blood vessels. The size of the hematoma, the severity of its condition and the duration of treatment are in direct proportion to the number of damaged vessels, their size and location.
In this regard, experts subdivide hematomas into subcutaneous and formed on the internal organs. In the latter case, the degree of damage, the potential danger to the patient's condition and the appointment of competent treatment for hematoma are determined exclusively in a medical hospital. The need for a compulsory visit to a medical institution is due to the fact that the accumulation of blood in the organs responsible for the life-supporting systems of the body, for example, with a hematoma of the brain, in a short time can lead to complete disability of the patient or even death.
Types of hematomas
The most dangerous hematomas include the following types:
- hematoma during pregnancy. An increasingly common pathology during childbearing is retrochorial hematoma. A deviation, which is quite dangerous for the life of the fetus and the mother, arises as a result of the detachment of the ovum from the chorion of the placenta. At the site of detachment, nutrition of the ovum stops and a hematoma is formed, sometimes of very large sizes. The consequence of retrochorial hematoma during pregnancy can be spontaneous abortion, frozen pregnancy, fetal hypoxia, intrauterine growth retardation and other pathologies.
- hematoma of the brain. Most often it occurs as a result of traumatic impact - impact or fall. The most common are the frontal and temporal hematomas of the brain. To confirm the diagnosis, the patient is prescribed a tomographic brain examination.
- epidural hematoma. This type of hematoma is an accumulation of blood clots in the epidural space (under the cranial surface).

- subdural hematoma. Formed in the space between the arachnoid and dura mater of the brain. It is considered the most dangerous type of hematoma, due to the fact that it almost always leads to abnormalities in brain activity. It usually occurs in patients over sixty years of age.
Symptoms of hematomas
Clearly diagnosed symptoms associated with hematomas include:
- soreness;
- the presence of limited swelling in the area of injury;
- change in the color of the skin from red-purple to green-yellow;
- with internal hematomas, characteristic symptoms are signs of compression of internal organs.
Hematoma treatment
The need and choice of tactics for treating hematomas is determined by specialists and primarily depends on their type. But if you are absolutely sure that the resulting hematoma is superficial, and you can cope with its treatment yourself, then you can recommend using the following remedies for hematomas.
In case of a hematoma in the face of the head, it is necessary to apply a cold compress (preferably ice) to the damaged area as soon as possible. As a result of exposure to cold, a sharp narrowing of the blood vessels will occur, and the hematoma will stop growing in size.
For an injury to a limb, the best remedy for hematoma is to apply a tight, pressure bandage. In this case, you need to be especially attentive to your condition, monitor your body temperature and general sensations, because it is highly likely that the process of resorption of the blood clot will not proceed actively enough, suppuration may occur in the area of the hematoma and then urgent medical attention will be required.
At the slightest suspicion of the occurrence of a brain hematoma, as well as subdural, epidural or retrochorial hematomas, the possibility of self-medication is completely excluded. The patient must be urgently hospitalized in a hospital for the necessary diagnostic procedures for the presence of a hematoma of the brain and to provide him with qualified assistance.
Folk remedies for hematomas

For traumatic injuries of small sizes, you can use the following recipes for folk remedies for hematomas:
- vodka compress (soak a gauze swab with vodka and put on the hematoma, wrap it in polyethylene, it is best to use it at night);
- salt dressings (dissolve two tablespoons of salt in 100 ml of water, soak a clean cloth made of natural fibers with the resulting solution, strengthen the salt lotion at the site of the hematoma with an elastic bandage);
- a compress from a mixture of vodka with vinegar (mix 100 ml of vodka and 100 ml of diluted table vinegar with 500 ml of cold boiled water, soak a tissue bandage with the resulting solution and apply it to the area of injury);
- a mixture of radish juice and mustard powder (mix the ingredients until gruel is obtained, apply on the hematoma and hold for a while, until a tolerable burning sensation is felt, then rinse with water at room temperature, for the most effective result - this compress is recommended to be applied daily).
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!