- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
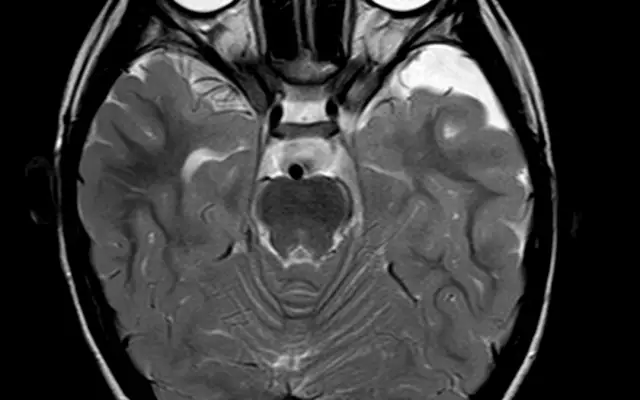
Arachnoid cyst

A brain cyst is a hollow pathological formation filled with a fluid similar in composition to the cerebrospinal fluid, which has different localization in the brain. There are two main types of brain cysts: arachnoid, retrocerebellar cysts.
An arachnoid cyst of the brain is a benign, hollow formation filled with fluid that forms on the surface of the brain in the region of its arachnoid (arachnoid) membranes.
The arachnoid meninges are one of the three meninges located between the superficial dura mater and the deep pia mater.
The walls of an arachnoid cyst are formed either by cells of the arachnoid membrane of the brain (primary cyst) or cicatricial collagen (secondary cyst). An arachnoid cyst can be of two types:
- Primary or congenital arachnoid cyst is a consequence of abnormalities in the development of the membranes of the brain in the fetus as a result of exposure to physical and chemical factors (drugs, radiation exposure, toxic agents);
- A secondary or acquired arachnoid cyst is a consequence of various diseases (meningitis, agenesis of the corpus callosum) or a complication after injuries, surgery (bruises, concussions, mechanical damage to the outer layers of the brain).
In most cases, the development of an arachnoid cyst is asymptomatic. Pronounced neurological symptoms are present only in 20% of cases.
Among the factors affecting the appearance and growth of an arachnoid cyst are:
- Inflammatory process of the meninges (virus, infection, arachnoiditis);
- An increase in fluid pressure inside the cystic formation;
- Concussion or any other trauma to the brain in a patient with a pre-existing arachnoid cyst.
Symptoms of arachnoid retrocerebellar cyst
In most cases, brain cysts (arachnoid, retrocerebellar cysts) are asymptomatic. These neoplasms are detected during the next examination of the patient or during the diagnosis of neurological diseases with similar symptoms. Symptoms of an arachnoid cyst are nonspecific. The severity of the symptoms of an arachnoid, retrocerebellar cyst depends on the location and size of the formation. In most patients, cerebral symptoms are observed, associated with compression of certain parts of the brain. It is extremely rare that focal symptoms are observed due to the formation of a hygroma, rupture of the arachnoid cyst.
The main symptoms of an arachnoid, retrocerebellar cyst:
- Dizziness not due to other factors (fatigue, anemia, medication, pregnancy in women);
- Nausea, vomiting, not caused by other factors (taking medications, poisoning, other diseases);
- Hallucinations, mental disorders;
- Convulsions;
- Loss of consciousness;
- Feelings of numbness in the limbs, hemiparesis;
- Headaches, lack of coordination;
- Feeling of throbbing, fullness in the head;
- Hearing and vision impairment;
- Clear recognition of tinnitus while preserving hearing;
- Feeling of heaviness in the head;
- Increased painful sensations when moving the head.
It should be noted that with a secondary type of arachnoid cyst, the clinical picture can be supplemented by symptoms of the underlying disease or trauma, which is the root cause of the formation of the cystic cavity.
Diagnostics of the arachnoid cerebrospinal fluid cyst
Various methods are used to diagnose arachnoid CSF cysts (CSF-filled cysts). The main ones among them are magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography to detect cystic formation, determine its localization, size. Intravenous administration of contrast makes it possible to differentiate the arachnoid CSF cyst from the tumor (the tumor accumulates contrast, the cyst does not).
It should be remembered that an arachnoid cyst is more often the result of another neurological disease or a dysfunction of any organ systems. To identify the root causes of an arachnoid cyst, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- Blood tests to detect viruses, infections, autoimmune diseases;
- Blood tests for clotting and cholesterol levels;
- Doppler study allows you to detect a violation of the patency of blood vessels, as a result of which a lack of cerebral blood supply develops;
- Blood pressure monitoring, recording pressure fluctuations per day;
- Heart research.

Accurate identification of the causes of the development of an arachnoid cyst allows you to choose the optimal treatment for cystic formation and minimize the risk of recurrence.
Arachnoid cyst treatment
According to the dynamics of development of arachnoid cysts, there are frozen cystic formations and progressive cysts. As a rule, frozen formations do not cause painful sensations to the patient, do not pose a risk to normal brain activity. In this case, treatment of the arachnoid cyst is not required. With frozen forms of cysts, diagnostics and treatment are aimed at identifying the root causes of cyst formation, as well as eliminating and preventing factors contributing to the formation of new cysts.
With a progressive type of cystic formations, the treatment of an arachnoid cyst involves a set of measures aimed at identifying and eliminating the causes of the cyst, as well as the direct removal of the cyst itself.
Medical treatment of an arachnoid cyst is aimed at eliminating inflammatory processes, normalizing cerebral blood supply, and restoring damaged brain cells.
In case of ineffectiveness or low efficiency of conservative methods of treatment of arachnoid cysts, radical methods are used. Indications for surgery are:
- Risk of rupture of the arachnoid cyst;
- Disorders of the mental state of the patient with increasing frequency of convulsive and epileptic seizures;
- Increased intracranial pressure;
- Strengthening focal symptoms.
The main methods of surgical treatment of an arachnoid cyst are:
- Drainage - removal of fluid from the cavity by needle aspiration;
- Shunting - creating a drainage for the outflow of fluid;
- Fenestration is the excision of a cyst.
Arachnoid cyst: consequences, prognosis, complications
With timely diagnosis and treatment of the arachnoid cyst, the prognosis is very favorable. The main risks associated with the development of an arachnoid cyst are an increase in the compressive effect of the cyst body on the brain centers, resulting in impaired body functions, as well as rupture of the cyst. After removal of the arachnoid cyst, the consequences can be impaired hearing and vision, speech function. If an arachnoid cyst is not diagnosed in time, the consequences can be extremely dangerous (hydrocephalus, cerebral hernia, death).
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!