- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Bartholin gland cyst
The content of the article:
-
Formation mechanism
Why is a cyst formed?
- Bartholin gland cyst symptoms
- Diagnostic methods
- Complications and consequences
-
How to treat
- Bartholin gland cyst: treatment without surgery
- Surgical intervention
- Video
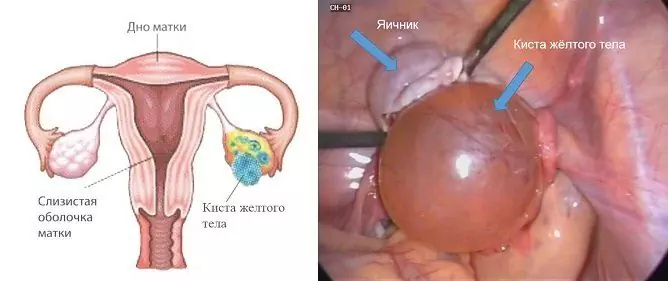
Diseases of the external genital organs are an intimate problem faced by many women of reproductive age. The cyst of the Bartholin gland is a benign formation that is located in the thickness of the labia. The disease may be asymptomatic, in which case the neoplasm is detected during self-examination or gynecological examination.

A large Bartholin gland cyst causes significant discomfort
Formation mechanism
Bartholin's glands are large vestibule glands that are located at the base of the labia majora. Their function is to produce a special fluid that moisturizes the vaginal mucosa during sexual arousal. The size of the Bartholin glands is small, normally up to 5 mm.
Why is a cyst formed?
A blockage of the excretory duct or too thick secretion of the glands can lead to the formation of pathology. If the excretory ducts are blocked, the secretion stops flowing and it begins to accumulate inside the glands. The walls of the obturated canal are stretched, which leads to the formation of a cyst. It usually grows slowly, gradually increasing in size. The size of the formation can reach 3-5 cm or more.
The disease can occur against the background of a chronic inflammatory process (bartholinitis). Inflammation is caused by the ingress of bacteria into the tissues of the Bartholin glands. The infection can be specific (chlamydia, gonococcus, ureaplasma, mycoplasma) and nonspecific (Escherichia coli, staphylococcus).
The development of pathology can be associated not only with inflammation, but also with other reasons:
- Injury to the skin during epilation or shaving.
- Failure to comply with the rules of intimate hygiene.
- Wearing tight synthetic underwear.
- Long stay in a wet swimsuit.
Bartholin gland cyst symptoms
With a small size of the formation, symptoms may be absent. In this case, cystic formation is detected by chance during a gynecological examination.
What is a cyst:
- rounded formation (as seen in the photo);
- size on average from 1 cm to 10 cm;
- painless with uncomplicated course;
- localization in the thickness of the labia majora.
The surrounding tissue may be swollen and reddened.
If the formation reaches a large size (several cm), other symptoms join - discomfort and soreness during walking, exercise, sexual intercourse.
Vivid symptoms appear with the development of complications - suppuration of the cyst and the formation of an abscess:
- An increase in body temperature to subfebrile or febrile numbers.
- Violation of well-being, weakness, lethargy.
- Locally - reddening of the skin, sharp pain and a feeling of fullness, local hyperthermia.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis is usually based on a characteristic clinical picture and gynecological examination. Additionally, studies can be undertaken that are aimed at identifying the causative agent of the infection. If there are no signs of infection, you can do just a gynecological examination.
| Diagnostic method | Indications, research results |
| Gynecological examination |
Shown in all cases when this pathology is suspected. A gynecological examination determines: rounded formation in the thickness of the labia majora (left or right); Unilateral edema of the labia; · Asymmetry of the genital gap; · Normal color leather. On palpation, the formation is painless, elastic consistency. Such changes are determined with an uncomplicated course of the disease. If the cyst festers, the examination results are slightly different. In addition to the presence of a rounded formation and unilateral edema, redness of the skin and pain on palpation are determined. Sometimes leakage of purulent contents is detected. |
| Microscopic examination of the discharge | It is prescribed additionally to determine which microorganism caused the infection. The contents of the cyst are examined under a microscope. |
| Bacteriological examination | Bacteriological culture is also aimed at detecting the causative agent of the infection. The material is sown on special media and growth is monitored. |
Complications and consequences
By itself, a cyst does not pose an immediate threat to a woman's health. The development of complications is dangerous, the most common of which is suppuration and the formation of an abscess. If the abscess is not treated promptly, the bacterial infection can spread further, leading to sepsis (blood poisoning) in severe cases.
Development of other complications is possible:
- fistula formation;
- relapse of the disease;
- vulvitis, vaginitis, urethritis, cervicitis.
With an uncomplicated course, the outcome of the disease is favorable. In some cases, the cystic formation resolves on its own, without external intervention.
How to treat
The tactics of treating the disease depends on many factors - the size of the formation, the severity of clinical manifestations, the presence of complications. Small cysts that do not cause physical discomfort should not be actively treated. Formations larger than 1-2 cm are often the cause of painful sensations, therefore they must be surgically removed.
Bartholin gland cyst: treatment without surgery
With a small size of cystic formation, you can do without surgery. A small cyst can resolve on its own due to a spontaneous improvement in the outflow of secretion from the Bartholin gland. In this case, treatment is aimed at preventing infection of the cystic formation. The following guidelines must be followed:
- wear underwear made from natural materials;
- adhere to the rules of intimate hygiene;
- do not wear tight underwear, thongs;
- visit a gynecologist regularly;
- avoid hypothermia;
- timely treat genital infections.
Conservative treatment of the disease includes the use of antiseptic solutions, Vishnevsky ointment. In chronic bartholinitis, antibiotics are additionally prescribed, which are selected depending on the causative agent of the infection.

The treatment tactics are determined by the gynecologist based on the examination results
Surgical intervention
The operation is aimed at restoring the outflow of fluid from the Bartholin gland. Various methods can be used - puncture, opening and drainage, catheter placement, marsupialization, exfoliation.
| Surgical intervention | Scope of operation, explanation |
| Puncturing |
Treatment consists in puncturing the cystic formation with a needle and dumping the contents. Often, a puncture is prescribed during pregnancy, when more traumatic operations are undesirable. There is a high risk of recurrence after puncture. |
| Opening and draining | To eliminate the cyst, its opening and drainage can be carried out (setting up a drainage for the outflow of secretion). As a rule, such an operation is not enough - after a while, a relapse of the disease occurs. This is due to the fact that the dissected tissues stick together and make it difficult for fluid to drain. |
| Installing a word catheter |
A modern method of treatment. A small incision is made over the pole of the formation, the contents are evacuated, and then a silicone catheter (word catheter) is inserted into the cavity. The catheter is left in the lumen for 4 weeks, during which time the natural excretory duct is formed. The risk of recurrence of the disease is minimal, since the outflow of fluid is not disturbed. |
| Marsupialization | Marsupialization consists in suturing the edges of the opened cyst wall to the edges of the surgical wound. Thus, a new excretory duct is formed. |
| Extirpation | This is the most radical method of treatment that is used for frequent relapses of the disease. The essence of the operation is to remove the cyst together with the gland. |
When an abscess is formed, it is opened, purulent contents are removed and drained.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!