- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
How to effectively treat bronchitis in children at home: treatment with traditional and folk remedies
The content of the article:
- How to treat bronchitis in children at home
- How to treat bronchitis and cough in children at home with folk remedies
- Causes and risk factors for the development of bronchitis in children
- Signs of bronchitis in children
- Prevention
- Video
How to treat bronchitis in children at home is an urgent question, since this disease is one of the most common pathologies of the human respiratory system, which occurs in all age groups.
If you suspect bronchitis in a child, in addition to physical diagnostics, a laboratory examination of blood, sputum, X-ray diagnostics, bronchoscopy may be required for the appointment of treatment.

Bronchitis is often a complication of acute respiratory infections, so such diseases should be carefully treated
How to treat bronchitis in children at home
Treatment of bronchitis is usually carried out at home, and only if the disease is severe and / or with complications - in a hospital. Medicines should be given to a child only after consulting a doctor.
It is recommended to adhere to bed and an abundant drinking regime, it is necessary to regularly ventilate the room in which the patient is located, and daily wet cleaning in it.
The appointment of certain medications for children depends on the cause of the disease and the existing clinical signs. Antibacterial drugs are used only if bacteria are the causative agent of bronchitis (or when a secondary bacterial infection is attached).
To facilitate the discharge of sputum, expectorant, mucolytic drugs may be prescribed to the child. It is strictly forbidden to take any antitussives on their own - in some cases, they can cause serious harm.
When the body temperature rises, antipyretic drugs may be used.
Inhalation helps, which helps to thin and remove phlegm, moisturize the mucous membrane, and also improve blood circulation in the lungs, which helps tissues to regenerate faster. It is recommended to start inhalation no earlier than 1.5 hours after eating, 1-2 times a day. Hot steam inhalation is not recommended for children; aerosol inhalers can be used, as well as inhalation with a nebulizer.
Soda or saline solutions, aromatic oils, infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs can be used as a solution for inhalation. Often used preparations from eucalyptus, calendula, chamomile, sage, oak bark, licorice root, St. John's wort, yarrow. According to Dr. Komarovsky, inhalations from a mixture of raspberries, linden flowers and coltsfoot are effective for bronchitis. Often, children are prescribed inhalation with Lazolvan.
With prolonged bronchitis, children can be given drainage, vibration, acupressure, cupping massage, as well as medical massage with honey. Massage is recommended in the morning before breakfast.
The therapeutic effect of mustard plasters for bronchitis is disputed by specialists; in any case, they should not be used in children under 5 years of age.
Of the physiotherapeutic procedures for bronchitis in children, electrophoresis, magnetotherapy, and ultraviolet irradiation can be used. Physiotherapy is indicated at the stage of recovery, only after the acute process subsides.
How to treat bronchitis and cough in children at home with folk remedies
The main treatment of bronchitis can be supplemented with folk remedies with the permission of a doctor.
Mixtures for ingestion based on honey are widely used. So, you can prepare products from honey and freshly squeezed juice from vegetables (beets, carrots), viburnum, radish juice, freshly prepared applesauce mixed with honey has immunostimulating properties. Often, with bronchitis, children are given boiled milk with the addition of sage and honey.
It is believed that black radish juice with honey will help to quickly cure bronchitis in a child. It is prepared as follows: thoroughly wash the black radish with a brush, but do not peel it. Cut off the top, gently make a recess with a knife, into which to put a teaspoon of honey, close with the top. After a while, the honey will mix with the released radish juice, it is taken 2 tablespoons before meals and before bedtime.
Popular decoctions of sage, peppermint, linden, ginger, elderberry, violet, as well as breast collection. Children with bronchitis are advised to drink tea with raspberries (dried, mashed with sugar or raspberry jam), after which they should wear woolen socks and a warm sweater. It is useful to consume figs cooked in milk, as well as warm whey. Cabbage and lingonberry juice have an expectorant effect.
You can prepare a remedy from peppermint (3 teaspoons) and wheatgrass (5 teaspoons), which are poured into 600 ml of water, brought to a boil and allowed to cool. Filter the finished product and drink 1/3 cup 3 times a day before meals.
For bronchitis and coughing in children, you can use a remedy from onions and garlic. To do this, chop 1 small onion and 3 cloves of garlic, add 1 glass of milk to the mixture, bring to a boil and cook until the garlic and onion soften. After that, the agent is removed from the heat, allowed to cool and filtered. You can add honey to the mixture. The remedy is taken in 0.5 tablespoon every hour throughout the day.
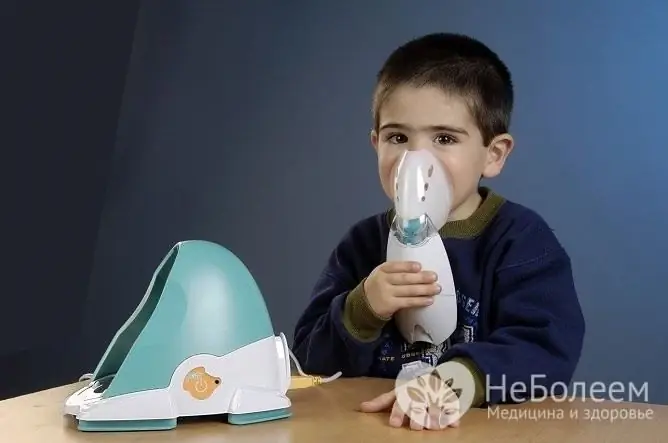

Children should not inhale hot steam, it is recommended to use a nebulizer
An effective means based on propolis. For its preparation, 50 g of pre-frozen propolis is grated, 300 g of melted butter is added, the mixture is kept in a water bath for 20 minutes, allowed to cool, filtered through 2 layers of gauze and consumed in a teaspoon with warmed milk 30 minutes before meals …
According to the reviews of parents of childhood patients, a lingering cough with bronchitis can be eliminated with the help of a remedy from 1 part of crushed aloe leaves, melted pork and badger fat (1 part each), 2 parts of honey and 1 part of chocolate. All ingredients are put into a saucepan, heated to 35-40 ° C, stirring thoroughly. Take 1 tablespoon 3 times a day before meals. In chronic bronchitis, the remedy is used for prophylaxis in spring and autumn.
To treat bronchitis and cough, you can use an infusion of licorice root and pine buds. The ingredients are mixed in a 1: 1 ratio, after which a tablespoon of the resulting mixture is poured with a glass of water, brought to a boil and left to cool. Take an infusion of 2 tablespoons 3 times a day before meals.
With bronchitis, compresses from grated horseradish or boiled potatoes, to which you can add a few drops of iodine, olive, linseed or sunflower oil, help.
You can use a chest compress made from honey, dry mustard and flour mixed in equal parts.
In addition, you can lubricate the baby's breast with honey, put a cloth soaked in vodka on top (vodka should be diluted with water in a ratio of 3: 1). It is convenient to put the compress at night, firmly fixing it on the body.
Causes and risk factors for the development of bronchitis in children
Bronchitis is an inflammatory disease of the bronchial mucosa.
There are primary and secondary bronchitis. In primary bronchitis, the pathological process begins to develop directly in the bronchi. With secondary bronchitis, the disease occurs against the background of another pathology (flu, heart disease, chronic diseases of the respiratory system, etc.). Usually, inflammation begins in the nasopharynx, and then goes to the bronchi, that is, often bronchitis is a complication of an acute respiratory infection.
In addition, bronchitis is classified as acute and chronic. Acute bronchitis usually has an infectious (viral, less often bacterial) etiology. Bronchitis caused by microscopic fungi is rare; it develops in children with significantly weakened immunity - in premature babies, as well as in weakened babies who have been treated with antibiotics for a long time.
The chronic form of bronchitis develops with improper therapy (or no treatment) of the acute form as a result of a prolonged stay of the infectious agent in the respiratory tract.
Risk factors for the development of bronchitis in children include exposure to the body but unfavorable environmental factors, frequent stress, hypothermia, prolonged exposure to damp and / or dusty rooms, inhalation of tobacco smoke, dust, allergens, chemicals, lack of oxygen in the inhaled air, undergone surgery.
Signs of bronchitis in children
In acute bronchitis in children, there is a sore throat, discharge from the nasal cavity, headache, cough (dry and then wet at the onset of the disease), fever (usually up to 37.5-38 ° C), lethargy, and impaired appetite. In the absence of complications and with the right treatment, recovery usually occurs in 1.5-2 weeks.
Chronic bronchitis is accompanied by violations of the secretory, protective and cleansing functions of the bronchi, has a long course. In this case, the body temperature usually does not rise, or rises slightly during exacerbations. Exacerbations of chronic bronchitis usually develop in the winter and off-season.
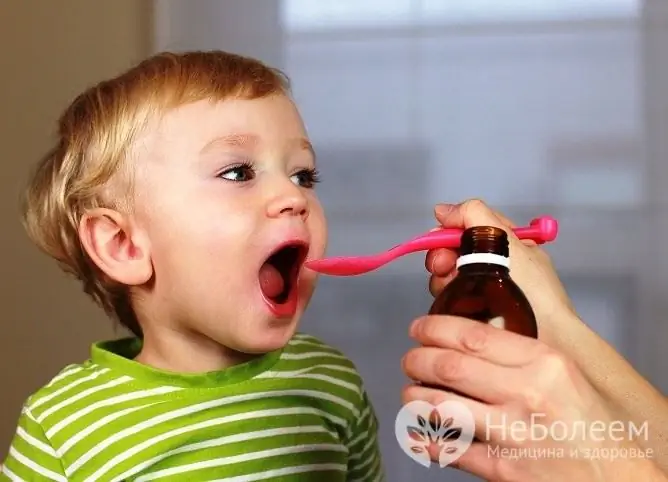

Any medication for bronchitis in children must be discussed with a doctor.
According to the type of inflammatory process and the nature of sputum, bronchitis is divided into the following forms:
- catarrhal - with increased production of mucus in the bronchi;
- mucopurulent - with the release of mucopurulent sputum;
- purulent - the production of purulent sputum is characteristic;
- fibrinous - very thick sputum due to increased release of fibrin;
- hemorrhagic - there is an admixture of blood in the sputum due to hemorrhage in the bronchial mucosa.
When small-caliber bronchi are blocked, patients complain of difficulty breathing.
On a functional basis, bronchitis is classified into non-obstructive and obstructive. With non-obstructive (simple) bronchitis, there is an increased secretion of mucus in the bronchi of medium and large caliber. The main symptom of non-obstructive bronchitis is a chest cough with a large amount of phlegm. With obstructive bronchitis, the child has shortness of breath, wheezing, and increasing weakness. At the initial stage of the disease, the changes are reversible; with the progression of the pathological process, qualitative changes can occur in the bronchi, which, in the absence of treatment, become irreversible.
Against the background of bronchitis in children, especially in the case of improper treatment of the disease, pneumonia, pulmonary emphysema, bronchial asthma, heart pathologies, etc. can develop.
Prevention
In order to prevent the development of bronchitis in children, it is recommended to vaccinate against influenza, a balanced diet, strengthen immunity, regular exercise, adhere to the rules of personal hygiene, teach children to breathe only through the nose, avoid physical and mental overload, timely treatment of acute respiratory diseases.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.