- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Good expectorants for bronchitis
The content of the article:
- The best expectorants for bronchitis
-
Good expectorants for bronchitis with secretory activity
- Liquorice root
- Mother and stepmother
- Altay
- The most popular mucolytic expectorants
- Why are expectorant drugs prescribed?
- Video
Expectorants for bronchitis are an indispensable component of the pharmacotherapy of the disease. These medications stimulate the production of phlegm, promoting a speedy recovery.
The group of expectorant drugs includes various means of both synthetic and natural (including plant) origin. The form of their release is diverse: tablets, dry mixtures, syrups, solutions for inhalation, drops, granules for solution preparation, etc.

The indication for the appointment of expectorants for bronchitis is a cough
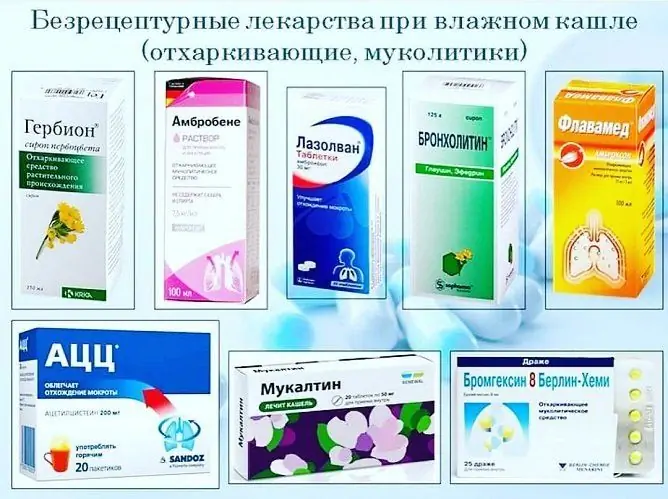
The best expectorants for bronchitis
Bronchial mucus consists of two fractions: soluble and insoluble. The basis of the insoluble component is mucin, a complex of glycoproteins with a jelly-like consistency.
Depending on the mechanism and specificity of the action of the active components, all drugs are divided into two more groups:
- Actually expectorant, that is, stimulating the process of removing sputum from the bronchi by increasing the production of its liquid component, the so-called secretomotor means.
- Mucolytic, the main effect of which is to thin the viscous mucus.
The action of secretomotor drugs is based on their ability to directly or reflexively stimulate the production of the liquid component of sputum. This not only improves its fluidity, but also increases its quantity.
Mucolytics act on thicker mucins, breaking their internal connections and making them as convenient as possible for removal from the bronchi. There is no increase in the amount of sputum.
Good expectorants for bronchitis with secretory activity
The group of secretomotor substances includes drugs for direct (resorptive) and reflex actions:
- reflex - when used, they irritate the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract. Such stimulation, indirectly acting through the vomiting center of the medulla oblongata, increases the production of the liquid component of bronchial mucus. The patient does not experience unpleasant sensations in the form of nausea or other dyspeptic disorders;
- the resorptive effect of secretomotor drugs is based on their ability to directly activate the production of the liquid fraction of sputum, significantly increasing its amount. The mucus becomes less viscous and more fluid.
Folk expectorants for bronchitis just belong to this group. The most famous of them: coltsfoot, thermopsis, marshmallow, licorice root, oregano, some essential oils.
Below are the options for using the most popular expectorant herbs for bronchitis in adult patients.
Liquorice root
Grind a few grams (no more than ten) of the root and pour a glass of boiling water, then heat in a water bath for about half an hour. After that, let stand for 1-2 hours, cool and strain through a sieve or cheesecloth. Add distilled or boiled water to the resulting solution to bring the volume to 200 ml. Take 3-4 times a day, one tablespoon.
At home, you can prepare an expectorant from licorice root according to a simplified recipe: 200 ml of boiling water is poured over a tablespoon with the top of chopped plant materials and left to cool. It is necessary to take the resulting infusion ¼ glass 3-4 times a day.
Mother and stepmother
One tablespoon of dried plant leaves is poured into a glass of boiling water. In this case, it is necessary to use enamel, ceramic or glassware. The container with leaves is covered with a lid and heats up in a water bath for 15-20 minutes. In the process, the leaves, filled with boiling water, must be stirred periodically. After the specified time, the infusion is removed from the heat, filtered and cooled at room temperature. In this case, the leaves must be carefully squeezed out of the liquid.
The resulting product is brought with distilled or boiled water to the volume of one glass, stored in a cool, dark place for no more than two days. It is necessary to take the infusion for ½ cup 2-3 times a day.
Some recipes involve the use of coltsfoot in the form of a decoction. Then the dried leaves are placed in an enamel container and boiled for 15 minutes. The resulting product is filtered, carefully squeezing out the leaves, and then allowed to cool and brew. Take one tablespoon three times a day.
Altay
Marshmallow root is used as a medicinal raw material. A tablespoon with a slide of crushed root is poured into a non-metallic dish and poured into ½ liter of distilled or boiled water at room temperature. Infused for at least a day. It is necessary to take it 3-4 times a day, half a tablespoon.

Marshmallow root has a powerful expectorant effect
For children, the indicated dosage is not suitable, a mandatory preliminary consultation with a specialist is required. It should be noted that in pediatric practice, the intake of drugs from herbal raw materials is not widely used and is extremely limited. This is due to the widespread prevalence of allergic reactions among young patients.
When making infusions and decoctions on your own, care should be taken to avoid overdose. When taking an excessive amount of the drug, a number of dyspeptic symptoms may develop: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea. This is due to the irritating effect of plant components on the gastric mucosa. For the same reason, it is recommended to take such funds an hour after a meal, not on an empty stomach.
In addition to herbal remedies, drugs such as potassium and sodium iodide, ammonium chloride and sodium bicarbonate are used as resorptive secretomotor agents for the treatment of bronchitis. The effect develops after oral administration and absorption into the systemic circulation. These drugs are characterized by specific side effects associated with the ability to activate the production of liquid secretions - nasal congestion, difficulty breathing and severe lacrimation.
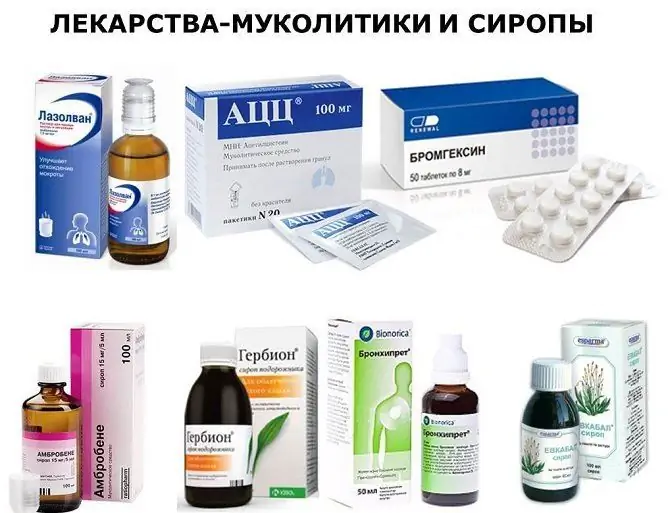
The most popular mucolytic expectorants
Mucolytics are fundamentally different from secretomotor drugs. They do not affect the liquid fraction of mucus, affecting only the chemical structure of mucins.
A feature of their action is the ability at the level of molecular bonds to "cut" long polypeptide chains of glycoproteins, thereby disrupting their structure. At the same time, the phlegm becomes less viscous and viscous, its elasticity decreases and discharge is much easier.
All drugs in this area can be divided into three main groups:
- Proteolytic enzymes (chymotrypsin, trypsin).
- Sulfur derivatives (e.g. acetylcysteine, also known as ACC).
- Vizicin derivatives (eg Ambroxol).
Proteolytic enzymes are currently not widely used. This is primarily due to their high allergic activity and the ability to provoke bronchospasm in compromised patients.
Sulfur-containing agents are actively used not only in the treatment of bronchitis, but also in the treatment of sinusitis, bronchiectasis, bronchial asthma, and some types of inflammation of the middle ear. They have a pronounced mucus-thinning effect.
These funds should be used with caution in debilitated patients and children, which is explained by the ability to intensive, rapid dilution of sputum, which is accompanied by a significant increase in its amount. In cases where the patient cannot effectively cough up, complications such as "waterlogging of the lungs" develop (extremely rarely). In this case, sputum is intensively formed, but stagnates in the bronchi, since it cannot be evacuated in full due to inadequate coughing. Favorable conditions are created for the addition of a secondary infection and the development of pneumonia.
In addition to phlegm, these products can also liquefy thick pus, improving its excretion.
The most effective and demanded group of drugs at the present time is mucoregulators. They cut the protein-like chains of mucin like scissors, just like sulfur derivatives. It is important that they do not cause an increase in the amount of bronchial secretions, which makes them indispensable for use in pediatrics and in debilitated patients unable to actively cough up.
Mucoregulators have a number of additional positive characteristics:
- improve the penetration of antibacterial drugs into bronchial mucus, which is extremely important when carrying out antimicrobial therapy;
- have their own antitussive activity;
- stimulate local immunity in the bronchopulmonary zone;
- activate the production of pulmonary surfactant;
- activate the cilia of the ciliated epithelium.
Numerous reviews of patients and doctors confirm the high efficiency and safety of mucoregulators and sulfur preparations in the treatment of bronchitis.
Acetyl and carbocisteine are currently used in the form of pleasant tasting effervescent dissolving tablets. Different dosages make it easy to use them in both adult and pediatric practice.
Inhalation is the most effective form of using mucoregulators. Inhalation of the medicinal aerosol is usually done twice a day. At the same time, the active substance is mixed with a solvent, which is saline (NaCl 0.9%). The use of nebulizer therapy provides targeted drug delivery directly to the focus of inflammation - the bronchial tree.
Why are expectorant drugs prescribed?
Under natural conditions, special goblet cells located in the ciliated epithelium of the bronchial tree produce tens of milliliters of mucus every day. Bronchial secretion has protective properties: microparticles of dirt, allergens, pathogenic bacteria and viruses adhere to it. The evacuation of mucus occurs when sneezing, coughing, most of it is swallowed, entering the digestive tract.
With the development of a local inflammatory process, the secretion of mucus increases significantly, its properties change. The secret becomes viscous, stringy. It clogs the lumen of small bronchi, significantly reducing the efficiency of breathing. The accumulation of non-evacuated sputum serves as an excellent medium for the addition of a secondary bacterial infection and the development of complications. In the most severe cases, the inflammatory process spreads to the lung tissue, pneumonia develops.

Children are not advised to take folk remedies for bronchitis
The production of mucus also changes in the absence of an infectious process, for example, with bronchitis of a smoker or toxic damage to the respiratory tract by occupational factors of aggression (dust, high temperatures, chemical vapors, etc.). In this case, not only the secretion increases, but also the ciliated epithelium is irreversibly damaged, the cilia of which sweep mucus from the bronchi.
To prevent stagnation of bronchial secretions in the airways and the development of complications, expectorant drugs are prescribed. The main indication for their use is the presence of a cough, which signals a violation of sputum excretion.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Olesya Smolnyakova Therapy, clinical pharmacology and pharmacotherapy About the author
Education: higher, 2004 (GOU VPO "Kursk State Medical University"), specialty "General Medicine", qualification "Doctor". 2008-2012 - Postgraduate student of the Department of Clinical Pharmacology, KSMU, Candidate of Medical Sciences (2013, specialty "Pharmacology, Clinical Pharmacology"). 2014-2015 - professional retraining, specialty "Management in education", FSBEI HPE "KSU".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.