- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Is angina transmitted by airborne droplets and other means from person to person
The content of the article:
-
How is angina transmitted from person to person
- Airborne transmission of angina
- Contact way
- Oral-genital route
- Perinatal route
- Factors that influence the development of the disease
- How to prevent infection
- Video
How angina is transmitted is a frequent question, the answer to which is especially important for people who are in close contact with the patient. What do you need to know in order not to get infected?
Most often, sore throat pathogens are transmitted by airborne droplets
Angina, or acute tonsillitis, is a fairly common infectious disease. In this case, the tonsils of the pharyngeal ring become inflamed, causing them to increase, as well as an increase in body temperature, sore throat and general symptoms of intoxication.
The causative agents of tonsillitis are:
- bacteria, most often streptococcus and staphylococcus;
- enteroviruses, influenza viruses, herpes viruses or papillomaviruses;
- mushrooms from the genus Candida.

The main causative agents of tonsillitis are viruses and bacteria.
Infection can enter the human body in different ways. Pathogenic microbes are introduced into the mucous membrane of the tonsils and cause inflammation, while poisoning the products of their vital activity.
The incubation period after infection can range from several hours to 7 days. Then the patient's body temperature rises sharply and other signs of the disease appear.
Treatment of angina, depending on the form and severity, can last from 4 to 10 days. Throughout this period, a person remains a source of infection (especially in the acute form of the disease).
How is angina transmitted from person to person
There are several ways of transmission of infection that can provoke a sore throat. If the immune system is working at full strength, the likelihood of getting sick is significantly reduced.
Airborne transmission of angina
Most often, bacteria and viruses, which later become the causative agents of sore throats, are transmitted by airborne droplets. They are localized on the mucous membrane of the patient's upper respiratory tract. For example, 1 ml of saliva can contain about 105 CFU of streptococcus. Within a minute, the body produces 2-3 ml of this biological fluid.
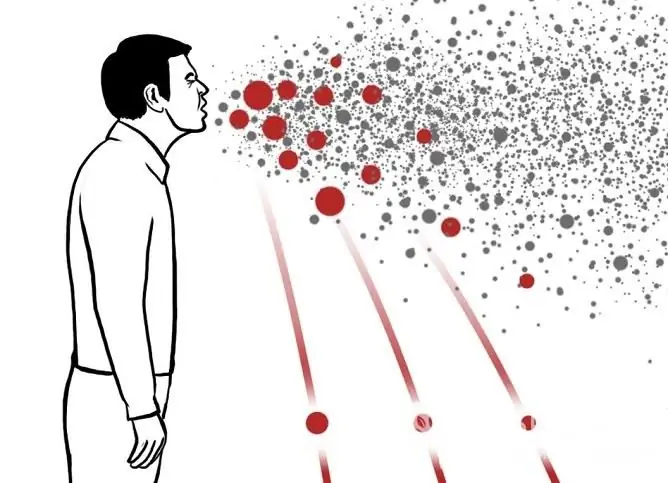
You can become infected with a sore throat while in the immediate vicinity of the patient.
During coughing, sneezing or talking, pathogenic microorganisms, along with saliva and mucus from the nose, enter the air, where they can live for some time. Droplets of liquid float in the air for a sufficiently long period, gradually sinking to different surfaces. Air currents can carry them a considerable distance from a sick person to those around him.
The droplets of liquid, together with the microbes contained there, with the inhaled air, enter the mucous membranes of a healthy person. If the immune system cannot cope with them, they are introduced into the tissues and become the cause of the inflammatory process. It is possible to become infected with a sore throat by airborne droplets only being in the immediate vicinity of the patient (at a distance of several meters).
Large droplets of liquid, although they contain a large number of viruses and bacteria, quickly settle. On surfaces, they dry out and pass into a dusty phase, at the same time their ability to infect is significantly reduced.
But on contaminated clothes, upholstered furniture or bedding, they can live for more than one day, while viruses die much faster than bacteria. Therefore, you can become infected with purulent sore throat simply by being in the room where the patient was present before.
Contact way
Purulent tonsillitis is transmitted by contact.
The causative agent of sore throat can be transmitted by direct contact, such as shaking hands
In this case, the contact can be:
- direct: the causative agent of the disease enters the body of a healthy person with a kiss or a handshake;
- indirect: infection occurs through household items, common dishes or towels.
Oral-genital route
Many microorganisms, including pathogenic ones, can live on the mucous membranes of not only the respiratory tract, but also the genitals. With oral contact, they are transmitted to the partner and, in some cases, cause the development of angina.
Perinatal route
In this way, tonsillitis is very rarely transmitted. Some pathogens can cross the placenta, infecting the fetus in utero. Also, the baby can become infected by passing through the birth canal of an infected mother.
Factors that influence the development of the disease
If an adult or child falls ill with a sore throat, this means that an infection has entered his body. How quickly it begins to develop and the severity of the disease can be influenced by various factors. The reduction of general and local immunity plays a special role.
Factors affecting the development of angina:
- frequent hypothermia, as well as the use of cold food or drinks;
- autoimmune diseases;
- pregnancy;
- hormonal disorders;
- work in dusty and gas-polluted rooms;
- frequent visits to crowded places;
- poor oral hygiene;
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking;
- the presence in the body of a focus of chronic infection (sinusitis, carious teeth);
- getting into stressful situations;
- climate change;
- excessive physical activity.
With improper treatment or shortening the period of taking antibiotics, the disease can become chronic. Affected tonsils become a source of chronic infection in the body. With a weakening of immunity, pathogenic microorganisms that live there begin to multiply actively, causing symptoms of an acute form of the disease.
How to prevent infection
To prevent sore throat you need:
- avoid crowded places during an epidemic of colds, if necessary, use personal protective equipment, such as a gauze bandage;
- rinse your nose with saline solution after visiting public places or traveling in transport;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene, wash your hands regularly;
- strengthen immunity, play sports, walk in the fresh air for a long time and temper;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- eat right: give preference to vegetables, fruits, white meat and fish, refuse fatty, salty and spicy foods;
- dress for the weather;
- treat all diseases in time, preventing them from becoming chronic;
- eliminate foci of chronic infection, such as caries;
- maintain cleanliness and regularly ventilate the apartment or office in which you have to work.

During epidemics, it is recommended to use personal protective equipment
Angina is a contagious disease, while it is important to understand that it is not the disease itself that is transmitted, but an infection that can cause the development of the disease. Therefore, if you have tonsillitis symptoms, you should take all the necessary measures so as not to infect others.
It is necessary to provide the patient with a separate room, in which wet cleaning and ventilation should often be carried out. He should also have separate dishes and a towel.
If symptoms of sore throat are detected, it is necessary to consult a doctor to prescribe adequate treatment. The implementation of all his recommendations will reduce the time of illness and minimize the likelihood of complications.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.