- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Exercise for osteochondrosis of the cervicothoracic and lumbar spine
The content of the article:
- Key recommendations
- Exercise during exacerbation of the disease
-
Gymnastics without exacerbation of the disease
- Exercise for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
- Exercises for osteochondrosis of the thoracic region
- Exercises for lumbar osteochondrosis
- Video
Exercise systematically performed in osteochondrosis has a beneficial effect on the condition of the spine, helps to slow down the development of degenerative-dystrophic processes in the intervertebral discs and helps to restore mobility, improve the general condition of patients.
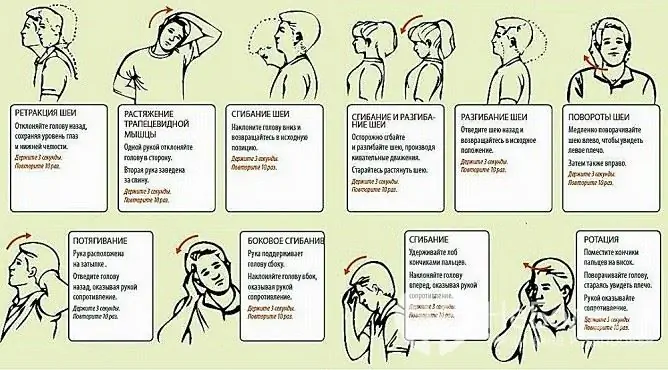
Key recommendations
In order for the effect of charging with osteochondrosis to be as pronounced as possible, experts recommend that patients adhere to the following rules:
- Regularity. A sedentary lifestyle contributes to a significant overstrain of the back muscles, as a result of which the load on the spine increases. This becomes the reason for the deterioration of metabolic processes in the intervertebral discs, provokes an increase in the rate of dystrophic changes. Therefore, it is very important to systematically give the muscles the opportunity to rest and recover, which is achieved by performing a special set of physical exercises.
- Recurrence. It has been proven that gymnastics for osteochondrosis is most effective if it is performed several times a day. It is advisable to take short breaks for exercise after every hour of working in a sitting position.
- Drink plenty of fluids. Drinking enough fluids throughout the day prevents dehydration of the intervertebral discs.
- Posture. In the fight against osteochondrosis, maintaining the correct posture plays an important role. This allows you to evenly distribute the static-dynamic loads on individual vertebral bodies, improves metabolic processes in the intervertebral discs.
Exercise during exacerbation of the disease
With an exacerbation of osteochondrosis, the patient develops back pain, as well as symptoms characteristic of pinching of the spinal nerve roots. During this period, he is recommended:
- carrying out drug therapy as prescribed by a doctor (painkillers, muscle relaxants, B vitamins);
- sleeping on a flat, hard surface in the supine position with a small cushion placed under the knees;
- maximum physical rest.
As the pain syndrome subsides, the patient's motor regime is gradually expanded. He is recommended physical therapy classes, which are best done under the supervision of a specialist.
Gymnastics without exacerbation of the disease
Without an exacerbation of osteochondrosis of the cervicothoracic region, exercise at home is as effective as morning exercises and exercises that are regularly performed in the office, in a public place. Consider various complexes of medical gymnastics.
Exercise for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
| Location | Description |
| Houses |
1. Starting position (IP) lying on your back. Raise your head slowly, trying to reach the sternum with your chin. Hold for 2-3 seconds in this position and return to I. P. 2. I. P. sitting. Throw your head back and then slowly return to I. P. 3. IP lying on its side with a small roller under the head. Raise your head and pull it to your shoulder. Return to I. P. Repeat 10 times, then turn on the other side and perform the exercise again. 4. I. P. lying on his back. Turn your head slowly, trying to reach the floor with your ear. Return to I. P. and make a turn in the opposite direction 5. I. P. lying on his back. Perform head bends alternately to the right and left shoulder. |
| In the office |
1. I. P. sitting with a straight back and straightened shoulders. Perform head turns left and right at a slow pace. 2. I. P. sitting. Tilt your head back slightly, and then turn left and right, trying to reach your shoulder with your ear. 3. I. P. sitting, head down, chin pressed to the sternum. Make smooth turns of the head to the right and to the left, without lifting the chin from the sternum. |
Each exercise must be performed 10-12 times. If pain or discomfort occurs, exercise should be interrupted and a doctor should be consulted.
Exercises for osteochondrosis of the thoracic region
| Location | Description |
| Houses |
1. I. P. lying on his back, arms extended along the body, palms pressed to the floor. Leaning on the palms, raise the upper body, bending your back back. Return to I. P. 2. I. P. lying on his stomach, hands along the body. Raise your legs and upper body, arch your back. 3. I. P. standing on all fours. Bend your back and stretch slightly forward. Hold for a few seconds in this position and smoothly return to I. P. |
| In a public place |
1. Constant control of correct posture. Patients should be aware that correct posture is the most important exercise for the back muscles. Sit at the desk with a straight back, leaning on the back of a chair. It is advisable to put a small stand under the feet. 2. I. P. sitting on a chair with a low back. Bend back slowly, trying to look at the wall behind you. 3. I. P. standing, feet shoulder width apart. Bend the body to the right and left. 4. I. P. sitting on a chair, hands down. Bring your shoulders back as far as possible, and then bring them forward. 5. I. P. standing or sitting on a chair. Raise and lower your shoulders, first at the same time and then alternately. |
Each exercise should be performed at least 7-10 times.
Exercises for lumbar osteochondrosis
This type of disease occurs most often. If you do not carry out its treatment, then over time it is complicated by the development of a herniated disc. Therapy includes not only medications, but also physical therapy, the use of orthopedic mattresses and chairs. The following complexes of gymnastic exercises are quite effective against the progression of degenerative-dystrophic processes in the intervertebral discs of the lumbar spine:
| Location | Description |
| Houses |
1. I. P. standing on all fours. Smoothly tear off the floor and extend the left arm and right leg. Return to I. P. Repeat the exercise by extending the right arm and left leg. 2. "Cat". I. P. standing on all fours. Arch your back like cats do, and then arch your back as much as possible. 3. I. P. lying on his back, legs raised. Perform movements with them as if you were pedaling a bicycle. 4. I. P. lying on his back, legs slightly raised above the floor. Use them in a movement similar to that of a scissor blade. 5. I. P. lying on the floor on his back, knees pulled up to the chest and clasped with his hands. Perform swaying movements with your whole body. |
| In a public place |
1. I. P. standing, feet shoulder width apart. Perform several forward bends of the torso and then to the sides. 2. I. P. standing, feet shoulder width apart. Put your fists on the lower back. Bend your knees slightly and bend back, resting on your fists. Hold this position for 15-20 seconds. Return to I. P. |
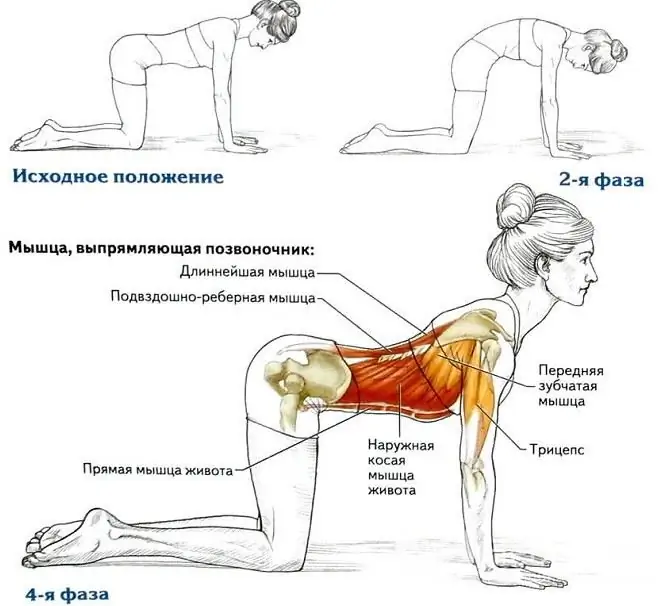
Back bends are useful for osteochondrosis of the thoracic and lumbar spine
In conclusion, it should be emphasized that, although osteochondrosis is a chronic disease, however, with due regard to its treatment (drug therapy, physiotherapy, physiotherapy exercises), it is possible to achieve a significant slowdown in its progression and maintain the health of the spine for many years.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Elena Minkina Doctor anesthesiologist-resuscitator About the author
Education: graduated from the Tashkent State Medical Institute, specializing in general medicine in 1991. Repeatedly passed refresher courses.
Work experience: anesthesiologist-resuscitator of the city maternity complex, resuscitator of the hemodialysis department.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.






