- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Exercises for chest osteochondrosis
The content of the article:
-
Charging for osteochondrosis of the thoracic region at home
Exercising with a gymnastic stick
- Recommendations for performing gymnastics
- Indications and contraindications
- Other treatments
-
General information about the disease
- The reasons
- Complications
- Symptoms
- Prevention
- Video
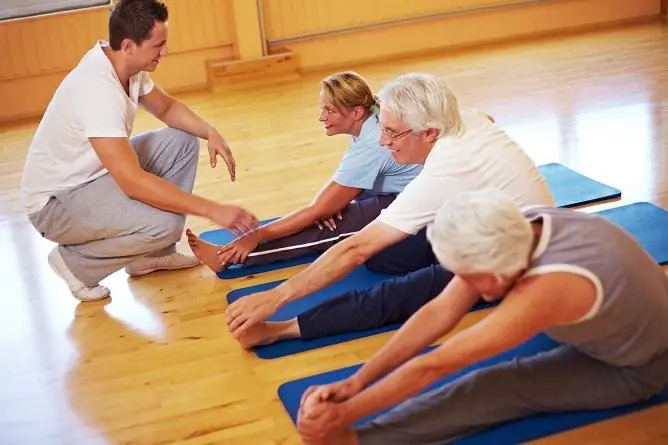
With thoracic osteochondrosis, exercise therapy exercises are an important component of comprehensive treatment. Therapeutic exercises should be carried out only as directed and under the supervision of a qualified specialist, since attempts at self-medication can aggravate the patient's condition and lead to the development of complications. You can perform exercises for thoracic osteochondrosis at home, having previously completed training with an instructor.

Exercise therapy classes, at least in the beginning, should be conducted by a specially trained instructor
Performing exercises from a complex of physiotherapy exercises allows you to increase the level of physical activity, achieve muscle relaxation and eliminate spasms, strengthen muscles, improve blood circulation and metabolism in tissues, and release squeezed nerve roots. An improvement in the condition is usually noticeable after a few sessions of physiotherapy exercises.
Exercise complexes developed by specialists (doctors Bonina, Bubnovsky, etc.) are often used.
Charging for osteochondrosis of the thoracic region at home
The main complex of exercise therapy for osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine:
- Take a standing position. Then you should alternately raise and lower each shoulder. These steps are repeated 10 times for each shoulder.
- Being in the same starting position, turn your head alternately to the right and left, fixing it for 10 seconds at the end points. 10 head turns are performed in each direction.
- Tilts the head towards the right and left shoulder, while using the palms of the hands to resist the bends.
- Tilting the head forward and backward, fixing it for a few seconds in each of the positions. Actions are repeated 10 times for each side.
- Place your palms on your back below the level of the shoulder blades and bend forward, remaining in this position for 10 seconds, after which you need to return to the starting position.
- Starting position lying on your stomach, arms outstretched to the sides. Simultaneously raise the head and upper limbs, hold them in this state for about 3 seconds, return to the starting position. Repeat 5 times.
- Starting position - lying on your stomach (hands are along the body). Bend the body, while lifting the head and legs up, return to the starting position. Repeat 5-8 times.
- From the starting position, standing on all fours, the patient raises his head while inhaling and bends his back, while exhaling he lowers his head, rounding his back. Actions are repeated 5 times at a slow pace.
- The starting position is sitting on a hard surface with your hands down, take your elbows back, trying to bring the shoulder blades together, stay in this position for 5 seconds and return to the starting position. The exercise is repeated 3 times.
- From the starting position, sitting on a chair, you need to grab the waist with your palms and spread your elbows to the sides. After that, the patient performs shoulder movements alternately forward and backward. The back is pressed against the back of the chair. Actions are repeated 3-4 times in each direction.
- The starting position is standing, after that you need to put your hands with your palms on your shoulders, then lower one shoulder, while raising the other. The head follows the shoulder that descends. These steps are repeated 4-6 times.
The listed exercises of therapeutic gymnastics for osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine can be performed by patients of all age groups.
Exercising with a gymnastic stick
The doctor may recommend exercising at home or in the gym with a gymnastic stick - this increases the effectiveness of the exercise. With the help of a gymnastic stick, it is possible to achieve a redistribution of the load and relaxation of the back muscles in the affected area.
The following exercises are performed with a gymnastic stick:
- Starting position standing, feet shoulder-width apart. Take a gymnastic stick with both hands, stretching them forward in front of you, and perform rotational movements with the stick (10-12 in each direction).
- From the same starting position, you need to take a deep breath, raise your hands with a gymnastic stick up, while exhaling, lower your hands. The actions are repeated 10 times, following the correct breathing.
- Being in the same starting position, the patient raises his arms up, tilts the body forward while inhaling, and assumes the starting position while exhaling. The exercise is repeated 7-10 times.
- The patient assumes a starting position sitting on a chair, holding a gymnastic stick with both hands. Make a movement with straight arms up and back, stretch after your arms for a while, while sitting straight. Return to starting position. Actions are repeated several times.
When performing these actions, you should avoid sudden movements and turns of the trunk, as this can have negative consequences for the spine.
Recommendations for performing gymnastics
To obtain the most effective result in the treatment of osteochondrosis with the help of physiotherapy exercises, it is recommended to adhere to the rules:
- do not make sudden movements (otherwise, this may increase the symptoms of pathology);
- if you experience pain or dizziness while doing any of the exercises, you should stop exercising and consult your doctor;
- the load should be increased gradually and under the supervision of a specialist;
- exercise should be done regularly;
- physical therapy should be done in a well-ventilated room, however, during the training itself, there should be no drafts in the room, you can do gymnastics on the street;
- for classes, you need to choose comfortable clothes that do not restrict movement and allow air to pass through;
- before and after the end of the session, the patient should measure the pulse and blood pressure (if there is a deviation from the norm, it may be necessary to reduce the load);
- stretching exercises are usually recommended as you exhale.
After eating, at least 1 hour should pass before the start of the lesson.
Indications and contraindications
Physiotherapy is used for the prevention and treatment of osteochondrosis of the spine, increases the effectiveness of the medicines used. Gymnastics helps to strengthen the muscle corset, form the correct posture, improve lung ventilation, and reduce the load on the spine.
Contraindications to performing remedial gymnastics:
- high myopia (myopia);
- increased intraocular and / or blood pressure;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- nervous disorders;
- postoperative period.
Individual indications and contraindications are determined by the attending physician.

The exercise therapy complex can be used not only for therapeutic, but also for prophylactic purposes.
Other treatments
Osteochondrosis responds best to treatment early in the development of the disease. Its progression in the absence of treatment or with improperly selected treatment is highly likely to cause the development of complications and disability of the patient with limited or disability.
At certain stages of the disease, drugs, massage, physiotherapy methods of treatment, dosed physical activity - swimming, yoga, balneotherapy, spinal traction can be prescribed. In some cases, an operation may be required.
An important condition for the effectiveness of treatment is the normalization of body weight, since excess weight contributes to the development of osteochondrosis. In this case, the diet should be balanced.
| Products you need | Foods to limit |
| Lean meat and fish | Smoked products |
| Vegetables | Salted and pickled foods |
| Fruit | Spice |
| Greens | Caffeinated foods and drinks |
| Herbal teas | Alcoholic drinks |
General information about the disease
Many people have experienced spine or chest pain at least once in their lives. If it appears regularly, it may indicate degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine - osteochondrosis.
The pathological process can occur in any part of the spine; osteochondrosis of the cervical, thoracic and lumbar (lumbosacral) regions is distinguished. Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is the rarest type, which is explained by the least mobility of this part of the spine, as well as greater protection (muscles and ribs).
The reasons
The main reasons include genetic predisposition, poor posture, a sedentary lifestyle, excessive physical activity, or, conversely, physical inactivity.
Contribute to the onset of the disease:
- sedentary work (especially long-term work at the computer in an uncomfortable position);
- physical and mental overload;
- overweight;
- hormonal disruptions;
- bad habits.
At risk are middle-aged and elderly people, poorly trained people, patients with flat feet and clubfoot, with a history of spinal injuries.
Complications
In the absence of timely, correctly selected treatment, patients may experience a hernia of the thoracic spine, compression of nerves and / or spinal cord, disruption of the heart, liver, organs of the urinary system, and the gastrointestinal tract.
Symptoms
With damage to the thoracic region, there may be:
- pain in the chest, which can increase at night, with hypothermia, prolonged stay in one position of the body, excessive physical exertion, deep breathing;
- pain between the shoulder blades, which appears when the patient lifts his arm up;
- pain between the ribs while walking;
- a feeling of squeezing the body;
- cooling of the lower extremities;
- burning sensation and itching in the legs;
- pain in the esophagus and / or pharynx;
- disorders of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
Chest pain may be accompanied by difficulty breathing, feeling short of breath. Pain can also occur in the flanks, upper abdomen.
Prevention
In order to prevent the disease, it is recommended to take regular breaks and warm-ups during sedentary work, to avoid hypothermia, excessive physical exertion, and stressful situations. It is important to maintain body weight in a healthy range.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.