- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Red moles on the body
The content of the article:
- Reasons for the appearance of red moles on the body
- Types and symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Why are red moles dangerous?
-
Treatment
Laser removal
- Video
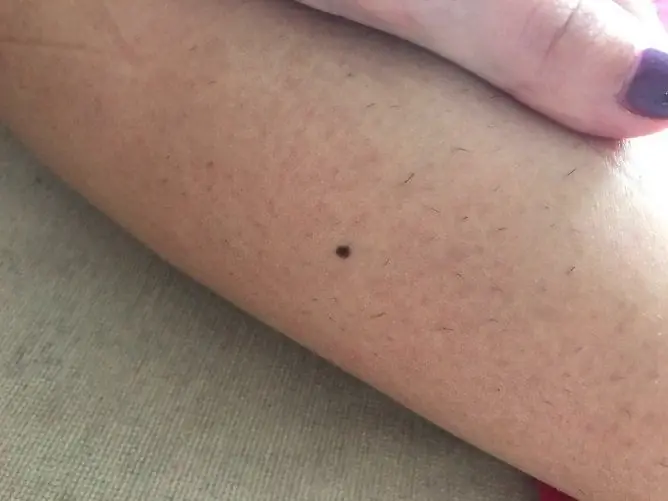
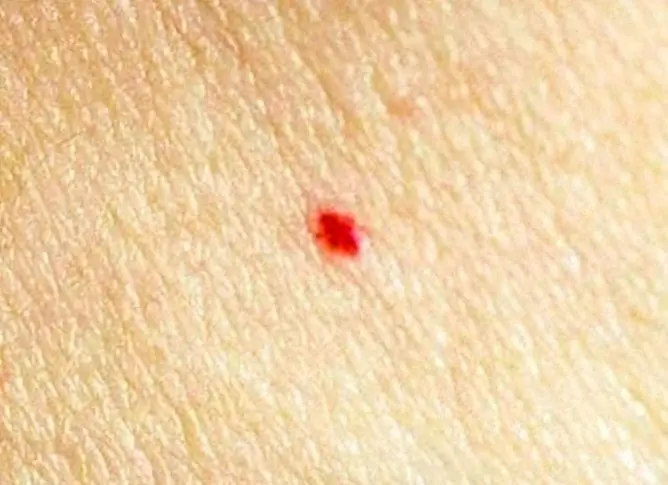
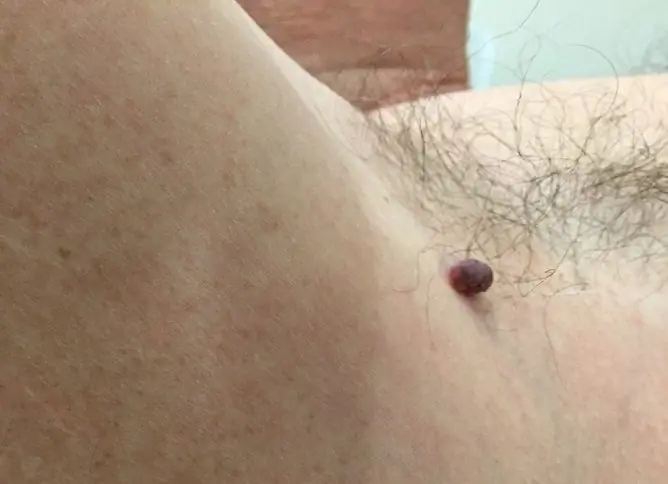
Red moles on the body are observed quite often. They are called angiomas and are benign skin growths that do not pose a threat to human life and health.
Angiomas often appear and disappear spontaneously, almost never undergo malignancy, and in most cases do not require any treatment.

Red moles are not uncommon, they are present on the skin of half of all people
Red moles are most commonly found on the scalp, face, neck, arms, chest, and upper abdomen. Formations are both single and multiple. With a large number of them, the disease is called angiomatosis.
Reasons for the appearance of red moles on the body
Angiomas are tumors, the occurrence of which is associated with an abnormality in the structure of blood vessels. They are of a congenital and acquired character.
The onset of congenital angiomas occurs at the stage of intrauterine development of the fetus, under the influence of various factors acting on the body of a pregnant woman:
- infections;
- bad habits;
- ionizing radiation;
- taking certain medications.
The size of congenital angiomas in a child usually does not exceed 10 mm. At primary school age, they disappear on their own.
In adults, red moles on the body usually begin to appear between the ages of 30 and 35. They are observed in about 50% of the population. Pathology affects both women and men with the same frequency. The reasons for the appearance of acquired forms of angiomas are:
- hormonal changes (pregnancy, menopause);
- increased fragility of the walls of blood capillaries due to a deficiency in the body of vitamins K and C;
- lipid metabolism disorders;
- hereditary predisposition;
- some autoimmune diseases;
- skin injuries;
- abuse of sunbathing or visiting a solarium;
- dysfunctions of the liver and pancreas (one of their symptoms is the appearance of bright burgundy moles on the upper torso);
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- inflammatory diseases of the digestive system (gastritis, enteritis, colitis);
- hemophilia;
- poor nutrition.
To date, the exact mechanism of angioma formation has not been established. However, given the reasons that cause their occurrence, it becomes clear that red moles by their appearance (especially multiple ones) signal any disturbances in the functioning of the body, the development of various diseases.
In the works of a number of scientists, it is said that angiomas should be considered as an intermediate link between a malformation and a tumor.
Types and symptoms
Depending on the features of the anatomical structure, red moles on the body are divided into several types. Let's consider them in more detail:
| Form of education | Description |
| Hypertrophic (capillary, simple) | Formed due to the proliferation of arterial or venous capillaries in the local area of the skin. The lesion looks like a bluish-purple or bright red spot. Its size is different: from a small dot to a giant spot with a diameter of over 15-20 cm. A characteristic symptom of the disease is the blanching of an angioma when pressed on it with fingers. Transformation into malignant hemangioendothelioma is extremely rare. |
| Cavernous (cavernous) |
This type of red mole is formed by a spongy cavity filled with blood. Outwardly, they look like convex nodes, of a soft-elastic consistency, with a bumpy surface of a bloody color. Palpation in their thickness is sometimes determined by dehydrated thrombi - angiolitis. Cavernous angioma is characterized by an erectile symptom (an increase in education when straining) and a symptom of temperature asymmetry (the tumor is perceived tactilely hotter than the surrounding skin). |
| Razeluznaya (branched) | It is formed by the interlacing of twisted and dilated blood vessels. This type of angioma is usually located on the limbs, much less often on the face. On palpation, trembling and noise are determined, as above an aneurysm. The slightest trauma to the formation can provoke profuse bleeding. |
| Combined | It is a combination of cavernous and simple forms. |
| Mixed | Mixed angiomas come from the blood vessels and the soft tissues surrounding them. |
Depending on the shape, red moles on the body are divided into several varieties:
- serpiginous;
- nodal;
- flat;
- stellate.
Senile angiomas are distinguished into a separate group. They occur in people over the age of 40-45 and have the appearance of rounded small formations of pink or light red color.
You can see detailed photos of different types of red body moles in the atlas of dermatological diseases.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of cutaneous angiomas is based on the data of visual examination and palpation of the formation. The diagnosis is confirmed by the identification of the following signs:
- blanching of a mole when you press on it with your fingers;
- decrease in compression and increase in muscle tension.
If necessary, ultrasound scanning of the vascular formation is performed, which allows you to find out:
- location features;
- structure;
- depth of propagation;
- the speed of blood flow in the vessels forming the tumor.
Red moles require differential diagnosis with nevi - pigmented skin neoplasms.
Why are red moles dangerous?
As a result of traumatic injuries and under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, red moles can undergo malignant transformation and degenerate into hemangioendothelioma. The main signs of malignancy in education are:
- color change;
- fast growth;
- peeling of the surface;
- itching or other discomfort.
Treatment
In most cases, red moles do not require any treatment. The main indications for their removal are:
- the appearance of signs of malignancy;
- location in a place where education is subject to constant trauma;
- a serious cosmetic defect, such as a large angioma on the face or sternum handle.
You should not try to remove red moles on your body yourself. This can provoke:
- profuse bleeding;
- wound infection;
- rapid growth of neoplasms;
- degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant one.
In hospitals, red moles are removed using various methods:
- Surgical excision. The tumor is excised under local anesthesia with a scalpel and the wound is sutured. The possibility of using this method depends on the size and location of the formation.
- Radiowave surgery. Angioma is removed using radio waves with a frequency of up to 4 MHz.
- Electrocoagulation. The tumor is burned out with high frequency electric current.
- Chemical hardening. In the capillaries that form the angioma, a drug is injected by injection, causing their walls to stick together.
- Cryodestruction. The destruction of the tumor is carried out by deep freezing of its tissues with liquid nitrogen.
- Laser vaporization.
The choice of a method for removing skin lesions is carried out in each case by the attending physician, taking into account the characteristics of the disease. However, in recent years, specialists have often preferred laser processing.

Laser mole removal has a number of advantages over other methods
Laser removal
Under local anesthesia, layer-by-layer burning (evaporation) of the skin formation to healthy tissues is performed. A small black scab forms at the site of exposure. After two weeks, it disappears and in its place remains clean healthy skin.
The main advantages of removing angiomas using laser radiation are:
- local effect on neoplasm with minimal damage to surrounding healthy tissues;
- no need for hospitalization of the patient, since the procedure can be carried out in an outpatient setting;
- maximum asepsis during the procedure, which is associated with the pronounced bactericidal properties of the laser;
- minimal blood loss during surgery, since the laser coagulates blood vessels;
- fast healing of the postoperative wound and the absence of postoperative scar, since laser radiation activates the regenerative capacity of tissues;
- low risk of recurrence of the disease.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Elena Minkina Doctor anesthesiologist-resuscitator About the author
Education: graduated from the Tashkent State Medical Institute, specializing in general medicine in 1991. Repeatedly passed refresher courses.
Work experience: anesthesiologist-resuscitator of the city maternity complex, resuscitator of the hemodialysis department.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.