- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Convex moles
The content of the article:
- Why did moles become convex
- What bulging moles look like on the body
- Hazard criteria
- When to see a doctor
- What can you do at home
- Surgery
- Video
A convex mole (nevus) is a benign neoplasm that can be congenital or acquired. Almost every person has nevi, in most cases they are completely safe.
Melanoma (the so-called malignant pigmented skin formation) is relatively rare, but if detected late, the disease cannot be treated and is fatal. It is with this that doctors are suspicious of moles.

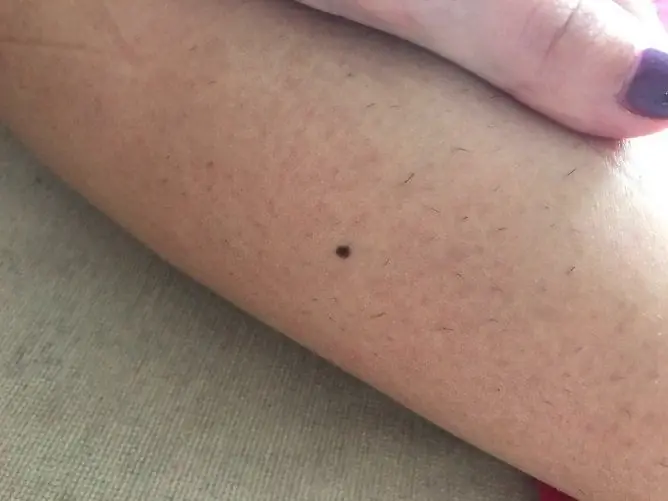
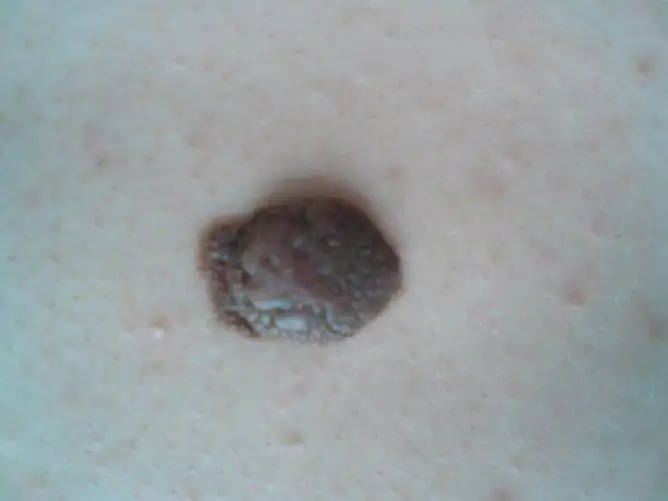
Bulging moles are not more dangerous than flat ones
Why did moles become convex
A nevus is formed as a result of the accumulation of melanocytes (skin cells that produce the pigment melanin) in the layers of the skin. The formation of moles is influenced by melanocyte-stimulating hormones, which are produced in the middle lobe of the pituitary gland.
Almost every healthy person has moles. They can be flat (birthmarks) or raised like a bump. Often the spots turn into convex formations over time. There is no single reason for this rebirth. This can be influenced by many factors at once - genetic, hormonal, environmental factors.
| Group of factors | Explanation |
| Genetic | The main factor in the formation of nevi is a genetic predisposition. Skin neoplasms are encoded at specific gene loci that are passed on to the child from the parents. It is impossible to influence this group of factors. |
| Hormonal | The appearance of a nevus can cause hormonal changes. Moles grow actively during puberty, in women during pregnancy. The main feature of such changes is dysfunction of the pituitary gland, in which melanocyte-stimulating hormones are produced. |
| Environmental factors |
Ultraviolet radiation can stimulate the growth of melanocytes. This explains the large number of moles in people who sunbathe a lot. |
The form of formation depends on which layer of the skin melanocytes accumulate. If melanocytes accumulate in the epidermis (surface layer of the skin), then the mole will be flat, and if in the dermis (deep layer), it will be convex.
What bulging moles look like on the body
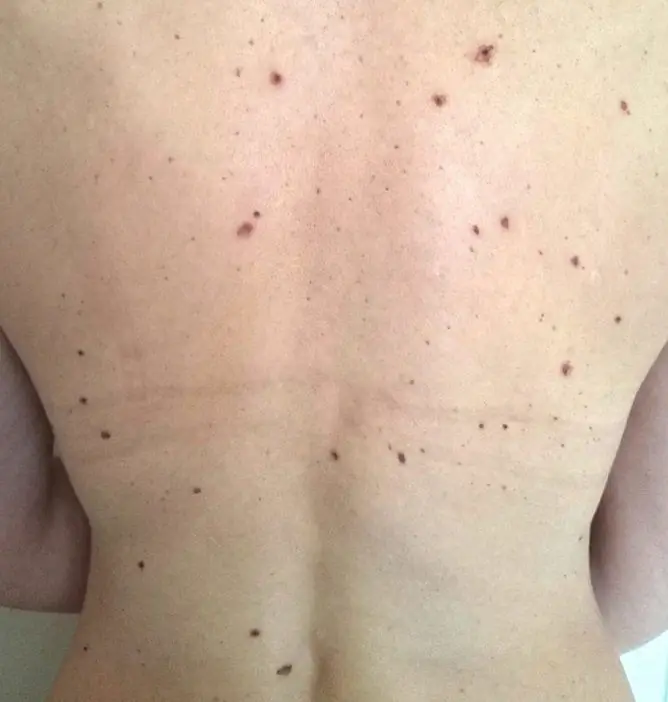
The appearance of a mole can be varied. It is often impossible to find two identical formations on the body of one person. They differ in color, size, surface, localization.
| Sign | What options can be |
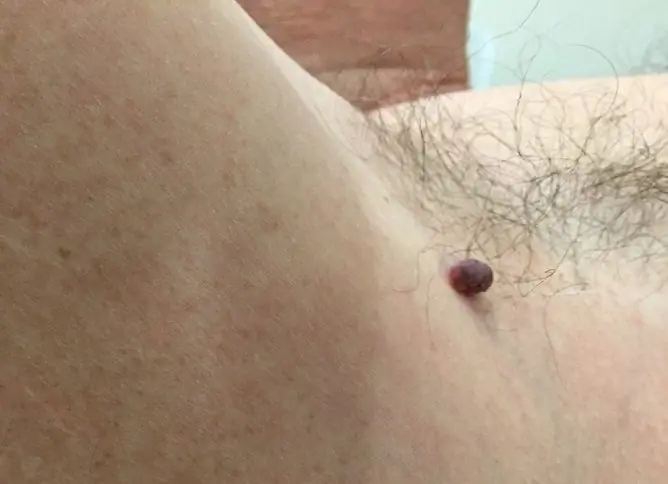
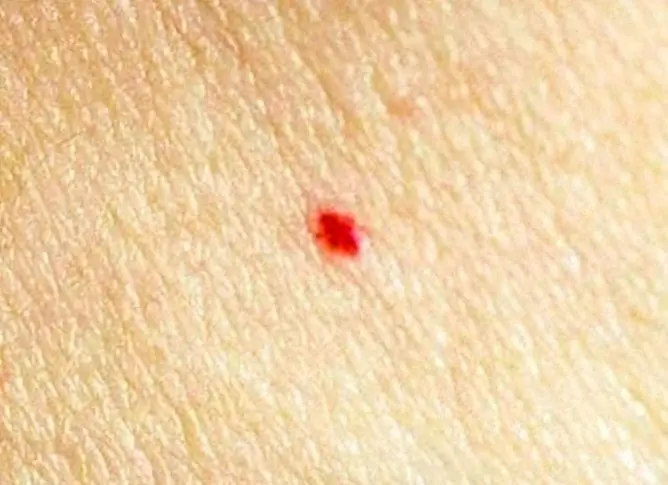
| Colour | The most common are brown and black formations. Less commonly, the color can be red and purple. A red mole is a proliferation of blood vessels (angioma). |
| The size | From spot to giant (5 cm or more). |
| Surface | A bulging nevus rises above the skin, hair can grow on the surface. |
| Localization |
Where neoplasms can be localized: · Face; Scalp; Neck; Back; · Chest; Belly; Buttocks; · Upper and lower limbs; · Mucous membranes. Its location does not affect the likelihood of malignancy of the neoplasm. However, localization often determines the tactics of treatment. For example, nevi on the face are often removed for aesthetic reasons, on the scalp and neck due to frequent trauma. |
Hazard criteria
You can decide whether a mole is dangerous or not at home. To do this, you need to examine the neoplasm and evaluate its asymmetry, edge, color, size and dynamics of development (abbreviated as AKORD).
| Criterion name | How to assess the norm | Danger sign |
| Asymmetry | Draw a line in the photo in the center of the formation and evaluate both halves. Normally, the halves should be symmetrical. | Asymmetry of the halves. |
| Edge | Normally, the edge of the nevus is even and smooth. The border between education and skin is clearly visible. | Blurred borders, jagged edges, jagged edges. |
| Coloration | It is necessary to evaluate not so much the color of the mole as the uniformity of the color. A good sign is the uniform color of the nevus and the absence of inclusions. | The color is uneven - there are light and dark areas, blotches of a different color. |
| The size | The larger the nevus, the higher the risk of malignancy. | The size of the formation is 6 mm or more. |
| Dynamics |
It is very important to monitor the nevus over time and evaluate how it changes over time. To do this, it is necessary to conduct an inspection at least once every several months. Particular attention should be paid to the change in size and surface. |
The formation grows rapidly, the surface becomes rough, ulceration appears. |
When to see a doctor
In most cases, the appearance of a convex mole does not require additional examination and treatment. But there are also exceptions - first of all, you need to consult a doctor when there are hazard criteria (at least one). Also, an indication for examination is the frequent trauma of the mole.
Persons at risk of nevus degeneration into melanoma should regularly undergo preventive examinations:
- men over 50;
- persons with a burdened heredity (melanoma in the next of kin);
- persons who have already been diagnosed with melanoma;
- faces with a characteristic phenotype: fair skin, freckles, white or red hair;
- persons who often have sunburn;
- persons with a large number of moles on the body (more than 100).
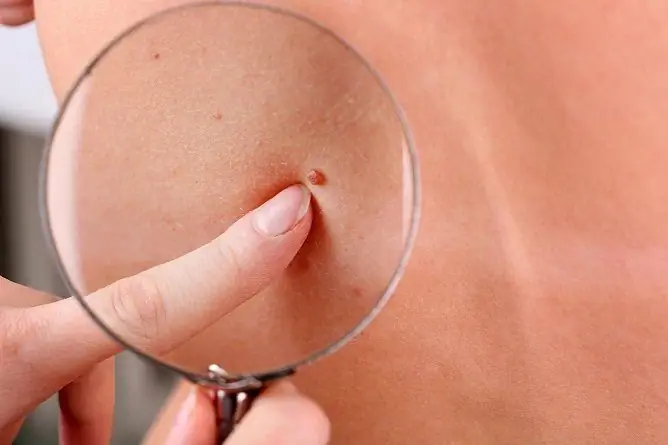
The main diagnostic method is dermatoscopy. The doctor examines the formation with a dermatoscope, a special instrument that magnifies the image 10 times. Such an examination makes it possible to consider all the changes on the surface of the nevus. However, dermatoscopy does not allow us to make a final diagnosis, that is, with a 100% probability of determining this melanoma or a benign neoplasm. For this purpose, a histological examination (biopsy) may be prescribed.

Dermatoscopy allows you to get an image of a mole at ten times magnification
What can you do at home
The main thing that can be done at home is to regularly examine the nevus according to the ACORD algorithm. At the slightest doubt, it is better to consult a dermatologist. This is enough to protect yourself from serious consequences.
Compliance with the following care guidelines will help reduce the risk of complications:
- cover the nevus with a bandage from direct sunlight;
- do not use scrubs, peels on this area;
- try not to injure education.
In no case should a nevus be removed at home. The use of medicines, folk remedies and improvised materials for this purpose is dangerous - traumatization of education can provoke the development of complications (malignancy, bleeding, attachment of bacterial flora).
Surgery
Not all nevi are subject to surgical removal.
What are the indications for treatment:
- suspicion of a malignant neoplasm based on examination results;
- frequent trauma;
- localization on the face, which leads to a cosmetic defect.
Various methods can be used for removal - surgical excision, laser therapy, electrocoagulation, cryodestruction.
| Treatment method | How is it done, the testimony | disadvantages |
| Surgical excision | The formation is excised with a scalpel, then the wound is sutured. The operation is performed under local or general anesthesia. The removed material is sent for histological examination. The main advantage of the method is the ability to remove formations of any size and nature. | The main disadvantage is that a noticeable scar remains after removal. Therefore, surgical excision is rarely used if the nevus is localized on the face. |
| Laser therapy | Laser therapy is a minimally invasive treatment. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, and a laser is used to remove it. Laser therapy can be used if the nevus is localized on the face (no scar remains on the skin). | Not used to remove melanoma. Another disadvantage is the high cost of the procedure. |
| Electrocoagulation | Another method of minimally invasive treatment is electrocoagulation. Treatment consists of cauterizing the nevus with a special instrument that generates an electric current. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. Electrocoagulation can be used to remove moles of any location (even on the face). | It is not used to remove malignant neoplasms. |
| Cryodestruction | Cryotherapy can be used to remove small moles. The method is based on exposure to liquid nitrogen. The nevus is frozen, which leads to its destruction. A day after the procedure, a bubble appears at the site of the neoplasm. The procedure is painless, there is no need for even local anesthesia. | Not used to remove large lesions. In addition, it is not always possible to achieve the desired result after the first session, sometimes several procedures are required. |
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.