- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Orthostatic hypotension - what is it?
The content of the article:
- What is orthostatic hypotension?
- Symptoms
- Causes of orthostatic hypotension
- First aid
- Treatment of orthostatic hypotension
- Video
Orthostatic hypotension is a condition of a sharp drop in blood pressure caused by a change in body position.
Hypotension is no less dangerous than hypertension. This pathological condition entails a decrease in the blood supply of all organs, which leads to their functional disorders. Insufficient blood circulation almost always means ischemia (insufficient tissue oxygen supply), which leads to degradation of the tissues of the most sensitive organs to it, which are key - the brain, heart, kidneys. A sudden onset of hypotension may even be accompanied by loss of consciousness.
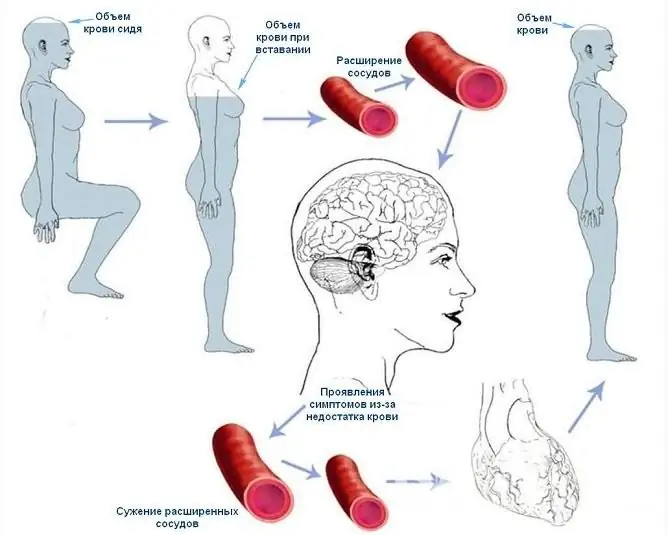
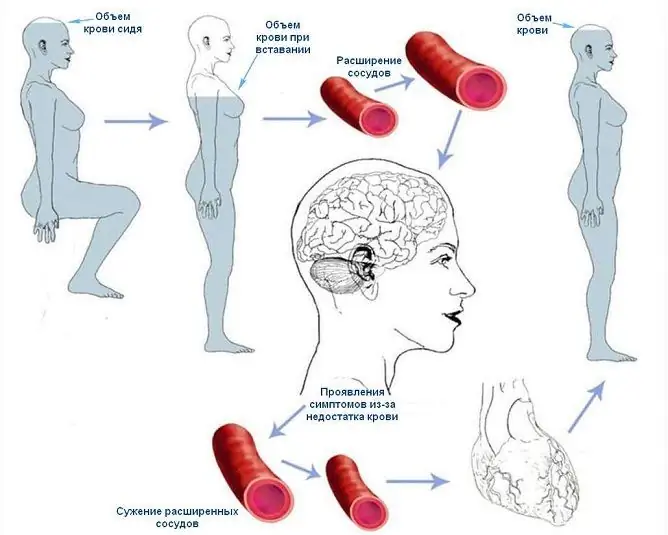
Orthostatic hypotension in most cases is caused by an abrupt change in body position
What is orthostatic hypotension?
This is a painful condition characterized by a sharp drop in blood pressure, which in most cases is caused by a change in body position from horizontal to vertical. It usually lasts from a few seconds to several minutes, but there are also long-term clinical forms. Pathology has a code according to ICD 10 (international classification of diseases) I95.1 in the category "Hypotension".
The diagnosis must be made by a specialist in accordance with international protocol. Signs of clinically stable hypotension are: persistence of symptoms of collapse for 2-5 minutes while standing quietly without exposure to external stimuli, drop in systolic pressure by more than 20 mm Hg. Art., and diastolic - by 10 mm Hg. Art.
If a short-term drop in blood pressure can be dangerous as a sudden loss of consciousness with subsequent trauma, then a long-term lack of blood circulation in many organs and systems leads to cell death, their replacement with connective tissue, after which the organ ceases to be able to perform its function in full. Therefore, this form of hypotension is treated with medication, maintaining a normal level of pressure.
The pathogenesis of the disease is almost the same in all cases: in the supine position of the body, the capacitive vessels (almost always the hollow veins and veins of the lower extremities) of the lower half of the body deposit most of all the blood in the circulation. When the position of the body changes, the body provides for a compensatory reaction, which consists in increasing the number of heart contractions and increasing the tone of the capacitive vessels to transfer blood to the main circulating pool. But if there is a violation on the part of the autonomic nervous system, which maintains vascular tone and heartbeat, or vascular insufficiency is observed at the moment of getting up, then the heart cannot cope with pumping the entire volume of blood, and it drains from the brain. This condition is called cerebral hypoperfusion and results in characteristic symptoms.
Symptoms
The symptoms of the disease are caused by the above-described state of cerebral hypoperfusion, that is, the lack of oxygen to the brain in the required volume. Therefore, most of the symptoms relate specifically to this area, but there are also those associated with the cardiovascular system:
- dizziness is the main symptom of a decrease in blood pressure and insufficient blood circulation in the arteries of the brain. It passes after a few seconds (sometimes up to a minute), when the blood filling of these vessels is restored;
- flies before the eyes, blurred images;
- violation of mental functions, faintness, drowsiness;
- muscle weakness, heaviness in the legs - evidence of poor energy supply to the musculoskeletal system at reduced pressure. Can last up to ten minutes;
- nausea, impaired coordination in space;
- fainting is a sudden loss of consciousness, which is dangerous when a person falls and subsequent injuries. Fainting is light and deep. During a lung, the heartbeat is restored over time, the patient comes to his senses without visible disturbances. With deep fainting, the function of the central nervous system is disrupted, sphincters can relax, which will lead to involuntary urination. Also, there is increased sweating, memory impairment, and occasionally tremors.
Causes of orthostatic hypotension
There are many reasons that can lead to a decrease in blood pressure.
- A sudden change in body position in space is the most common problem, but such hypertension is quickly compensated for and rarely leads to serious consequences. If the symptoms do not go away for a long time, this may indicate vascular insufficiency and serve as a reason to see a doctor.
- Heavy physical work - hypotension can be caused by any activity that promotes the outflow of blood from the brain. Such activities are lifting weights, endurance tests (long running, physical activity without interruption).
- Overheating - an increase in temperature leads to vasodilation. If this happens in all cavity vessels, then the blood will flow there, and the pressure will drop.
- Hypovolemia - a decrease in the volume of circulating blood. It can be caused by insufficient fluid intake throughout the day, increased utilization of fluid (in hot weather by evaporation, with sweat), or a sharp loss of fluid by the body (with profuse diarrhea, forced diuresis, urinary incontinence).
- Heart disease - first of all, they cause stable bradycardia, which helps to reduce blood pressure. Pathologies such as congenital heart valve defects reduce the compensatory abilities of this muscular organ; it does not respond to pressure changes in time.
- Organic pathologies of blood vessels and the endocrine system.
Often, the pressure drops while taking certain groups of drugs that act on the cardiovascular or central nervous system. For example, hypotension can occur with the first dose of strong antihypertensive drugs like Clonidine - this is one of the classic side effects for this drug. All antihypertensive drugs, especially beta-blockers, have this side effect. In addition, hypotension is characteristic of the action of drugs like Viagra, Levitra and other drugs designed to treat erectile dysfunction.
Some drugs cause a decrease in pressure, affecting the nervous system - these include tricyclic antidepressants, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, ganglion blockers (muscle relaxants), and other vasodilators of the central mechanism of action. Hypotension is observed with cannabis use.
First aid
If a person next to him becomes ill, he complains of dizziness, weakness, fainting, then it is necessary to support the patient, not let him fall, it is convenient to sit down or lay on a flat, hard surface. After that, you should call an ambulance. The symptoms of pathology are rather blurred and similar to other diseases, so only a doctor can establish an accurate diagnosis.
After the patient has been secured from falls and injuries, the pressure can be raised with improvised means. It is necessary to bend his knees, raise him above the level of his head - this will provide blood flow to the brain. You can wet his hands up to the elbows with cold water, the same can be done with the lower limbs. This will lead to a narrowing of the lumen of the peripheral vessels and an increase in pressure. If you have an elastic bandage, you can tightly wrap the lower limbs and help blood flow to the upper half of the body (however, you should not leave the bandage for any length of time).
If the patient has come to his senses, you can give him strong coffee, tea or an energy drink (tonic, energy drink) - this will increase the pressure.
Treatment of orthostatic hypotension
Drug therapy should be carried out only with an established diagnosis and as directed by a doctor. It is necessary to start with a lifestyle correction - increase the amount of payload, normalize fluid intake (it is best to drink water, and not other drinks). Hypotensive patients can eat salty foods in moderation, as well as coffee and tea. You should give up alcohol, which dilates blood vessels. It is forbidden to stay in the sun for a long time, overheat.

Medicines for blood pressure should only be taken as directed by a doctor, including because they can cause hypotension
How is severe orthostatic hypotension treated? Pharmacopoeial drugs that help with hypotension include Mezaton (increases vascular tone, their peripheral resistance, and therefore pressure) and Midodrin, which blocks the expansion of blood vessels and prevents pressure from falling for a long time.
Natural adaptogens are used, which include lemongrass, ginseng, eleutherococcus, pantocrine. These drugs provide a burst of energy, maintain vascular tone, and increase the overall resistance of the body.
After prolonged periods of hypotension, it is recommended to take Cinnarizine or Piracetam, which have a nootropic effect, to restore cerebral circulation.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Nikita Gaidukov About the author
Education: 4th year student of the Faculty of Medicine No. 1, specializing in General Medicine, Vinnitsa National Medical University. N. I. Pirogov.
Work experience: Nurse of the cardiology department of the Tyachiv Regional Hospital No. 1, geneticist / molecular biologist in the Polymerase Chain Reaction Laboratory at VNMU named after N. I. Pirogov.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.