- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Torsion of the legs of the ovarian cyst
The content of the article:
- Why does torsion occur?
- Why is the complication dangerous?
- Torsion of the ovarian cyst: symptoms
- How to diagnose pathology
-
Treatment methods
- What to do at home
- Surgical intervention
- Forecast and possible consequences
- How to avoid dangerous pathology
- Video
An ovarian cyst is a benign formation, which is a cavity with liquid contents. The disease itself is often asymptomatic, but with the development of complications, acute pain in the lower abdomen occurs. One of the dangerous complications is torsion of the ovarian cyst leg. Treatment of such a condition is only surgical, and help should be provided immediately. Otherwise, peritonitis and sepsis may develop.
Attention! Photo of shocking content.
Click on the link to view.
Why does torsion occur?
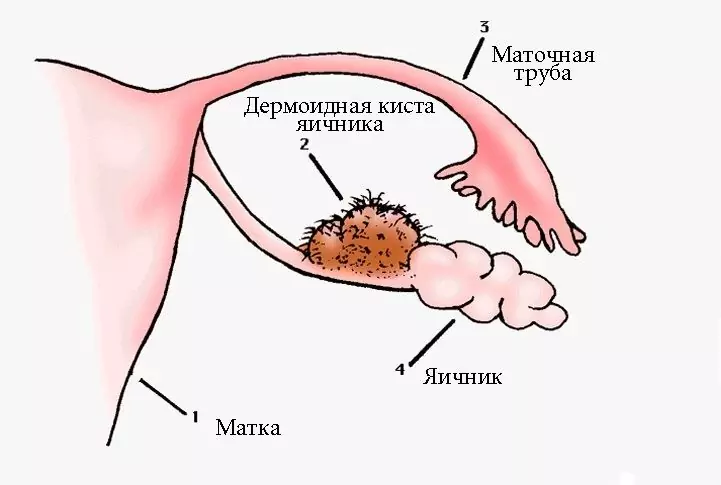
Torsion of any ovarian formation is possible - various types of cysts, cystomas, tumors. More often, formations that have high mobility are subject to this - paraovarian and dermoid cysts and cystomas. The development of complications is facilitated by the asymmetric form of education, uneven density.
The reasons that lead to such a complication are not fully understood. The following factors are important for the occurrence of torsion:
- Abruptly performed movements - physical activity, dancing, gymnastic exercises. It is believed that the torsion is caused by a sudden stop of the rotational movements of the trunk, when the rotation of the cyst around the leg continues by inertia.
- Increased intra-abdominal pressure - with straining, coughing, increased peristalsis of the small intestine.
Why is the complication dangerous?
When the legs are twisted, the vessels that supply the ovary (ovarian artery, branches of the uterine artery, veins) are bent. The intensity of circulatory disorders depends on whether the vessels are completely or partially compressed. If the vessels are completely pinched, the blood supply to the neoplasm stops. This leads to necrosis and the development of inflammation of the surrounding tissues. If the vessels are partially pinched, the changes are less pronounced. Venous outflow is impaired, arterial blood supply is usually preserved.
Torsion of the ovarian cyst: symptoms
With this complication, symptoms develop sharply. The severity of symptoms depends on the speed of development of torsion and its degree.
With complete torsion, symptoms of an acute abdomen develop:
| Symptom | Explanation |
| Pain | The main symptom of pathology is severe pain. Painful sensations are intense, localized in the lower abdomen, occur in paroxysms. |
| Intoxication |
Due to tumor necrosis, signs of intoxication appear: · nausea, vomiting; · Increased body temperature; · Decrease in blood pressure, tachycardia; Pallor of the skin, cold sweat. |
| Other disorders |
If the inflammation spreads to other organs, the following symptoms may occur: • disruption of the intestines: flatulence, gas and stool retention; · Damage to the organs of the urinary system: frequent urge, painful urination; · Damage to the uterus - bleeding from the vagina. |
How to diagnose pathology
The presence of a complication can be suspected by a characteristic clinic and anamnesis. If a woman with a previously identified ovarian cyst has symptoms of an acute abdomen, this indicates the development of complications (torsion of the cyst leg or rupture). The doctor conducts a physical examination - on palpation, the pain and tension of the anterior abdominal wall is determined.
However, these signs are non-specific, that is, they can be present in various diseases. It is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis with those diseases that cause the clinic of an acute abdomen. It is often necessary to differentiate torsion of the ovarian cyst leg with the following diseases:
- acute appendicitis;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- ovarian apoplexy;
- acute intestinal obstruction;
- renal colic.
To confirm the diagnosis, additional diagnostic methods are prescribed. An ultrasound examination (ultrasound) allows you to confirm the diagnosis, other tests are prescribed for the purpose of differential diagnosis. In difficult cases, diagnostic laparoscopy is performed.
| Diagnostic method | Explanation |
| Ultrasound of the pelvic organs |
Ultrasound is most commonly used. What changes are characteristic: · The tumor is visualized; · Education has blurred outlines; · The capsule is thickened; · In a small pelvis the effusion is determined. |
| Complete blood count (CBC) | In the KLA, signs of inflammation are often detected - an increase in ESR, leukocytosis. |
| Plain X-ray of the abdominal organs | Radiography is prescribed for the purpose of differential diagnosis. When the legs of the cyst are twisted, changes are usually absent, except for those cases when the inflammation has spread to the peritoneum. |
| Diagnostic laparoscopy | It is carried out in cases where other studies failed to confirm or exclude the diagnosis. |
Treatment methods
Emergency care is an urgent operation. Surgery is the only effective treatment. Medicines and folk remedies will not help get rid of the pathology.
What to do at home
If you suspect torsion of the leg of the ovarian cyst, you should immediately call an ambulance. All further treatment should be carried out in a hospital setting.
At home, you should take a lying position, exclude sudden movements, do not apply heat to the abdomen.

Acute abdominal pain is the main symptom of torsion of the leg of the ovarian cyst
Surgical intervention
The operation can be performed laparoscopic or laparotomy. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Laparoscopy - its advantage is less trauma. To access the ovaries, 3 punctures are made on the anterior abdominal wall. The operation is performed using a laparoscope - a special device equipped with a video camera, lenses and a magnification system.
- Laparotomy is a more traumatic operation, but it gives the surgeon a better view. In a laparotomy, an incision is made on the anterior abdominal wall.
The choice of access, as well as the scope of the operation, depends on the time elapsed since the torsion and the severity of necrotic changes.
| Operation volume | Indications | Description |
| Laparotomy with oophorectomy | Late onset of surgery, necrosis, peritonitis |
In this operation, the leg of the tumor is cut off without preliminary unwinding, and the ovary is removed. Then, the abdominal cavity is revised, if necessary, drainage is installed. |
| Laparoscopy with tumor detorsion | Early start of surgery, blood flow is restored | If the operation is started early, an organ-preserving intervention is performed - tumor detorsion. In this operation, the twisted legs of the tumor are unwound. If after 15 minutes there are signs of restoration of blood circulation, the ovary is not removed. Removal of the cyst or resection of the ovary (removal of the cystic formation with part of the ovary) is performed. |
Forecast and possible consequences
With timely operation, the prognosis is favorable, complete recovery occurs. Organ-preserving surgeries allow patients to preserve their reproductive function.
How to avoid dangerous pathology
Prevention consists in conducting regular preventive examinations of a gynecologist with ultrasound of the pelvic organs. If an ovarian cyst is detected, appropriate treatment is necessary - a planned operation or the use of oral contraceptives. Before the operation, it is recommended to exclude sudden movements and significant physical activity.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.