- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
6 weeks pregnant
At 6 weeks of gestation, the age of the embryo is already 4 weeks. It is growing and developing at a fairly fast pace. A delay in the next menstruation for 2 weeks and characteristic changes in well-being cannot go unnoticed by a woman. At this time, pregnancy is most often known.
What happens to the fetus

At the 6th week of pregnancy, the laying of the vital systems of the unborn child continues. During this period, the fetus is especially sensitive to unfavorable external influences, which can disrupt the formation of its organs at the initial stages.
The size of the fetus at 6 weeks gestation is approximately 7 - 9 mm in length, and the weight is up to 1 g. The limbs continue to grow, the rudiments of the fingers become more noticeable. Cartilage tissue is actively formed, which will give rise to bones and tendons. At 6 weeks of gestation, the laying of the chest occurs.
In the same period, the thymus is laid - the thymus gland, located in children in the upper mediastinum just behind the chest. The thymus is larger than all other endocrine organs at 6 weeks of age. An important role of the thymus is the participation and regulation of immune processes in the developing organs of the fetus, although the mechanisms of this have not been fully understood.
The fetal heart tube continues to develop and grow. The heart is already beating regularly and with a higher frequency, about 146 - 154 beats per minute. It contains the rudiment of the common ventricle and atrium.
An ultrasound scan at the 6th week of pregnancy shows how the features of the future face - the jaw, nose, mouth, ears, are more clearly visible. Already at such an early period, the rudiments of milk teeth are laid. The eyes, which were previously in the form of rudiments on both sides of the head, move closer to each other and into the frontal plane. Their size remains quite large compared to other organs.
At 6 weeks, the embryo's neural tube, from which the brain is formed, is completely tightened. Starting at 6 weeks of gestation, the first convolutions form in the brain, and the muscles and heart receive nerve connections with it.
From 6 weeks, the placenta begins to develop, it is very small in size and does not yet perform all functions. The umbilical cord with vessels inside departs from it, through which nutrients and oxygen are delivered to the fetus, and metabolic products and carbon dioxide are removed from it.
Changes in a woman's body at 6 weeks of gestation
At 6 weeks gestation, there may be signs of early toxicosis and increased fatigue.

The changes also affect the mammary glands - blood supply improves, which leads to their filling and increase in size. The nipple becomes darker, and the nipples themselves become more sensitive.
The uterus continues to grow, but the belly is not yet visible at 6 weeks gestation. In general, the uterus at this time is entirely under the influence of progesterone. Under the influence of hormones at the 6th week of pregnancy, discharge from the genital tract is normally light and transparent, more abundant than usual.
Examination at 6 weeks of pregnancy
Pregnancy and lifestyle recommendations are the same as at 5 weeks. If a woman found out about her situation, then she should not hesitate to register for pregnancy. The pregnancy test at 6 weeks is already clearly positive - a sufficient amount of chorionic gonadotropin has accumulated in the urine.
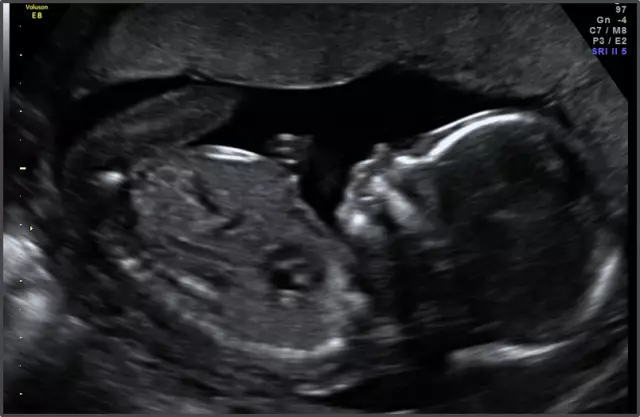
Ultrasound at the 6th week of pregnancy allows you to find out the number of fetuses in the uterine cavity (from two in the case of multiple pregnancies), as well as assess the growth rate of the unborn baby. Outwardly, the fruit looks like a bean, and you can clearly hear its heartbeat.
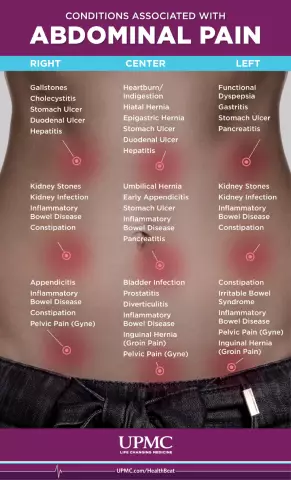
Ultrasound as a possibility of differential diagnosis is also prescribed if the stomach hurts at 6 weeks of pregnancy. Pulling and cramping pain at this time can be both the result of sprains under the influence of hormones, and the threat of termination of pregnancy, especially if the pain is accompanied by bleeding.
YouTube video related to the article:
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.