- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
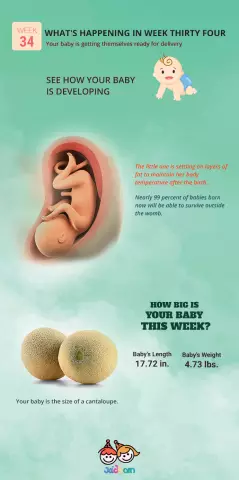
34 weeks pregnant

At 34 weeks gestation, the baby in the belly turns 32 weeks old, according to the lunar calendar this is the middle of the ninth month of pregnancy. He is already quite viable and will be able to breathe on his own in the event of a premature birth.
Changes in the fetus
At 34 weeks of gestation, the main changes affect the development of the central nervous system of the fetus. The growth and development of the cerebellum, the part of the brain responsible for the coordination of movements and the position of the body in space, is accelerated. Myelination of nerve fibers continues - they are covered with a special sheath, thanks to which the conduction of excitation through them is accelerated. Due to new nerve connections, the mass of the fetus's brain at 34 weeks of gestation increases.
New unconditioned reflexes appear, they help the baby to adapt to extrauterine life after birth. A newborn who is born at 34 weeks of gestation will be able to suckle on its own breast or bottle.
The expectant mother feels less fetal movements at 34 weeks of gestation, since the fetus is already getting cramped in the uterus. By this time, he usually takes his permanent position in the uterine cavity.
According to ultrasound, at 34 weeks of gestation, the growth of the fetus ranges from 40 to 43 cm, it weighs 2-2.2 kg. In general, his body at this time is adapted to life outside the uterine cavity.
Changes in a woman's body at 34 weeks of gestation
The height of the standing of the fundus of the uterus in the abdomen at 34 weeks of gestation above the bosom is 33-34 cm, the amount of amniotic fluid gradually decreases, and now the fetus occupies the bulk of the uterus. The belly at this stage of pregnancy looks large, in some, the navel begins to protrude above its surface. The skin of the abdomen is stretched and becomes thin, quite often it itches.
If the pelvic bones of a pregnant woman are widely spaced by nature, then outwardly the belly at 34 weeks of gestation may seem small. This is due to the fact that the uterus with the fetus fit inside the pelvic bone ring, which has enough space for them. By the size of the abdomen, it is not entirely correct to judge the proportions of the fetus, ultrasound helps to determine the mass and growth indicators of the future baby more accurately.

A woman is increasingly feeling Braxton-Hicks contractions, they are manifested by irregular abdominal tension, there are no pains at 34 weeks of pregnancy with such contractions. Abdominal tension often appears after exercise and goes away on its own if a woman lies down to rest. Pain at 34 weeks of gestation can be regarded as the onset of labor.
The mammary glands continue to prepare for childbirth, so the release of yellowish drops of colostrum from them at 34 weeks of gestation is a variant of the norm. The breast has increased in size, and the venous network is visible through the surface of its skin. Such changes are caused by the hormone prolactin, in the formation of which the placenta is now partly involved.
The calves of the legs of a pregnant woman at 34 weeks of gestation can have cramps, more often it happens at night and at rest.
Examination at 34 weeks of gestation
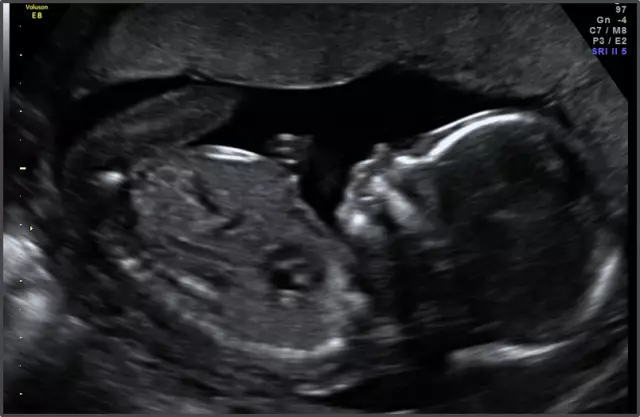
A pregnant woman should visit those specialists whose examination was recommended by an obstetrician-gynecologist, if she has not yet had time to do this. Ultrasound at 34 weeks of gestation is carried out only if there is evidence or if the fetus is suspected of being unwell. This study helps to assess the condition of the placenta, umbilical cord (including its entanglement around the fetal body), amniotic fluid and the fetus itself. Sometimes the ultrasound result at 34 weeks of gestation can affect the method of delivery.
If the doctor has a suspicion that the future baby is suffering in utero, then he recommends cardiotocography.
YouTube video related to the article:
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.