- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
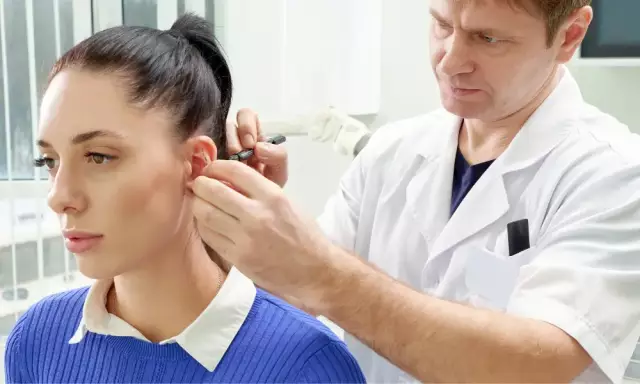
Otoplasty

Otoplasty or plastic auricle - an operation to correct the shape of the ears. There are different forms of ear deformities, for which patients often seek the help of a plastic surgeon. The main problem is the complete absence of the auricle or its congenital underdevelopment, as well as various congenital defects in the development of the auricle, leading to an aesthetically ugly shape of the ears. Often, patients decide to undergo otoplasty after traumatic defects of the auricle, as well as when the auricle is too far from the head (lop-eared).
Indications for otoplasty
Most often, otoplasty is decided by, according to reviews, patients with protruding ears. The causes of lop-earedness are:
- Excessive depth of the auricle bowl leading to the external auditory canal.
- Congenital malformation or underdevelopment of the antihelix of the auricle. In this case, the auricle looks flat and far from the head.
- The earlobes can also be located at a great distance from the head.
The patient may have only one of the above problems, and possibly all three at the same time. Otoplasty, according to reviews, helps to correct all these defects with a single operation.
The goal of otoplasty is to move the ear closer to the head, giving it a more aesthetic position, and to restore the natural contour of the auricle. Unfortunately, it is impossible to give both ears full symmetry. It is even more difficult to achieve symmetry if the patient has only one ear protruding. Therefore, even with a lop-eared ear of one ear, both are usually operated on.
The operation plan must be agreed with the patient, all his wishes regarding the shape of the ears after otoplasty and the degree of their distance from the head are taken into account. The operation can be done at any age, even at school. But, as a rule, parents of young children should not rush to the operation until the child himself wants to correct the shape of the ears. In this case, the operation will not cause psychological problems in the little patient. Otoplasty can be done using local anesthesia, without any pain. For children and some emotionally labile patients, it is advisable to undergo otoplasty under general anesthesia in order to avoid excessive emotional stress.
Preparing for otoplasty
Before undergoing surgery, the patient needs to undergo a standard medical examination no more than two weeks before surgery. The scope of the examination depends on the type of anesthesia used (general or local).

Two weeks before the operation and a week after, it is advisable to exclude the use of any means that reduce blood clotting. In the evening immediately before the operation, the patient should wash his hair with shampoo. If you will be using general anesthesia for the operation, you should not eat or drink for six hours before the operation. Before starting the operation, the patient is photographed. This is done so that the patient can compare their ears after otoplasty and before it.
Operation progress
Behind the auricle, an incision is made into the auricle itself, slightly receding from the fold behind the ear. The length of the incision depends on the surgical method chosen by the surgeon and the amount of changes. The ear cartilage is then processed to reshape it. The depth of the auricle decreases, an antihelix is formed, and the lobe is pressed. All these manipulations can be performed simultaneously or separately - it depends on the causes of protruding ears. When carrying out otoplasty, the following surgical techniques are used: removal or excision of cartilage fragments, notches on the cartilage, suture on the cartilage. At the end of the change in the shape of the ears, the doctor compares the auricles and, if necessary, makes additional corrections in order to achieve symmetry.
At the end of the operation, the behind-the-ear incision is closed with a non-absorbable suture, and a bandage is applied to the ears after otoplasty.
Postoperative period
The bandage after otoplasty is removed only after three days. On the first day after otoplasty, the dressing is changed. The first few days after the operation, the patient may experience severe pain, which is relieved with the help of analgesics (ketans). The first five days after the operation, the patient is prescribed antibiotics. Ears after otoplasty look swollen and bluish for about two weeks. After this time, hematomas disappear, while the main edema subsides in about two months. For two months after otoplasty, a decreased sensitivity of the auricles is observed. For up to three weeks after surgery, it is recommended that you wear a bandage over your ears at night to avoid accidentally damaging your ears while sleeping. The stitches behind the ears are usually removed within 10-14 days.
Excessive physical activity is not recommended for three weeks after surgery. It is not recommended to expose the ears to ultraviolet radiation for two months after surgery. The final result of otoplasty can be seen in about six months.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.