- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Nicotinic acid bufus
Nicotinic acid bufus: instructions for use and reviews
- 1. Release form and composition
- 2. Pharmacological properties
- 3. Indications for use
- 4. Contraindications
- 5. Method of application and dosage
- 6. Side effects
- 7. Overdose
- 8. Special instructions
- 9. Application during pregnancy and lactation
- 10. Use in childhood
- 11. For violations of liver function
- 12. Drug interactions
- 13. Analogs
- 14. Terms and conditions of storage
- 15. Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
- 16. Reviews
- 17. Price in pharmacies
Latin name: Nicotinic acid bufus
ATX code: C10AD02
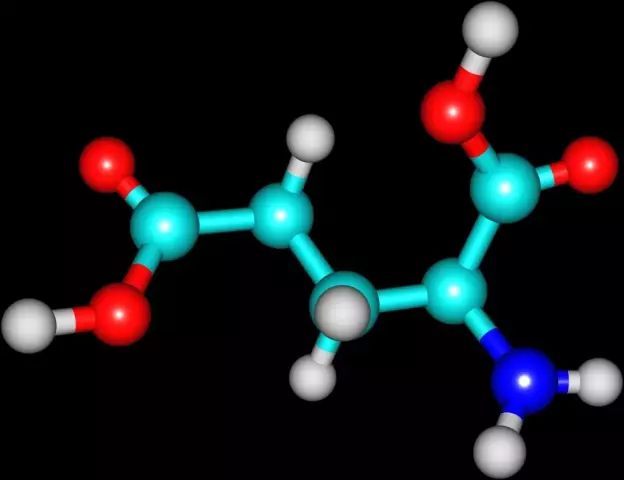
Active ingredient: nicotinic acid (Nicotinic acid)
Producer: JSC PFC Obnovlenie (Russia)
Description and photo update: 2019-08-07
Prices in pharmacies: from 58 rubles.
Buy
Nicotinic acid bufus is an antipellagric drug, has hypolipidemic, vasodilating, anticoagulant activity, improves microcirculation.
Release form and composition
The drug is available in the form of a solution for injection: a colorless transparent liquid (1 ml each in polymer ampoules, in a cardboard box of 10 or 100 ampoules and instructions for the use of Nicotinic acid bufus).
1 ml of solution contains:
- active substance: nicotinic acid - 10 mg;
- auxiliary components: sodium bicarbonate, water for injection.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Nicotinic acid bufus is a specific antipellagric preparation designed to compensate for the deficiency of vitamin PP (vitamin B 3) in the body. It has hypolipidemic activity, normalizes the concentration of blood lipoproteins, lowers the content of total cholesterol, low density lipoproteins. It has a pronounced short-term vasodilator effect, improves microcirculation, carbohydrate and nitrogen metabolism.
In the body, nicotinic acid is transformed into nicotinamide. Being a water-soluble vitamin, nicotinamide binds to hydrogen-carrying enzymes - coenzymes of codehydrogenase I and II [NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and NADP (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate)]. Participates in tissue respiration, metabolism of fats, amino acids, proteins and purines, in synthetic processes, glycogenolysis.
The drug improves microcirculation and has a vasodilating effect at the level of the vessels of the brain and other small vessels. The weak anticoagulant effect of nicotinamide increases the fibrinolytic activity of the blood.
Pharmacokinetics
After parenteral administration, nicotinic acid is rapidly distributed in tissues. Its accumulation mainly occurs in the liver, but also in the kidneys and adipose tissue.
Turning into an amine in the liver, it is incorporated into NAD, which carries hydrogen and participates in redox processes.
Nicotinic acid is metabolized in the liver to form two main metabolites with no pharmacological activity: N-methyl-2-pyridone-3-carboxamide and N-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide.
With the participation of pyridoxine (vitamin B 6) and riboflavin (vitamin B 12), nicotinic acid can be synthesized in the intestine from tryptophan ingested with food with the participation of the bacterial flora.
The half-life is 45 minutes.
It is excreted through the kidneys in the form of metabolites, when taken in high doses - mainly unchanged.
Renal clearance depends on the level of the active substance in the blood plasma; at a high concentration of nicotinic acid in the plasma, it may decrease.
Indications for use
- hypovitaminosis PP;
- pellagra (PP avitaminosis);
- Hartnup's disease (hereditary disease caused by impaired absorption of tryptophan and other amino acids);
- ischemic disorders of cerebral circulation;
- neuritis of the facial nerve;
- vasospasm of the limbs, biliary tract, urinary tract;
- obliterating diseases of the vessels of the extremities (Raynaud's disease, obliterating endarteritis);
- diabetes mellitus, including complications such as diabetic polyneuropathy, microangiopathy.
Contraindications
Absolute:
- severe arterial hypertension;
- gout;
- atherosclerosis;
- hyperuricemia;
- period of pregnancy;
- breast-feeding;
- childhood;
- hypersensitivity to drug components.
With caution, injections of nicotinic acid bufus should be prescribed during the period of exacerbation of gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer, with hyperacid gastritis, arterial hypotension, hemorrhages, liver failure, glaucoma.
Nicotinic acid bufus, instructions for use: method and dosage
Nicotinic acid bufus is intended for subcutaneous (s / c), intramuscular (i / m) and intravenous (i / v) slow administration.
Recommended dosage:
- pellagra: s / c, i / m or i / v - 10 mg (1 ml) 2-3 times a day for 10-15 days;
- ischemic stroke: IV - 10 mg;
- Hartnup's disease: 40 to 200 mg per day;
- other indications: 10 mg 1-2 times a day, course duration - 10-15 days.
The maximum single dose is 100 mg, the daily dose is 300 mg.
Side effects
- on the part of the cardiovascular system: rush of blood to the skin of the face, hyperemia of the skin of the upper half of the body and face; after rapid intravenous injection - orthostatic hypotension, collapse;
- from the nervous system: headache, paresthesia, dizziness;
- allergic reactions: itching, skin rash, urticaria, stridor breathing;
- local reactions: soreness in the places of s / c and i / m injection.
Overdose
Symptoms: itching, transient rush of blood to the upper half of the trunk and head, gastrointestinal upset.
Treatment: the appointment of symptomatic therapy.
special instructions
The use of nicotinic acid bufus should be accompanied by monitoring of liver function. To prevent complications from the liver, the patient's diet should include cottage cheese and other methionine-rich foods. In addition, the simultaneous use of lipotropic drugs, methionine, lipoic acid is shown.
Application during pregnancy and lactation
The appointment of injections of nicotinic acid bufus is contraindicated during gestation and breastfeeding.
Pediatric use
It is contraindicated to use nicotinic acid bufus in the treatment of children.
For violations of liver function
Caution should be exercised when using nicotinic acid bufus when treating patients with hepatic insufficiency.
Drug interactions
It should be borne in mind that with the simultaneous use of Nicotinic acid bufus with sulfonylurea preparations, the risk of an increase in the level of glucose concentration in the blood increases.
Care is required with concomitant therapy with anticoagulants, antihypertensive drugs, ascorbic acid.
When administered as part of a combination therapy with neomycin, the drug helps to reduce its toxicity, prevents a neomycin-induced decrease in the concentration of high density lipoproteins and cholesterol.
Analogs
Nicotinic acid bufus analogs are: Nicotinic acid, Nicotinic acid-Vial, Nicotinic acid-SOLOpharm, Enduracin, Nikoshpan, etc.
Terms and conditions of storage
Keep out of the reach of children.
Store at temperatures up to 25 ° C in a dark place.
The shelf life is 5 years.
Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
Dispensed by prescription.
Reviews about Nicotinic acid bufus
Reviews about Nicotinic acid bufus are positive. Patients note that the inclusion of a vitamin preparation in the complex therapy helps to reduce spasms, muscle pain.
Price for Nicotinic acid bufus in pharmacies
The price for Nicotinic acid bufus for a package containing 10 ampoules of 1 ml can be 52-84 rubles, 100 ampoules of 1 ml - 144-167 rubles.
Nicotinic acid bufus: prices in online pharmacies
|
Drug name Price Pharmacy |
|
Nicotinic acid bufus 10 mg / ml solution for injection 1 ml 10 pcs. RUB 58 Buy |
|
Nicotinic acid bufus solution for in. 1% 1ml 10 pcs. 93 rbl. Buy |

Maria Kulkes Medical journalist About the author
Education: First Moscow State Medical University named after I. M. Sechenov, specialty "General Medicine".
Information about the drug is generalized, provided for informational purposes only and does not replace the official instructions. Self-medication is hazardous to health!