- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Thyroid cyst
The content of the article:
- Causes and risk factors
- Symptoms of a thyroid cyst in women and men
- Complications
- Diagnostics
-
Thyroid cyst treatment
- Drug therapy
- Puncture
- Laser coagulation
- Surgical removal
- Folk remedies
- Video
A thyroid cyst is a fluid-filled cavity. This type of benign neoplasms differs from the thyroid nodules in structure (nodular formations, i.e. tumors are formed from glandular cells). Cystic formations of the thyroid gland can be single and multiple, make up 3-5% of the total number of all neoplasms of the gland, more often appear in females over the age of 40
A cyst in the thyroid gland - is it dangerous? The forecast depends on the type of education. Benign cystic neoplasms can be completely healed and sometimes resolve spontaneously. In some cases, relapses of pathology are observed. In some cases, malignancy may occur, i.e. degeneration into a malignant tumor - then the prognosis worsens.
Thyroid cysts are more common in women over 40
In order to prevent the development of cystic formations of the thyroid gland, it is recommended that the consumption of iodine and vitamins covers the needs of the body, avoiding exposure to the body of ionizing radiation.
Causes and risk factors
The thyroid gland is located in front of the trachea under the larynx and, as seen in the photo, consists of two lobes, which are connected by an isthmus. Fibrous septa divide the organ into pseudo-lobules, consisting of closed vesicles (follicles, acini). The gland produces calcitonin, as well as iodine-containing hormones (thyroxine and triiodothyronine), which take part in metabolism, stimulate the growth and development of the body, and tissue differentiation. Both iodine-containing hormones are synthesized in epithelial follicular cells (thyrocytes). The follicles are filled with colloid, when the outflow of which is disturbed, excess fluid accumulates in the follicle, which leads to an increase in its size and the formation of a cystic formation. Neoplasms can also occur with microbleeds, hyperplasia, follicular dystrophy.
The reasons include:
- infectious diseases of viral etiology;
- a history of chronic diseases;
- genetic predisposition;
- exposure of the body to ionizing radiation (including during radiation therapy);
- lack of iodine in the body.
The development of pathology can be facilitated by:
- toxic effects on the body of phenols, gasoline, paints, varnishes, heavy metals;
- hypothermia and overheating of the body;
- exposure to stress;
- neck injuries.
Symptoms of a thyroid cyst in women and men
Clinical signs in women and men are identical, as a rule, they appear when the neoplasm reaches a large size. Small cysts 0.3-0.5 cm in diameter usually have no external manifestations.
Usually, the lesions are painless and do not cause discomfort in the neck. On palpation, they are defined as dense elastic smooth formations, easily palpable under the skin.
Patients may experience:
- difficulty and pain when swallowing;
- feeling of a coma and / or sore throat;
- neck pain, which can radiate to the lower jaw and ear;
- change the timbre of the voice.
Cystic neoplasms of the thyroid gland with the progression of the pathological process can become noticeable, taking the form of protrusions on the front of the neck, or leading to a noticeable asymmetry of the neck. The reason for a person's self-seeking medical help is often the detection of a formation that is noticeable visually and deforms the neck. In such cases, neoplasms often exceed 3 cm in diameter and may not respond to conservative treatment.
In its development, cystic formation goes through several stages, which are presented in the table.
| Stage | Explanation |
| Formation | The patient usually has no symptoms at this stage. |
| Height |
The neoplasm increases in size, symptoms of pathology may appear |
| Resorption | In some patients (with normal immunity), the neoplasm disappears on its own |
Clinically, thyroid cystic lesions can behave in an unpredictable manner. So, long-term neoplasms can spontaneously increase in size or disappear.
Complications
In case of dysfunction of the thyroid gland and the rapid growth of cystic formations, they are capable of malignancy. Due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure, the cysts of the right lobe of the thyroid gland are more susceptible to malignant degeneration, while the formations of the left lobe usually do not increase to large sizes and, as a rule, respond well to conservative therapy.
It is possible to suspect a malignant degeneration of a cystic formation if the patient has the following signs:
- weight loss for no objective reason;
- a rapid increase in education in size;
- enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes;
- chronic fatigue and fatigue;
- mood swings, insomnia.
Complications also include edema and secondary infection of the cyst, in which it can fill with purulent contents. With the development of an infectious and inflammatory process, the patient's body temperature may rise, a sharp pain in the neck occurs, and symptoms of intoxication are observed.
Significantly enlarged neoplasms can put pressure on adjacent anatomical structures. In this case, there is a risk of respiratory disorders. If the cyst is accompanied by hyperthyroidism, the patient may have a high pulse, palpitations, a feeling of heat, emotional lability, exophthalmos.
Diagnostics
A neoplasm can be detected by palpation during a medical examination, and hardware diagnostics are also performed.
| Method | What is it used for |
| Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) | An affordable, inexpensive and effective method used to visualize the tumor, allows you to determine the size and structure of the cyst, and makes it possible to carry out differential diagnostics. |
| Determination of hormone levels | To assess thyroid function |
| Immunological research | To exclude autoimmune thyroiditis |
| Aspiration biopsy | A tissue sample is taken for histological examination, which makes it possible to determine the cellular composition of the neoplasm and its nature (benign, malignant) |
| CT / MRI | Upon detection of large cystic formations, it will be possible to determine their exact characteristics and relationship with the underlying tissues |
To clarify the diagnosis, angiography, laryngoscopy, bronchoscopy can be used. In the presence of education more than 3 mm in diameter, it is necessary to undergo an examination by an endocrinologist once every 6 months (dispensary observation).
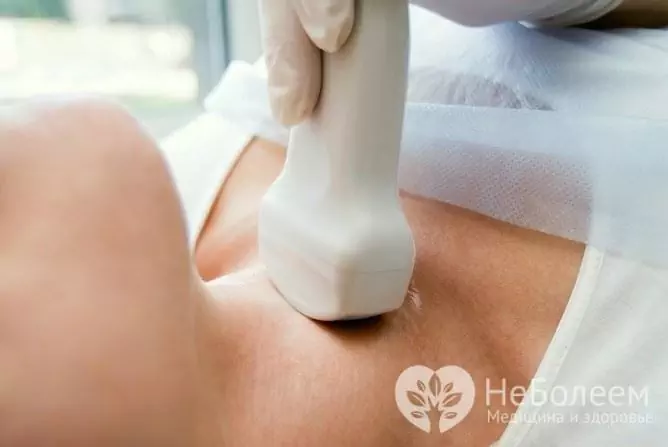
The main method for diagnosing cysts is ultrasound of the thyroid gland
Thyroid cyst treatment
If cystic lesions are found less than 1 cm in diameter, expectant tactics are usually chosen.
Drug therapy
In some cases, drug therapy may be prescribed. To restore the function of the organ, it may be necessary to use hormonal drugs, anti-inflammatory, decongestants, drugs to improve blood circulation and metabolism in the affected area, vitamin and mineral complexes.
The effectiveness of drug therapy using hormonal drugs is monitored by laboratory determination of hormone levels and ultrasound examination of the gland, which is also used to monitor treatment with iodine-containing drugs.
After completion of treatment, the patient should undergo a control ultrasound examination once a year.
Puncture
Puncture of the thyroid cyst is carried out not only for diagnostic, but also for therapeutic purposes. In this case, the cavity is freed from the liquid contents, after which substances with a sclerosing effect are introduced into it. Such atraumatic intervention allows you to effectively cure pathology in the early stages of development: in about 50% of cases, cystic formations subside after emptying, and subsequently the fluid in them no longer accumulates.
In case of relapse, benign neoplasms (in the absence of inflammation) can usually be punctured again. If the cyst quickly accumulates after emptying, surgery to remove it is usually indicated.
Laser coagulation
If it is necessary to remove a cystic formation, the method of laser coagulation can be used; this procedure can be performed on an outpatient basis. The advantages of the method include a low risk of side effects, no scars after surgery, less trauma, and painlessness.
Surgical removal
To treat a cystic formation is surgically indicated for:
- the rapid increase in the tumor;
- persistent inflammation;
- a significant deterioration in the patient's quality of life against the background of this pathology.
If it is necessary to remove the cystic formation by surgery, hemithyroidectomy (removal of one lobe of the gland) is usually performed. In the presence of neoplasms in both lobes of the gland, bilateral subtotal or total resection is performed. The gold standard of the operation is endoscopy - a minimally invasive method that does not require an extensive incision to access the affected organ, that is, it provides high cosmetology (no visible scar after surgery).
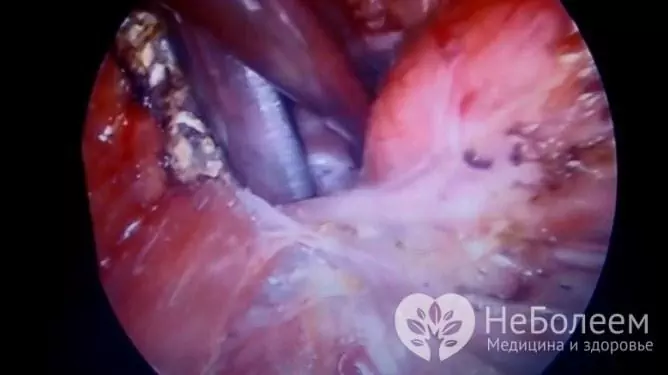
In some cases, one (affected by a cyst) lobe of the thyroid gland is removed - hemithyroidectomy
An absolute indication for surgery is malignant degeneration of the formation. In this case, it may be necessary to completely remove the gland (thyroidectomy) with regional lymph nodes, followed by treatment with radioactive iodine.
Folk remedies
For cystic formations, in addition to main therapy, traditional medicine methods can be used to improve the patient's condition. Their use requires mandatory supervision by the attending physician.
- Tincture of walnut leaves. To prepare the product, 1 glass of young leaves is poured with 0.5 liters of alcohol, insisted for 2 weeks. The tincture is taken in 5 drops (you can drink it with water or dissolve in it) 3 times a day.
- Infusion of walnut leaves. To make this medicine, 100 g of leaves are poured with 500 ml of boiling water and insisted for 30 minutes, after which the product is filtered and drunk several times a day.
- Potentilla root tincture. To prepare a product according to this recipe, 100 g of dry raw materials are poured into 1 liter of vodka, insisted for 1 month. The finished tincture is taken in 30 drops 30 minutes before meals (before the main meals).
- Flax oil. With this pathology, the use of flax oil, 1 teaspoon 2 times a day, can help.
- Beetroot cold compress. You need to make a compress from chopped (you can grate) raw beets, which are applied to the neck in the affected area.
Patients are advised to drink fresh juices from beets, carrots, cucumbers. With this pathology, in the absence of contraindications, you can drink teas (2 times a day), which include St. John's wort, string, nettle, yarrow, buckwheat.
Warming compresses and any other thermal procedures should not be used, as this can contribute to an increase in tumor size and the development of other adverse consequences. Neck compresses should not be wrapped or covered with plastic.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!






